Abstract
Purpose
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is currently the most exploited strategy in the clinical practice to provide a regenerative stimulus for tendon healing. The aim of the present study was to systematically review the available evidence on the treatment of the main tendon disorders where PRP is currently applied.
Methods
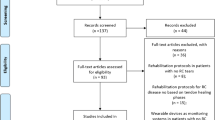
A systematic review of the literature was performed on the use of PRP as a treatment for tendinopathies focusing on the following sites: Achilles tendon, patellar tendon, rotator cuff tendons, and lateral elbow tendons. The following inclusion criteria for relevant articles were used: clinical trials written in English language up to 21 June 2016 on the use of PRP in the conservative or surgical treatment of the aforementioned tendinopathies.
Results
The research identified the following clinical trials dealing with the application of PRP in the selected tendons: 19 papers on patellar tendon (6 being RCTs: 4 dealing with PRP conservative application and 2 surgical), 24 papers on Achilles tendon (4 RCTs: 3 conservative and 1 surgical), 29 on lateral elbow tendons (17 RCTs, all conservative), and 32 on rotator cuff (22 RCTs: 18 surgical and 3 conservative).
Conclusion
Patellar tendons seem to benefit from PRP injections, whereas in the Achilles tendon, PRP application is not indicated neither as a conservative approach nor as a surgical augmentation. Lateral elbow tendinopathy showed an improvement in most of the high-level studies, but the lack of proven superiority with respect to the more simple whole-blood injections still questions its use in the clinical practice. With regard to rotator cuff pathology, the vast majority of surgical RCTs documented a lack of beneficial effects, whereas there is still inconclusive evidence concerning its conservative application in rotator cuff disorders.
Level of evidence
Systematic review of level I–IV trials, Level IV.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andia I, Latorre PM, Gomez MC et al (2014) Platelet-rich plasma in the conservative treatment of painful tendinopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of controlled studies. Br Med Bull 110(1):99–115
Andriolo L, Di Matteo B, Kon E et al (2015) PRP augmentation for ACL reconstruction. Biomed Res Int. 2015:371746
Antuña S, Barco R, Martínez Diez JM et al (2013) Platelet-rich fibrin in arthroscopic repair of massive rotator cuff tears: a prospective randomized pilot clinical trial. Acta Orthop Belg 79(1):25–30
Barber FA, Hrnack SA, Snyder SJ et al (2011) Rotator cuff repair healing influenced by platelet-rich plasma construct augmentation. Arthroscopy 27(8):1029–1035
Behera P, Dhillon M, Aggarwal S et al (2015) Leukocyte-poor platelet-rich plasma versus bupivacaine for recalcitrant lateral epicondylar tendinopathy. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 23(1):6–10
Bergeson AG, Tashjian RZ, Greis PE et al (2012) Effects of platelet-rich fibrin matrix on repair integrity of at-risk rotator cuff tears. Am J Sports Med 40(2):286–293
Boswell SG, Cole BJ, Sundman EA et al (2012) Platelet-rich plasma: a milieu of bioactive factors. Arthroscopy 28(3):429–439
Brkljac M, Kumar S, Kalloo D et al (2015) The effect of platelet-rich plasma injection on lateral epicondylitis following failed conservative management. J Orthop 12(Suppl 2):S166–S170
Carr AJ, Murphy R, Dakin SG et al (2015) Platelet-rich plasma injection with arthroscopic acromioplasty for chronic rotator cuff tendinopathy: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Sports Med 43(12):2891–2897
Castricini R, Longo UG, De Benedetto M et al (2011) Platelet-rich plasma augmentation for arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Sports Med 39(2):258–265
Charousset C, Zaoui A, Bellaiche L et al (2014) Are multiple platelet-rich plasma injections useful for treatment of chronic patellar tendinopathy in athletes? A prospective study. Am J Sports Med 42(4):906–911
Charousset C, Zaoui A, Bellaïche L et al (2014) Does autologous leukocyte-platelet-rich plasma improve tendon healing in arthroscopic repair of large or massive rotator cuff tears? Arthroscopy 30(4):428–435
Chaudhury S, de La Lama M, Adler RS et al (2013) Platelet-rich plasma for the treatment of lateral epicondylitis: sonographic assessment of tendon morphology and vascularity (pilot study). Skeletal Radiol 42(1):91–97
