Abstract
Purpose
Starting from the hypothesis that a deep-dished highly congruent tibial insert in cruciate-retaining total knee arthroplasty would prevent the increase in patellar tendon angle and anterior patellar translation by reducing the paradoxical anterior femoral translation, the main purpose of the present study was to investigate the effect of this prosthesis design, and secondary to assess the clinical outcomes at 6-month follow-up.
Methods
Twenty patients treated with cruciate-retaining total knee arthroplasty with navigation technique were enrolled and prospectively followed up at 6 months. The median value of age was 71 years (57–83). Before and after surgery, the following parameters were calculated: patellar tendon angle, anterior–posterior and medio-lateral patellar translation, patellar height and range of motion. All patients were assessed with the SF-36 Physical Functioning and the Knee injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score ADL scores.
Results
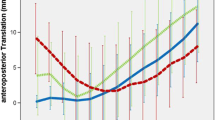
Patellar tendon angle and anterior patellar translation significantly increased in post-operative conditions (p < 0.0001); a statistically significant medial patellar translation was found (p < 0.0001), while patellar height did not show any difference between pre- and post-operative conditions (n.s). A significant correlation was found between patellar tendon angle and anterior patellar translation and the clinical scores (p < 0.0417). There was a significant post-operative decrease (p < 0.0033) in the range of motion.
Conclusions
The present study failed to demonstrate that deep-dished highly congruent tibial insert prevents the anterior translation of the patella in cruciate-retaining total knee arthroplasty, thus causing inferior clinical scores. It provided useful information about the biomechanical role of the patella in total knee arthroplasty, allowing to choose the most appropriate surgical approach.
Level of evidence
Case series, Level IV.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abolghasemian M, Samiezadeh S, Sternheim A, Bougherara H, Barnes CL, Backstein DJ (2013) Effect of patellar thickness on knee flexion in total knee arthroplasty: a biomechanical and experimental study. J Arthroplast 29(1):80–84
Anagnostakos K, Lorbach O, Reiter S, Kohn D (2011) Comparison of five patellar height measurement methods in 90° knee flexion. Int Orthop 35(12):1791–1797
Andriacchi TP, Yoder D, Conley A, Rosenberg A, Sum J, Galante JO (1997) Patellofemoral design influences function following total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplast 12(3):243–249
Anglin C, Brimacombe JM, Hodgson AJ, Masri BA, Greidanus NV, Tonetti J, Wilson DR (2008) Determinants of patellar tracking in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 23(7):900–910
Anglin C, Ho KC, Briard JL, de Lambilly C, Plaskos C, Nodwell E, Stindel E (2008) In vivo patellar kinematics during total knee arthroplasty. Comput Aided Surg 13(6):377–391
Armstrong AD, Brien HJ, Dunning CE, King GJ, Johnson JA, Chess DG (2003) Patellar position after total knee arthroplasty: influence of femoral component malposition. J Arthroplast 18(4):458–465
Bellemans J, Banks S, Victor J, Vandenneucker H, Moemans A (2002) Fluoroscopic analysis of the kinematics of deep flexion in total knee arthroplasty. Influence of posterior condylar offset. J Bone Jt Surg Br 84(1):50–53
Belvedere C, Catani F, Ensini A, Moctezuma de la Barrera JL, Leardini A (2007) Patellar tracking during total knee arthroplasty: an in vitro feasibility study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 15(8):985–993
Bertin KC, Komistek RD, Dennis DA, Hoff WA, Anderson DT, Langer T (2002) In vivo determination of posterior femoral rollback for subjects having a NexGen posterior cruciate-retaining total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplast 17(8):1040–1048
Casino D, Martelli S, Zaffagnini S, Lopomo N, Iacono F, Bignozzi S, Visani A, Marcacci M (2009) Knee stability before and after total and unicondylar knee replacement: in vivo kinematic evaluation utilizing navigation. J Orthop Res 27(2):202–207
Chonko DJ, Lombardi AV Jr, Berend KR (2004) Patella baja and total knee arthroplasty (TKA): etiology, diagnosis, and management. Surg Technol Int 12:231–238
Christen B, Neukamp M, Aghayev E (2012) No difference in anterior tibial translation with and without posterior cruciate ligament in less invasive total knee replacement. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 20(3):503–509
Cole GK, Nigg BM, Ronsky JL, Yeadon MR (1993) Application of the joint coordinate system to three-dimensional joint attitude and movement representation: a standardization proposal. J Biomech Eng 115(4A):344–349
Daniilidis K, Höll S, Gosheger G, Dieckmann R, Martinelli N, Ostermeier S, Tibesku CO (2013) Femoro-tibial kinematics after TKA in fixed- and mobile-bearing knees in the sagittal plane. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21(10):2392–2397
Roos EM, Lohmander LS (2003) The Knee injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (KOOS): from joint injury to osteoarthritis. Health Qual Life Outcomes 1:64
Fantozzi S, Catani F, Ensini A, Leardini A, Giannini S (2006) Femoral rollback of cruciate-retaining and posterior-stabilized total knee replacements: in vivo fluoroscopic analysis during activities of daily living. J Orthop Res 24(12):2222–2229
Flören M, Davis J, Peterson MG, Laskin RS (2007) A mini-midvastus capsular approach with patellar displacement decreases the prevalence of patella baja. J Arthroplast 22(6 Suppl 2):51–57
Grelsamer RP, Weinstein CH (2001) Applied biomechanics of the patella. Clin Orthop Relat Res 389:9–14
Grood ES, Suntay WJ (1983) A joint coordinate system for the clinical description of three-dimensional motions: application to the knee. J Biomech Eng 105(2):136–144
