Abstract
Purpose
The flexion–extension axis (FEA) of the femur is substantially changed after mechanically aligned total knee arthroplasty (TKA) due to a discrepancy in bone cut thickness between the posterior and distal femoral regions. This study assessed the bony gap changes and FEA displacement caused by this problem in osteoarthritis patients.
Methods
The study enrolled 60 knees from 60 patients for whom primary TKA was planned due to medial knee osteoarthritis. All patients underwent computed tomography, and 3-dimensional (3D) bone models were reconstructed on 3D-planning software. Bone cuts of the distal femur and proximal tibia were simulated to be perpendicular to each mechanical axis. Bony gap change was computed as the difference in bone cut thickness between medial and lateral compartments. Each femoral condyle was assessed for potential FEA displacement, as the difference in bone cut thickness between posterior and distal femoral regions.
Results
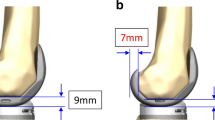
The mean magnitude of bony gap discrepancy necessary for mediolateral balancing was 1.6 ± 3.3 mm (range −7 to 8.2 mm) at 0° extension and −0.2 ± 2.6 mm (range −6.4 to 4.3 mm) at 90° flexion. At least 2 mm of bony gap discrepancy at 0° extension and 90° flexion was found in 40 patients (67%) and 26 patients (43%), respectively. In terms of femoral bone cut, posterior bone cut thickness was significantly larger than distal bone cut thickness in the medial compartment (p < 0.001). Bony gap discrepancy between distal and posterior regions of the femoral condyle was ≥2 mm in 28 patients (47%).
Conclusions
This study focused on two flaws of mechanically aligned TKA in OA patients. Substantial numbers of patients inevitably required >2 mm of medial collateral ligament release at 0° extension and showed a bone cut discrepancy between distal and posterior regions, carrying a risk of FEA displacement and subsequent unnatural knee motions during knee extension and flexion.
Level of evidence IV.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bellemans J, Colyn W, Vandenneucker H, Victor J (2012) The Chitranjan Ranawat award: is neutral mechanical alignment normal for all patients? The concept of constitutional varus. Clin Orthop Relat Res 470:45–53
Berend ME, Ritter MA, Meding JB, Faris PM, Keating EM, Redelman R, Faris GW, Davis KE (2004) Tibial component failure mechanisms in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 428:26–34
Chauhan SK, Clark GW, Lloyd S, Scott RG, Breidahl W, Sikorski JM (2004) Computer-assisted total knee replacement. A controlled cadaver study using a multi-parameter quantitative CT assessment of alignment (the Perth CT Protocol). J Bone Joint Surg 86B:818–823
Choong PF, Dowsey MM, Stoney JD (2009) Does accurate anatomic alignment result in better function and quality of life? Comparing conventional and computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 24:560–569
Churchill DL, Incavo SJ, Johnson CC, Beynnon BD (1998) The transepicondylar axis approximates the optimal flexion axis of the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res 356:111–118
Colle F, Lopomo N, Bruni D, Visani A, Iacono F, Zaffagnini S, Marcacci M (2014) Analysis of knee functional flexion axis in navigated TKA: identification and repeatability before and after implant positioning. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 22:694–702
Dossett HG, Estrada NA, Swartz GJ, LeFevre GW, Kwasman BG (2014) A randomised controlled trial of kinematically and mechanically aligned total knee replacements: two-year clinical results. Bone Joint J 96B:907–913
Eckhoff DG, Bach JM, Spitzer VM, Reinig KD, Bagur MM, Baldini TH, Flannery NM (2005) Three-dimensional mechanics, kinematics, and morphology of the knee viewed in virtual reality. J Bone Joint Surg Am 87(Suppl 2):71–80
Fang DM, Ritter MA, Davis KE (2009) Coronal alignment in total knee arthroplasty: just how important is it? J Arthroplasty 24(6 Suppl):39–43
Gu Y, Roth JD, Howell SM, Hull ML (2014) How frequently do four methods for mechanically aligning a total knee arthroplasty cause collateral ligament imbalance and Change Alignment from Normal in White Patients? AAOS Exhibit Selection. J Bone Joint Surg Am 96:e101
Howell SM, Papadopoulos S, Kuznik KT, Hull ML (2013) Accurate alignment and high function after kinematically aligned TKA performed with generic instruments. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21:2271–2280
Hungerford DS, Kenna RV, Krackow KA (1982) The porous-coated anatomic total knee. Orthop Clin North Am 13:103–122
