Abstract
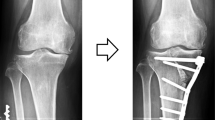
A 14-year-old girl suffering from severe bilateral late-onset Blount’s disease was treated by triple proximal tibial osteotomy. Surgical procedures included dome, respectively, closing wedge valgus osteotomy of the tibia, elevating osteotomy of the medial tibial plateau and lateralising osteotomy of the anterior tibial tuberosity. Mechanical leg axis was restored close to normal, the depression of the medial tibial plateau corrected and the extensor apparatus of the knee realigned. At 7.5 (right side) and 5.5 (left side) months of follow-up, all osteotomies had radiologically consolidated and the patient did not complain of knee pain or instability.
Level of evidence IV.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Accabled F, Laville JM, Harper L (2003) One-step treatment for evolved Blount’s disease : four cases and review of the literature. J Pediatr Orthop 23:747–752
Amer AR, Khanfour AA (2010) Evaluation of treatment of late-onset tibia vara using gradual angulation translation high tibial osteotomy. Acta Orthop Belg 76:360–366
Blount WP (1937) Tibia vara: osteochondrosis deformans tibiae. J Bone Jt Surg 19:1–29
Brilhault J, Lautman S, Favard L, Burdin P (2002) Lateral femoral sliding osteotomy. Lateral release in total knee arthroplasty for a fixed valgus deformity. J Bone Jt Surg Br 84:1131–1137
Catonne Y (1997) La maladie de Blount. Conférences d’enseignement de la SOFCOT. Elsevier, pp 147–163
Doyle BS, Volk AG, Smith CF (1996) Infantile Blount disease: long-term follow-up of surgically treated patient at skeletal maturity. J Pediatr Orthop 16:469–476
Fitoussi F, Ilharreborde B, Lefevre Y, Souchet P, Presedo A, Mazda K, Penneçot GF (2011) Fixator-assisted medial tibial plateau elevation to treat severe Blount’s disease: outcomes at maturity. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 97:172–178
Gregosiewicz A, Wosko I, Kandzierski G, Drabik Z (1989) Double-elevating osteotomy of tibiae in the treatment of severe cases of Blount’s disease. J Pediatr Orthop 9:178–181
Hayek S, Segev E, Ezra E, Lokiec F, Wientroub S (2000) Serrated W/M osteotomy. Results using a new technique for the correction of infantile tibia vara. J Bone Jt Surg Br 82:1026–1029
Janoyer M, Jabbari H, Rouvillain JL, Sommier J, Py G, Catonne Y, Colombani JF (2007) Infantile Blount’s disease treated by hemiplateau elevation and epiphyseal distraction using a specific external fixator: preliminary report. J Pediatr Orthop B 16:273–280
Jones S, Hosalkar HS, Hill RA, Hartley J (2003) Relapsed infantile Blount’s disease treated by hemiplateau elevation using the Ilizarov frame. J Bone Jt Surg 85:565–571
Langenskiöld A (1975) An operation for partial closure of an epiphyseal plate in children, and its experimental basis. J Bone Jt Surg Br 57:325–330
Langenskiöld A (1989) Tibia vara: a critical review. Clin Orthop Relat Res 246:195–207
Laville JM, Chau E, Willemen L et al (1999) Blount’s disease: classification and treatment. J Pediatr Orthop 8:19–25
Miller S, Radomisli T, Ulin R (2000) Inverted arcuate osteotomy and external fixation for adolescent tibia vara. J Pediatr Orthop 20:450–454
Ogbemudia AO, Bafor A, Ogbemudia PE (2011) Anterior posterior inverted-‘U’ osteotomy for tibia vara: technique and early results. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 131:437–442
Oh CW, Kim SJ, Park SK, Kim HJ, Kyung HS, Cho HS, Park BC, Ihn JC (2011) Hemicallotasis for correction of varus deformity of the proximal tibia using a unilateral external fixator. J Orthop Sci 16:44–50
Pandya NK, Clarke SE, McCarthy JJ, Horn BD, Hosalkar HS (2009) Correction of Blount’s disease by a multi-axial external fixation system. J Child Orthop 3:291–299
Rab GT (1988) Oblique tibial osteotomy for Blount’s disease (tibia vara). J Pediatr Orthop 8:715–720
Rab GT (2010) Oblique tibial osteotomy revisited. J Child Orthop 4:169–172
Sasaki T, Yagi T, Monji J et al (1986) Transepiphyseal plate osteotomy for severe tibia vara in children: follow-up study of four cases. J Pediatr Orthop 6:61–65
Schoenecker PL, Meade WC, Pierron RL, Sheridan JJ, Capelli AM (1985) Blount’s disease: a retrospective review and recommendations for treatment. J Pediatr Orthop 5:181–186
Schoenecker PL, Johnston R, Rich MM, Capelli AM (1992) Elevation of the medial plateau of the tibia in the treatment of Blount disease. J Bone Jt Surg 74(A):351–358
Sevastikoglou JA, Eriksson I (1967) Familial infantile osteochondrosis deformans tibiae. Idiopathic tibia vara. A case report. Acta Orthop Scand 38:81–87
Siffert RS, Katz JF (1970) The intra-articular deformity in osteochondrosis deformans tibiae. J Bone Jt Surg Am 52:800–804
Van Huyssteen AL, Hastings CJ, Olesak M, Hoffman EB (2005) Double-elevating osteotomy for late-presenting infantile Blount’s disease: the importance of concomitant lateral epiphysiodesis. J Bone Jt Surg Br 87:710–715
Zayer M (1992) Hemicondylar tibial osteotomy in Blount’s disease. A report of 12 cases. Acta Orthop Scand 63:350–352
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Putzeys, P., Wilmes, P. & Merle, M. Triple tibial osteotomy for the correction of severe bilateral varus deformity in a patient with late-onset Blount’s disease. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 21, 731–735 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-012-2061-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-012-2061-z