Abstract
Purpose
Extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) is known to accelerate the healing of musculoskeletal tissue. The purpose of this study was to test the hypothesis that ESWT stimulates rotator cuff healing after arthroscopic repair.
Methods
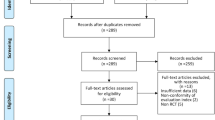
Seventy-one consecutive patients with a small- to large-sized rotator cuff tear underwent arthroscopic rotator cuff repair. The patients were randomized into two groups: 35 patients underwent ESWT at 6 weeks after surgery (ESWT group) and 36 patients did not (control group). Cuff integrity was evaluated with computed tomographic arthrography at 6 months after surgery. Constant and UCLA scores were measurable outcomes.
Results
All patients were available for a minimum one-year follow-up. The mean age of the ESWT and control groups was 59.4 (SD: 7.7) and 58.6 years (SD: 7.8) (n.s.). There were no significant differences in tear size and repair method between the two groups (n.s.). The mean Constant and UCLA scores, respectively, increased from 54.6 to 90.6 (P < 0.001) and from 18.5 to 27.4 (P < 0.001) in the ESWT group, and from 58.9 to 89.3 (P < 0.001) and 18.5 to 27.4 in the control group. Computed tomographic arthrography was performed in 26 patients from the ESWT group and 24 from the control group, and cuff integrity was maintained in 46 out of 50 patients. Definite re-tear was observed in two patients of the ESWT group and four of the controls. There were no complications associated with ESWT.
Conclusion
This study failed to prove that ESWT stimulates rotator cuff healing after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair. Additional ESWT after rotator cuff repair could theoretically be advantageous, and it was proven to be safe in this study.
Level of evidence
II.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson K, Boothby M, Aschenbrener D, van Holsbeeck M (2006) Outcome and structural integrity after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair using 2 rows of fixation: minimum 2-year follow-up. Am J Sports Med 34(12):1899–1905
Bennett WF (2003) Arthroscopic repair of full-thickness supraspinatus tears (small-to-medium): A prospective study with 2- to 4-year follow-up. Arthroscopy 19(3):249–256
Birnbaum K, Wirtz DC, Siebert CH, Heller KD (2002) Use of extracorporeal shock-wave therapy (ESWT) in the treatment of non-unions. A review of the literature. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 122(6):324–330
Chen HS, Chen LM, Huang TW (2001) Treatment of painful heel syndrome with shock waves. Clin Orthop Relat Res 387:41–46
Chen YJ, Wang CJ, Yang KD, Kuo YR, Huang HC, Huang YT, Sun YC, Wang FS (2004) Extracorporeal shock waves promote healing of collagenase-induced Achilles tendinitis and increase TGF-beta1 and IGF-I expression. J Orthop Res 22(4):854–861
Cho NS, Yi JW, Lee BG, Rhee YG (2010) Retear patterns after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: single-row versus suture bridge technique. Am J Sports Med 38(4):664–671
Durst HB, Blatter G, Kuster MS (2002) Osteonecrosis of the humeral head after extracorporeal shock-wave lithotripsy. J Bone Jt Surg Br 84(5):744–746
Furia JP (2005) Safety and efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for chronic lateral epicondylitis. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ) 34(1):13–19
Furia JP (2005) The safety and efficacy of high energy extracorporeal shock wave therapy in active, moderately active, and sedentary patients with chronic plantar fasciitis. Orthopedics 28(7):685–692
Gerdesmeyer L, Wagenpfeil S, Haake M, Maier M, Loew M, Wortler K, Lampe R, Seil R, Handle G, Gassel S, Rompe JD (2003) Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for the treatment of chronic calcifying tendonitis of the rotator cuff: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 290(19):2573–2580