Creaney L, Wallace A, Curtis M et al (2011) Growth factor-based therapies provide additional benefit beyond physical therapy in resistant elbow tendinopathy: a prospective, single-blind, randomised trial of autologous blood injections versus platelet-rich plasma injections. Br J Sports Med 45(12):966–971
Crescibene A, Napolitano M, Sbano R et al (2015) Infiltration of autologous growth factors in chronic tendinopathies. J Blood Transfus. 2015:924380
Dallaudière B, Pesquer L, Meyer P et al (2014) Intratendinous injection of platelet-rich plasma under US guidance to treat tendinopathy: a long-term pilot study. J Vasc Interv Radiol 25(5):717–723
de Almeida AM, Demange MK, Sobrado MF et al (2012) Patellar tendon healing with platelet-rich plasma: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Am J Sports Med 40(6):1282–1288
De Carli A, Lanzetti RM, Ciompi A et al (2016) Can platelet-rich plasma have a role in Achilles tendon surgical repair? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 24(7):2231–2237
de Jonge S, de Vos RJ, Weir A et al (2011) One-year follow-up of platelet-rich plasma treatment in chronic Achilles tendinopathy: a double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial. Am J Sports Med 39(8):1623–1629
de Vos RJ, Weir A, van Schie HT et al (2010) Platelet-rich plasma injection for chronic Achilles tendinopathy: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 303(2):144–149
Deans VM, Miller A, Ramos J (2012) A prospective series of patients with chronic Achilles tendinopathy treated with autologous-conditioned plasma injections combined with exercise and therapeutic ultrasonography. J Foot Ankle Surg 51(6):706–710
Del Buono A, Oliva F, Osti L et al (2013) Metalloproteases and tendinopathy. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J 3(1):51–57
DeLong JM, Russell RP, Mazzocca AD (2012) Platelet-rich plasma: the PAW classification system. Arthroscopy 28(7):998–1009
Di Benedetto P, Di Benedetto ED, Beltrame A et al (2016) Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair with or without PrP: our experience. Acta Biomed 87(Suppl 1):75–83
Di Matteo B, Filardo G, Kon E et al (2015) Platelet-rich plasma: evidence for the treatment of patellar and Achilles tendinopathy-a systematic review. Musculoskelet Surg. 99(1):1–9
Dohan Ehrenfest DM, Bielecki T, Jimbo R et al (2012) Do the fibrin architecture and leukocyte content influence the growth factor release of platelet concentrates? An evidence-based answer comparing a pure platelet-rich plasma (P-PRP) gel and a leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF). Curr Pharm Biotechnol 13(7):1145–1152
Dohan Ehrenfest DM, Rasmusson L, Albrektsson T (2009) Classification of platelet concentrates: from pure platelet-rich plasma (P-PRP) to leucocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF). Trends Biotechnol 27(3):158–167
Dragoo JL, Wasterlain AS, Braun HJ et al (2014) Platelet-rich plasma as a treatment for patellar tendinopathy: a double-blind, randomized controlled trial. Am J Sports Med 42(3):610–618
Ferrero G, Fabbro E, Orlandi D et al (2012) Ultrasound-guided injection of platelet-rich plasma in chronic Achilles and patellar tendinopathy. J Ultrasound 15(4):260–266
Filardo G, Kon E, Della Villa S et al (2010) Use of platelet-rich plasma for the treatment of refractory jumper’s knee. Int Orthop 34(6):909–915
Filardo G, Kon E, Di Matteo B et al (2014) Platelet-rich plasma injections for the treatment of refractory Achilles tendinopathy: results at 4 years. Blood Transfus. 12(4):533–540
Filardo G, Kon E, Di Matteo B et al (2013) Platelet-rich plasma for the treatment of patellar tendinopathy: clinical and imaging findings at medium-term follow-up. Int Orthop 37(8):1583–1589
Filardo G, Kon E, Roffi A et al (2015) Platelet-rich plasma: why intra-articular? A systematic review of preclinical studies and clinical evidence on PRP for joint degeneration. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 23(9):2459–2474
Filardo G, Presti ML, Kon E et al (2010) Nonoperative biological treatment approach for partial Achilles tendon lesion. Orthopedics. 33(2):120–123
Finnoff JT, Fowler SP, Lai JK et al (2011) Treatment of chronic tendinopathy with ultrasound-guided needle tenotomy and platelet-rich plasma injection. PM R. 3(10):900–911