Iacono F, Bruni D, Bignozzi S, Colle F, Marcacci M (2014) Does total knee arthroplasty modify flexion axis of the knee? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 22:1728–1735
Jeffery RS, Morris RW, Denham RA (1991) Coronal alignment after total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 73:709–714
Markolf KL, Mensch JS, Amstutz HC (1976) Stiffness and laxity of the knee—the contributions of the supporting structures. A quantitative in vitro study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 58:583–594
Mochizuki T, Tanifuji O, Koga Y, Sato T, Kobayashi K, Nishino K, Watanabe S, Ariumi A, Fujii T, Yamagiwa H, Omori G, Endo N (2016) Sex differences in femoral deformity determined using three-dimensional assessment for osteoarthritic knees. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. doi:10.1007/s00167-016-4166-2
Mullaji AB, Sharma A, Marawar S, Kanna R (2009) Quantification of effect of sequential posteromedial release on flexion and extension gaps: a computer-assisted study in cadaveric knees. J Arthroplasty 24:795–805
Nakano N, Matsumoto T, Hashimura M, Takayama K, Ishida K, Araki D, Matsushita T, Kuroda R, Kurosaka M (2016) Coronal lower limb alignment in normal knees-a radiographic analysis of 797 normal knee subjects. Knee 23:209–213
Nielsen S, Kromann-Andersen C, Rasmussen O, Andersen K (1984) Instability of cadaver knees after transection of capsule and ligaments. Acta Orthop Scand 55:30–34
Niki Y, Harato K, Nagai K, Suda Y, Nakamura M, Matsumoto M (2015) Effects of reduction osteotomy on gap balancing during total knee arthroplasty for severe varus deformity. J Arthroplasty 30:2116–2120
Niki Y, Nagai K, Sassa T, Harato K, Suda Y (2016) Comparison between cylindrical axis-reference and articular surface-reference femoral bone-cut for total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. doi:10.1007/s00167-016-4251-6
Ritter MA, Davis KE, Davis P, Farris A, Malinzak RA, Berend ME, Meding JB (2013) Preoperative malalignment increases risk of failure after total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 95:126–131
Ritter MA, Davis KE, Meding JB, Pierson JL, Berend ME, Malinzak RA (2011) The effect of alignment and BMI on failure of total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am 93:1588–1596
Sharkey PF, Hozack WJ, Rothman RH, Shastri S, Jacoby SM (2002) Why are total knee arthroplasties failing today? Clin Orthop Relat Res 404:7–13
Tang WM, Zhu YH, Chiu KY (2000) Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am 82:1603–1608
Tei K, Ishida K, Matsumoto T, Kubo S, Sasaki H, Shibanuma N, Akisue T, Nishida K, Kurosaka M, Kuroda R (2012) Novel image-matching software for postoperative evaluation after TKA. Orthopedics 35:e1711–e1715
Thienpont E, Cornu O, Bellemans J, Victor J (2015) Current opinions about coronal plane alignment in total knee arthroplasty: a survey article. Acta Orthop Belg 81:471–477
Urabe K, Mahoney OM, Mabuchi K, Itoman M (2008) Morphologic differences of the distal femur between Caucasian and Japanese women. J Orthop Surg 16:312–315
Vanlommel L, Vanlommel J, Claes S, Bellemans J (2013) Slight undercorrection following total knee arthroplasty results in superior clinical outcomes in varus knees. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21:2325–2330
Wang JW, Wang CJ (2002) Total knee arthroplasty for arthritis of the knee with extra articular deformity. J Bone Joint Surg Am 84:1769–1774
Wolff AM, Hungerford DS, Pepe CL (1991) The effect of extra articular varus and valgus deformity on total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 271:35–51
Yin L, Chen K, Guo L, Cheng L, Wang F, Yang L (2015) Identifying the functional flexion-extension axis of the knee: an in-vivo kinematics study. PLoS One 10:e0128877
Young SW, Walker ML, Bayan A, Briant-Evans T, Pavlou P, Farrington B (2016) No difference in 2-year functional outcomes using kinematic versus mechanical alignment in TKA: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin Orthop Relat Res. doi:10.1007/s11999-016-4844-x
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Niki, Y, Sassa T, Nagai K, Harato K, Kobayashi S, and Yamashita T declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niki, Y., Sassa, T., Nagai, K. et al. Mechanically aligned total knee arthroplasty carries a risk of bony gap changes and flexion–extension axis displacement. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 25, 3452–3458 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-017-4459-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-017-4459-0