Harniman E, Carette S, Kennedy C, Beaton D (2004) Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for calcific and noncalcific tendonitis of the rotator cuff: a systematic review. J Hand Ther 17(2):132–151
Haupt G (1997) Use of extracorporeal shock waves in the treatment of pseudarthrosis, tendinopathy and other orthopedic diseases. J Urol 158(1):4–11
Jo CH, Kim JE, Yoon KS, Lee JH, Kang SB, Han HS, Rhee SH, Shin S (2011) Does platelet-rich plasma accelerate recovery after rotator cuff repair? A prospective cohort study. Am J Sports Med 39(10):2082–2090
Jones CK, Savoie FH 3rd (2003) Arthroscopic repair of large and massive rotator cuff tears. Arthroscopy 19(6):564–571
Jost B, Zumstein M, Pfirrmann CW, Gerber C (2006) Long-term outcome after structural failure of rotator cuff repairs. J Bone Jt Surg Am 88(3):472–479
Kim DH, Elattrache NS, Tibone JE, Jun BJ, DeLaMora SN, Kvitne RS, Lee TQ (2006) Biomechanical comparison of a single-row versus double-row suture anchor technique for rotator cuff repair. Am J Sports Med 34(3):407–414
Kim KC, Shin HD, Lee WY, Han SC (2011) Repair integrity and functional outcome after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: double-row versus suture-bridge technique. Am J Sports Med. doi:10.1177/0363546511425657
Ko JY, Chen HS, Chen LM (2001) Treatment of lateral epicondylitis of the elbow with shock waves. Clin Orthop Relat Res 387:60–67
Koh KH, Kang KC, Lim TK, Shon MS, Yoo JC (2011) Prospective randomized clinical trial of single- versus double-row suture anchor repair in 2- to 4-cm rotator cuff tears: clinical and magnetic resonance imaging results. Arthroscopy 27(4):453–462
Lafosse L, Brozska R, Toussaint B, Gobezie R (2007) The outcome and structural integrity of arthroscopic rotator cuff repair with use of the double-row suture anchor technique. J Bone Jt Surg Am 89(7):1533–1541
Leung KS, Qin L, Fu LK, Chan CW (2002) A comparative study of bone to bone repair and bone to tendon healing in patella-patellar tendon complex in rabbits. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 17(8):594–602
Liu HM, Chao CM, Hsieh JY, Jiang CC (2006) Humeral head osteonecrosis after extracorporeal shock-wave treatment for rotator cuff tendinopathy. A case report. J Bone Jt Surg Am 88(6):1353–1356
Liu SH, Panossian V, Al-Shaikh R, Tomin E, Shepherd E, Finerman GA, Lane JM (1997) Morphology and matrix composition during early tendon to bone healing. Clin Orthop Relat Res 339:253–260
Loew M, Daecke W, Kusnierczak D, Rahmanzadeh M, Ewerbeck V (1999) Shock-wave therapy is effective for chronic calcifying tendinitis of the shoulder. J Bone Jt Surg Br 81(5):863–867
Loew M, Jurgowski W, Mau HC, Thomsen M (1995) Treatment of calcifying tendinitis of rotator cuff by extracorporeal shock waves: a preliminary report. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 4(2):101–106
Lu H, Qin L, Fok P, Cheung W, Lee K, Guo X, Wong W, Leung K (2006) Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound accelerates bone-tendon junction healing: a partial patellectomy model in rabbits. Am J Sports Med 34(8):1287–1296
Mihata T, Watanabe C, Fukunishi K, Ohue M, Tsujimura T, Fujiwara K, Kinoshita M (2011) Functional and structural outcomes of single-row versus double-row versus combined double-row and suture-bridge repair for rotator cuff tears. Am J Sports Med 39(10):2091–2098
Ogden JA, Toth-Kischkat A, Schultheiss R (2001) Principles of shock wave therapy. Clin Orthop Relat Res 387:8–17
Oh JH, Kim SH, Ji HM, Jo KH, Bin SW, Gong HS (2009) Prognostic factors affecting anatomic outcome of rotator cuff repair and correlation with functional outcome. Arthroscopy 25(1):30–39
Pleiner J, Crevenna R, Langenberger H, Keilani M, Nuhr M, Kainberger F, Wolzt M, Wiesinger G, Quittan M (2004) Extracorporeal shockwave treatment is effective in calcific tendonitis of the shoulder. A randomized controlled trial. Wien Klin Wochenschr 116(15–16):536–541