Flury M, Rickenbacher D, Schwyzer HK et al (2016) Does pure platelet-rich plasma affect postoperative clinical outcomes after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair? A randomized controlled trial. Am J Sports Med. doi:10.1177/0363546516645518
Ford RD, Schmitt WP, Lineberry K et al (2015) A retrospective comparison of the management of recalcitrant lateral elbow tendinosis: platelet-rich plasma injections versus surgery. Hand (NY) 10(2):285–291
Gautam VK, Verma S, Batra S et al (2015) Platelet-rich plasma versus corticosteroid injection for recalcitrant lateral epicondylitis: clinical and ultrasonographic evaluation. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 23(1):1–5
Gaweda K, Tarczynska M, Krzyzanowski W (2010) Treatment of Achilles tendinopathy with platelet-rich plasma. Int J Sports Med 31(8):577–583
Glanzmann MC, Audigé L (2015) Platelet-rich plasma for chronic lateral epicondylitis: Is one injection sufficient? Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 135(12):1637–1645
Gosens T, Den Oudsten BL, Fievez E et al (2012) Pain and activity levels before and after platelet-rich plasma injection treatment of patellar tendinopathy: a prospective cohort study and the influence of previous treatments. Int Orthop 36(9):1941–1946
Gosens T, Peerbooms JC, van Laar W et al (2011) Ongoing positive effect of platelet-rich plasma versus corticosteroid injection in lateral epicondylitis: a double-blind randomized controlled trial with 2-year follow-up. Am J Sports Med 39(6):1200–1208
Guelfi M, Pantalone A, Vanni D et al (2015) Long-term beneficial effects of platelet-rich plasma for non-insertional Achilles tendinopathy. Foot Ankle Surg. 21(3):178–181
Gumina S, Campagna V, Ferrazza G et al (2012) Use of platelet-leukocyte membrane in arthroscopic repair of large rotator cuff tears: a prospective randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 94(15):1345–1352
Hak A, Rajaratnam K, Ayeni OR et al (2015) A double-blinded placebo randomized controlled trial evaluating short-term efficacy of platelet-rich plasma in reducing postoperative pain after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: a pilot study. Sports Health. 7(1):58–66
Hechtman KS, Uribe JW, Botto-vanDemden A et al (2011) Platelet-rich plasma injection reduces pain in patients with recalcitrant epicondylitis. Orthopedics. 34(2):92
Ilhanli I, Guder N, Gul M (2015) Platelet-rich plasma treatment with physical therapy in chronic partial supraspinatus tears. Iran Red Crescent Med J 17(9):e23732
Jo CH, Kim JE, Yoon KS et al (2011) Does platelet-rich plasma accelerate recovery after rotator cuff repair? A prospective cohort study. Am J Sports Med 39(10):2082–2090
Jo CH, Shin JS, Lee YG et al (2013) Platelet-rich plasma for arthroscopic repair of large to massive rotator cuff tears: a randomized, single-blind, parallel-group trial. Am J Sports Med 41(10):2240–2248
Kaniki N, Willits K, Mohtadi NG et al (2014) A retrospective comparative study with historical control to determine the effectiveness of platelet-rich plasma as part of nonoperative treatment of acute Achilles tendon rupture. Arthroscopy 30(9):1139–1145
Karaduman M, Okkaoglu MC, Sesen H et al (2016) Platelet-rich plasma versus open surgical release in chronic tennis elbow: A retrospective comparative study. J Orthop 13(1):10–14
Kaux JF, Bruyere O, Croisier JL et al (2015) One-year follow-up of platelet-rich plasma infiltration to treat chronic proximal patellar tendinopathies. Acta Orthop Belg 81(2):251–256
Kaux JF, Croisier JL, Bruyere O et al (2015) One injection of platelet-rich plasma associated to a submaximal eccentric protocol to treat chronic jumper’s knee. J Sports Med Phys Fitness 55(9):953–961
Kaux JF, Croisier JL, Forthomme B et al (2016) Using platelet-rich plasma to treat jumper’s knees: exploring the effect of a second closely-timed infiltration. J Sci Med Sport. 19(3):200–204
Kaux JF, Croisier JL, Léonard P et al (2014) Exuberant inflammatory reaction as a side effect of platelet-rich plasma injection in treating one case of tendinopathy. Clin J Sport Med 24(2):150–152
Kearney RS, Parsons N, Costa ML (2013) Achilles tendinopathy management: a pilot randomised controlled trial comparing platelet-rich plasma injection with an eccentric loading programme. Bone Joint Res 2(10):227–232
Kesikburun S, Tan AK, Yilmaz B et al (2013) Platelet-rich plasma injections in the treatment of chronic rotator cuff tendinopathy: a randomized controlled trial with 1-year follow-up. Am J Sports Med 41(11):2609–2616