Hartford JM, Banit D, Hall K, Kaufer H (2001) Radiographic analysis of low contact stress meniscal bearing total knee replacements. J Bone Jt Surg Am 83-A(2):229–234
Heim CS, Postak PD, Plaxton NA, Greenwald AS (2001) Classification of mobile-bearing knee designs: mobility and constraint. J Bone Jt Surg Am 83-A(Suppl 2(Pt 1)):32–37
Hofmann AA, Tkach TK, Evanich CJ, Camargo MP (2000) Posterior stabilization in total knee arthroplasty with use of an ultracongruent polyethylene insert. J Arthroplast 15(5):576–583
Hollinghurst D, Stoney J, Ward T, Pandit H, Beard D, Murray DW (2007) In vivo sagittal plane kinematics of the Avon patellofemoral arthroplasty. J Arthroplast 22(1):117–123
Hsu HC, Luo ZP, Rand JA et al (1996) Influence of patellar thickness on patellar tracking and patellofemoral contact characteristics after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplast 11:69–80
Innocenti B, Pianigiani S, Labey L, Victor J, Bellemans J (2011) Contact forces in several TKA designs during squatting: a numerical sensitivity analysis. J Biomech 44(8):1573–1581
Kellgren JH, Lawrence JS (1957) Radiological assessment of osteo-arthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis 16(4):494–502
Laskin RS, Maruyama Y, Villaneuva M, Bourne R (2000) Deep-dish congruent tibial component use in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized prospective study. Clin Orthop Relat Res 380:36–44
Li G, Papannagari R, Nha KW, Defrate LE, Gill TJ, Rubash HE (2007) The coupled motion of the femur and patella during in vivo weightbearing knee flexion. J Biomech Eng 129(6):937–943
Louisia S, Siebold R, Canty J, Bartlett RJ (2005) Assessment of posterior stability in total knee replacement by stress radiographs: prospective comparison of two different types of mobile bearing implants. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 13:476–482
Martelli S, Zaffagnini S, Bignozzi S, Bontempi M, Marcacci M (2006) Validation of a new protocol for computer-assisted evaluation of kinematics of double-bundle ACL reconstruction. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 21(3):279–287
Massin P, Boyer P, Sabourin M (2012) Less femorotibial rotation and AP translation in deep-dished total knee arthroplasty. An intraoperative kinematic study using navigation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 20(9):1714–1719
Meneghini RM, Ritter MA, Pierson JL, Meding JB, Berend ME, Faris PM (2006) The effect of the Insall-Salvati ratio on outcome after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplast 21(6 Suppl 2):116–120
Merican AM, Ghosh KM, Baena FR, Deehan DJ, Amis AA (2012) Patellar thickness and lateral retinacular release affects patellofemoral kinematics in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. doi:10.1007/s00167-012-2312-z
Merican AM, Ghosh KM, Iranpour F, Deehan DJ, Amis AA (2011) The effect of femoral component rotation on the kinematics of the tibiofemoral and patellofemoral joints after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 19(9):1479–1487
Miller RK, Goodfellow JW, Murray DW, O’Connor JJ (1998) In vitro measurement of patellofemoral force after three types of knee replacement. J Bone Jt Surg Br 80(5):900–906
Pal S, Besier TF, Draper CE, Fredericson M, Gold GE, Beaupre GS, Delp SL (2012) Patellar tilt correlates with vastus lateralis: vastus medialis activation ratio in maltracking patellofemoral pain patients. J Orthop Res 30(6):927–933
Pandit H, Van Duren BH, Gallagher JA, Beard DJ, Dodd CA, Gill HS, Murray DW (2008) Combined anterior cruciate reconstruction and Oxford unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: in vivo kinematics. Knee 15(2):101–106
Price AJ, Rees JL, Beard DJ, Gill RH, Dodd CA, Murray DM (2004) Sagittal plane kinematics of a mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty at 10 years: a comparative in vivo fluoroscopic analysis. J Arthroplast 19(5):590–597
Sakai N, Luo ZP, Rand JA, An KN (2000) The influence of weakness in the vastus medialis oblique muscle on the patellofemoral joint: an in vitro biomechanical study. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 15(5):335–339
Stagni R, Fantozzi S, Catani F, Leardini A (2010) Can patellar tendon angle reveal sagittal kinematics in total knee arthroplasty? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 18(7):949–954
Tibesku CO, Daniilidis K, Vieth V, Skwara A, Heindel W, Fuchs-Winkelmann S (2011) Sagittal plane kinematics of fixed- and mobile-bearing total knee replacements. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 19(9):1488–1495
Ware JE Jr, Sherbourne CD (1992) The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Med Care 30(6):473–483
Weale AE, Murray DW, Newman JH, Ackroyd CE (1999) The length of the patellar tendon after unicompartmental and total knee replacement. J Bone Jt Surg Br 81(5):790–795
Wiles AD, Thompson DG, Frantz DD (2004) Accuracy assessment and interpretation for optical tracking systems. Proc SPIE 5367:421–432
Yue B, Varadarajan KM, Rubash HE, Li G (2012) In vivo function of posterior cruciate ligament before and after posterior cruciate ligament-retaining total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop 36(7):1387–1392
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to particularly thank Silvia Bassini for her remarkable contribution to improve the graphics of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akkawi, I., Colle, F., Bruni, D. et al. Deep-dished highly congruent tibial insert in CR-TKA does not prevent patellar tendon angle increase and patellar anterior translation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 23, 1622–1630 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-014-2889-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-014-2889-5