Post M, Silver R, Singh M (1983) Rotator cuff tear. Diagnosis and treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res 173:78–91
Qin L, Lu H, Fok P, Cheung W, Zheng Y, Lee K, Leung K (2006) Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound accelerates osteogenesis at bone-tendon healing junction. Ultrasound Med Biol 32(12):1905–1911
Randelli P, Arrigoni P, Ragone V, Aliprandi A, Cabitza P (2011) Platelet rich plasma in arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: a prospective RCT study, 2-year follow-up. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 20(4):518–528
Roessler W, Steinbach P, Nicolai H, Hofstaedter F, Wieland WF (1993) Effects of high-energy shock waves on the viable human kidney. Urol Res 21(4):273–277
Rompe JD, Hopf C, Nafe B, Burger R (1996) Low-energy extracorporeal shock wave therapy for painful heel: a prospective controlled single-blind study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 115(2):75–79
Sistermann R, Katthagen BD (1998) Complications, side-effects and contraindications in the use of medium and high-energy extracorporeal shock waves in orthopedics. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb 136(2):175–181
Smith CD, Alexander S, Hill AM, Huijsmans PE, Bull AM, Amis AA, De Beer JF, Wallace AL (2006) A biomechanical comparison of single and double-row fixation in arthroscopic rotator cuff repair. J Bone Jt Surg Am 88(11):2425–2431
Sugaya H, Maeda K, Matsuki K, Moriishi J (2007) Repair integrity and functional outcome after arthroscopic double-row rotator cuff repair. A prospective outcome study. J Bone Jt Surg Am 89(5):953–960
Wang CJ, Chen HS, Chen CE, Yang KD (2001) Treatment of nonunions of long bone fractures with shock waves. Clin Orthop Relat Res 387:95–101
Wang CJ, Huang HY, Pai CH (2002) Shock wave-enhanced neovascularization at the tendon-bone junction: an experiment in dogs. J Foot Ankle Surg 41(1):16–22
Wang CJ, Ko JY, Chen HS (2001) Treatment of calcifying tendinitis of the shoulder with shock wave therapy. Clin Orthop Relat Res 387:83–89
Wang CJ, Wang FS, Yang KD, Weng LH, Hsu CC, Huang CS, Yang LC (2003) Shock wave therapy induces neovascularization at the tendon-bone junction. A study in rabbits. J Orthop Res 21(6):984–989
Wang CJ, Wang FS, Yang KD, Weng LH, Sun YC, Yang YJ (2005) The effect of shock wave treatment at the tendon-bone interface-an histomorphological and biomechanical study in rabbits. J Orthop Res 23(2):274–280
Wang L, Qin L, Lu HB, Cheung WH, Yang H, Wong WN, Chan KM, Leung KS (2008) Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in treatment of delayed bone-tendon healing. Am J Sports Med 36(2):340–347
Wong MW, Qin L, Tai JK, Lee SK, Leung KS, Chan KM (2004) Engineered allogeneic chondrocyte pellet for reconstruction of fibrocartilage zone at bone-tendon junction–a preliminary histological observation. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 70(2):362–367
Ko SH, Friedman D, Seo DK, et al.(2009) A prospective therapeutic comparison of simple suture repairs to massive cuff stitch repairs for treatment of small- and medium-sized rotator cuff tears? Arthroscopy 25(6):583–9, 589.e1–4
Bhatia S, Piasecki DP, Nho SJ et al (2010) Early return to work in workers’ compensation patients after arthroscopic full-thickness rotator cuff repair? Arthroscopy 26(8):1027–1034
Acknowledgments
This Research was supported by the Chung-Ang University Research Grants in 2008.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J.Y., Lee, J.S. & Park, C.W. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy is not useful after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 20, 2567–2572 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-012-1923-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-012-1923-8