Khaliq A, Khan I, Inam M et al (2015) Effectiveness of platelets rich plasma versus corticosteroids in lateral epicondylitis. J Pak Med Assoc 65(11 Suppl 3):S100–S104
Kon E, Filardo G, Delcogliano M et al (2009) Platelet-rich plasma: new clinical application: a pilot study for treatment of jumper’s knee. Injury. 40(6):598–603
Kon E, Filardo G, Di Matteo B et al (2013) PRP for the treatment of cartilage pathology. Open Orthop J. 3(7):120–128
Krogh TP, Ellingsen T, Christensen R et al (2016) Ultrasound-guided injection therapy of Achilles tendinopathy with platelet-rich plasma or saline: a randomized, blinded, placebo-controlled trial. Am J Sports Med. doi:10.1177/0363546516647958
Krogh TP, Fredberg U, Stengaard-Pedersen K et al (2013) Treatment of lateral epicondylitis with platelet-rich plasma, glucocorticoid, or saline: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Am J Sports Med 41(3):625–635
Kujala UM, Sarna S, Kaprio J (2015) Cumulative incidence of Achilles tendon rupture and tendinopathy in male former elite athletes. Clin J Sport Med 15(3):133–135
Lebiedziński R, Synder M, Buchcic P et al (2015) A randomized study of autologous conditioned plasma and steroid injections in the treatment of lateral epicondylitis. Int Orthop 39(11):2199–2203
Lian OB, Engebretsen L, Bahr R (2005) Prevalence of jumper’s knee among elite athletes from different sports: a cross-sectional study. Am J Sports Med 33(4):561–567
Malavolta EA, Gracitelli ME, Ferreira Neto AA et al (2014) Platelet-rich plasma in rotator cuff repair: a prospective randomized study. Am J Sports Med 42(10):2446–2454
Mautner K, Colberg RE, Malanga G et al (2013) Outcomes after ultrasound-guided platelet-rich plasma injections for chronic tendinopathy: a multicenter, retrospective review. PM R. 5(3):169–175
Mautner K, Malanga GA, Smith J et al (2015) A call for a standard classification system for future biologic research: the rationale for new PRP nomenclature. PM R. 7(4 Suppl):S53–S59
McCarrel TM, Minas T, Fortier LA (2012) Optimization of leukocyte concentration in platelet-rich plasma for the treatment of tendinopathy. J Bone Joint Surg Am 94(19):e143(1–8)
Mishra A, Pavelko T (2006) Treatment of chronic elbow tendinosis with buffered platelet-rich plasma. Am J Sports Med 34(11):1774–1778
Mishra AK, Skrepnik NV, Edwards SG et al (2014) Efficacy of platelet-rich plasma for chronic tennis elbow: a double-blind, prospective, multicenter, randomized controlled trial of 230 patients. Am J Sports Med 42(2):463–471
Montalvan B, Le Goux P, Klouche S et al (2016) Inefficacy of ultrasound-guided local injections of autologous conditioned plasma for recent epicondylitis: results of a double-blind placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial with one-year follow-up. Rheumatology (Oxford) 55(2):279–285
Monto RR (2014) Platelet-rich plasma efficacy versus corticosteroid injection treatment for chronic severe plantar fasciitis. Foot Ankle Int 35(4):313–318
Murawski CD, Smyth NA, Newman H et al (2014) A single platelet-rich plasma injection for chronic midsubstance Achilles tendinopathy: a retrospective preliminary analysis. Foot Ankle Spec. 7(5):372–376
Oloff L, Elmi E, Nelson J, Crain J (2015) Retrospective analysis of the effectiveness of platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of Achilles tendinopathy: pretreatment and posttreatment correlation of magnetic resonance imaging and clinical assessment. Foot Ankle Spec. 8(6):490–497
Owens RF Jr, Ginnetti J, Conti SF et al (2011) Clinical and magnetic resonance imaging outcomes following platelet rich plasma injection for chronic midsubstance Achilles tendinopathy. Foot Ankle Int 32(11):1032–1039
Palacio EP, Schiavetti RR, Kanematsu M et al (2016) Effects of platelet-rich plasma on lateral epicondylitis of the elbow: prospective randomized controlled trial. Rev Bras Ortop. 51(1):90–95
Pandey V, Bandi A, Madi S et al (2016) Does application of moderately concentrated platelet-rich plasma improve clinical and structural outcome after arthroscopic repair of medium-sized to large rotator cuff tear? A randomized controlled trial. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2016.01.036
Peerbooms JC, Sluimer J, Bruijn DJ et al (2010) Positive effect of an autologous platelet concentrate in lateral epicondylitis in a double-blind randomized controlled trial: platelet-rich plasma versus corticosteroid injection with a 1-year follow-up. Am J Sports Med 38(2):255–262
Perdisa F, Filardo G, Di Matteo B et al (2014) Platelet rich plasma: a valid augmentation for cartilage scaffolds? A systematic review. Histol Histopathol 29(7):805–814
Perut F, Filardo G, Mariani E et al (2013) Preparation method and growth factor content of platelet concentrate influence the osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells. Cytotherapy. 15(7):830–839
Peters JA, Zwerver J, Diercks RL et al (2016) Preventive interventions for tendinopathy: a systematic review. J Sci Med Sport. 19(3):205–211
Raeissadat SA, Rayegani SM, Hassanabadi H et al (2014) Is Platelet-rich plasma superior to whole blood in the management of chronic tennis elbow: one year randomized clinical trial. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 18(6):12
Raeissadat SA, Sedighipour L, Rayegani SM et al (2014) Effect of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) versus autologous whole blood on pain and function improvement in tennis elbow: a randomized clinical trial. Pain Res Treat. 2014:191525
Randelli P, Arrigoni P, Ragone V et al (2011) Platelet rich plasma in arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: a prospective RCT study, 2-year follow-up. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 20(4):518–528
Randelli PS, Arrigoni P, Cabitza P et al (2008) Autologous platelet rich plasma for arthroscopic rotator cuff repair. A pilot study. Disabil Rehabil 30(20–22):1584–1589
Rha DW, Park GY, Kim YK et al (2013) Comparison of the therapeutic effects of ultrasound-guided platelet-rich plasma injection and dry needling in rotator cuff disease: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Rehabil. 27(2):113–122
Riley G (2004) The pathogenesis of tendinopathy. A molecular perspective. Rheumatology (Oxford) 43(2):131–142
Rodeo SA, Delos D, Williams RJ et al (2012) The effect of platelet-rich fibrin matrix on rotator cuff tendon healing: a prospective, randomized clinical study. Am J Sports Med 40(6):1234–1241
Ruiz-Moneo P, Molano-Muñoz J, Prieto E et al (2013) Plasma rich in growth factors in arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: a randomized, double-blind, controlled clinical trial. Arthroscopy 29(1):2–9
Salini V, Vanni D, Pantalone A et al (2015) Platelet Rich Plasma therapy in non-insertional Achilles tendinopathy: the efficacy is reduced in 60-years old people compared to young and middle-age individuals. Front Aging Neurosci. 10(7):228
Sánchez M, Anitua E, Azofra J et al (2007) Comparison of surgically repaired Achilles tendon tears using platelet-rich fibrin matrices. Am J Sports Med 35(2):245–251
Scarpone M, Rabago D, Snell E et al (2013) Effectiveness of platelet-rich plasma injection for rotator cuff tendinoplasty: a prospective open-label study. Glob Adv Health Med. 2(2):26–31
Schepull T, Kvist J, Norrman H et al (2011) Autologous platelets have no effect on the healing of human Achilles tendon ruptures: a randomized single-blind study. Am J Sports Med 39(1):38–47
Seijas R, Cuscó X, Sallent A et al (2016) Pain in donor site after BTB-ACL reconstruction with PRGF: a randomized trial. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 136(6):829–835
Tan XX, Ju HY, Yan W et al (2016) Autologous platelet lysate local injections for the treatment of refractory lateral epicondylitis. J Orthop Surg Res. 11:17
Tetschke E, Rudolf M, Lohmann CH et al (2015) Autologous proliferative therapies in recalcitrant lateral epicondylitis. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 94(9):696–706
Thanasas C, Papadimitriou G, Charalambidis C et al (2011) Platelet-rich plasma versus autologous whole blood for the treatment of chronic lateral elbow epicondylitis: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Am J Sports Med 39(10):2130–2134
Tol JL, Spiezia F, Maffulli N (2012) Neovascularization in Achilles tendinopathy: have we been chasing a red herring? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 20(10):1891–1894
Tonk G, Kumar A, Gupta A (2014) Platelet rich plasma versus laser therapy in lateral epicondylitis of elbow. Indian J Orthop. 48(4):390–393
Torricelli P, Fini M, Filardo G et al (2011) Regenerative medicine for the treatment of musculoskeletal overuse injuries in competition horses. Int Orthop 35(10):1569–1576
Tschon M, Fini M, Giardino R et al (2011) Lights and shadows concerning platelet products for musculoskeletal regeneration. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 1(3):96–107
Vannini F, Di Matteo B, Filardo G et al (2014) Platelet-rich plasma for foot and ankle pathologies: a systematic review. Foot Ankle Surg. 20(1):2–9
Verhaegen F, Brys P, Debeer P (2016) Rotator cuff healing after needling of a calcific deposit using platelet-rich plasma augmentation: a randomized, prospective clinical trial. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 25(2):169–173
Vetrano M, Castorina A, Vulpiani MC et al (2013) Platelet-rich plasma versus focused shock waves in the treatment of jumper’s knee in athletes. Am J Sports Med 41(4):795–803
Virchenko O, Aspenberg P (2006) How can one platelet injection after tendon injury lead to a stronger tendon after 4 weeks? Interplay between early regeneration and mechanical stimulation. Acta Orthop 77(5):806–812
Volpi P, Quaglia A, Schoenhuber H et al (2010) Growth factors in the management of sport-induced tendinopathies: results after 24 months from treatment. A pilot study. J Sports Med Phys Fitness 50(4):494–500
von Wehren L, Blanke F, Todorov A et al (2015) The effect of subacromial injections of autologous conditioned plasma versus cortisone for the treatment of symptomatic partial rotator cuff tears. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. doi:10.1007/s00167-015-3651-3
Wang A, McCann P, Colliver J et al (2015) Do postoperative platelet-rich plasma injections accelerate early tendon healing and functional recovery after arthroscopic supraspinatus repair? A randomized controlled trial. Am J Sports Med 43(6):1430–1437
Weber SC, Kauffman JI, Parise C et al (2013) Platelet-rich fibrin matrix in the management of arthroscopic repair of the rotator cuff: a prospective, randomized, double-blinded study. Am J Sports Med 41(2):263–270
Weibrich G, Hansen T, Kleis W et al (2004) Effect of platelet concentration in platelet-rich plasma on peri-implant bone regeneration. Bone 34(4):665–671
Werthel JD, Pelissier A, Massin P et al (2014) Arthroscopic double row cuff repair with suture-bridging and autologous conditioned plasma injection: functional and structural results. Int J Shoulder Surg. 8(4):101–106
Wesner M, Defreitas T, Bredy H et al (2016) A pilot study evaluating the effectiveness of platelet-rich plasma therapy for treating degenerative tendinopathies: a randomized control trial with synchronous observational cohort. PLoS ONE 11(2):e0147842
Yadav R, Kothari SY, Borah D (2015) Comparison of local injection of platelet rich plasma and corticosteroids in the treatment of lateral epicondylitis of humerus. J Clin Diagn Res 9(7):RC05-7
Zayni R, Thaunat M, Fayard JM et al (2015) Platelet-rich plasma as a treatment for chronic patellar tendinopathy: comparison of a single versus two consecutive injections. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J 5(2):92–98
Zhang Z, Wang Y, Sun J (2016) The effect of platelet-rich plasma on arthroscopic double-row rotator cuff repair: a clinical study with 12-month follow-up. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 50(2):191–197
Zumstein MA, Rumian A, Lesbats V et al (2014) Increased vascularization during early healing after biologic augmentation in repair of chronic rotator cuff tears using autologous leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF): a prospective randomized controlled pilot trial. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 23(1):3–12
Zumstein MA, Rumian A, Thélu CÉ et al (2016) SECEC Research Grant 2008 II: use of platelet- and leucocyte-rich fibrin (L-PRF) does not affect late rotator cuff tendon healing: a prospective randomized controlled study. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 25(1):2–11
Acknowledgments
The present study was partially supported by PRRU (Emilia-Romagna Region/University of Bologna Project) 2010–2012.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding
There is no funding source.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
For this kind of study (systematic review of literature) formal consent is not required.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Filardo, G., Di Matteo, B., Kon, E. et al. Platelet-rich plasma in tendon-related disorders: results and indications. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 26, 1984–1999 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-016-4261-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-016-4261-4