Abstract
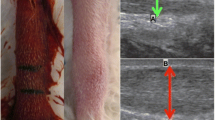
Sclerosing therapy has in recent studies showed promising results in patients with clinically and ultrasonographically diagnosed tendinosis in Achilles and patellar tendons. The aim of this investigation was to study the presence of intratendinous colour Doppler (CD) flow in horses with clinically diagnosed chronic tendinopathy and to test if experience from human studies could be extrapolated to horses. Special interest was focused on the treatment with sclerosing therapy and whether we could obtain the same successful peroperative findings as in humans. Four horses with clinically diagnosed unilateral chronic tendinosis in the forelimbs were examinated with both grey-scale ultrasonography (US) and CD. The horses were to be euthanised according to standard procedure is such cases. The US findings were used for guidance of sclerosing therapy. All horses showed abnormal findings on US, especially intratendinous neovascularisation in the affected limb but not in the contralateral limb. The CD findings had the same appearance as seen in human Achilles tendons with chronic tendinopathy. In all cases the intratendinous neovascularisation was successfully “shut down” peroperatively. The horses showed no signs of discomfort or worsening of symptoms during the short follow-up period after the procedure. The results indicate that the promising results from human medicine might be transferred to treatment of horses with chronic tendinopathy. In the future it will hopefully be possible to use the model from overused tendons in the horse to determine the best treatment of overuse injuries in humans as well. The animal model will allow experimental studies including substantial tissue sampling for mechanical and molecular biological analysis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfredson H, Ohberg L (2005) Sclerosing injections to areas of neo-vascularisation reduce pain in chronic Achilles tendinopathy: a double-blind randomised controlled trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 13:338–344
Alfredson H, Ohberg L (2005) Neovascularisation in chronic painful patellar tendinosis-promising results after sclerosing neovessels outside the tendon challenge the need for surgery. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 13:74–80
Alfredson H, Harstad H, Haugen S, Ohberg L (2006) Sclerosing polidocanol injections to treat chronic painful shoulder impingement syndrome-results of a two-centre collaborative pilot study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 14:1321–1326
Boesen MI, Koenig MJ, Torp-Pedersen S, Bliddal H, Langberg H (2006) Tendinopathy and Doppler activity: the vascular response of the Achilles tendon to exercise. Scand J Med Sci Sports 16:463–469
Cook JL, Khan KM, Purdam C (2002) Achilles tendinopathy. Man Ther 7:121–130
Dowling BA, Dart AJ, Hodgson DR, Smith RKW (2000) Superficial digital flexor tendonitis in the horse. Equine Vet J 32:369–378
Goodwin DW (2000) Imaging of the Achilles’ tendon. Foot Ankle Clin. 5:135–148, vii
Koenig MJ, Torp-Pedersen S, Qvistgaard E, Terslev L, Bliddal H (2004) Preliminary results of colour Doppler-guided intratendinous glucocorticoid injection for Achilles tendonitis in five patients. Scand J Med Sci Sports 14:100–106
Kristoffersen M, Ohberg L, Johnston C, Alfredson H (2005) Neovascularisation in chronic tendon injuries detected with colour Doppler ultrasound in horse and man: implications for research and treatment. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 13:505–508
Kvist M (1994) Achilles tendon injuries in athletes. Sports Med 18:173–201
Lind B, Ohberg L, Alfredson H (2006) Sclerosing polidocanol injections in mid-portion Achilles tendinosis: remaining good clinical results and decreased tendon thickness at 2-year follow-up. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 14:1327–1332
Marr CM, Murray M, Boyd JS, McMillan I, Wright NG (1993) Ultrasonographic and histopathological findings in equine superficial digital flexor tendon injury. Equine Vet J 25:23–29
Newman JS, Adler RS, Bude RO, Rubin JM (1994) Detection of soft-tissue hyperemia: value of power Doppler sonography. Am J Roentgenol 163:385–389
Ohberg L, Lorentzon R, Alfredson H (2001) Neovascularisation in Achilles tendons with painful tendinosis but not in normal tendons: an ultrasonographic investigation. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 9:233–238
Reef VB, Sertich PL, Turner RM (1998) Musculoskeletal ultrasonography. In: Reef VB, Sertich PL, Turner RM (eds) Equine diagnostic ultrasound. WB Saunders Co., Philadelphia, pp 39–186
Reef VB (2001) Superficial digital flexor tendon healing: ultrasonographic evaluation of therapies. Vet Clin North Am Equine Pract 17:159–178
Reiter M, Ulreich N, Dirisamer A, Tscholakoff D, Bucek RA (2004) Colour and power Doppler sonography in symptomatic Achilles tendon disease. Int J Sports Med 25:301–305
Rowley S (2001) Theory to practice. Aseptic non-touch technique. Nurs Times 97:VI–VIII
Terslev L, Qvistgaard E, Torp-Pedersen S, Laetgaard J, Danneskiold-Samsoe B, Bliddal H (2001) Ultrasound and power Doppler findings in jumper’s knee—preliminary observations. Eur J Ultrasound 13:183–189
Torp-Pedersen T, Torp-Pedersen S, Bliddal H (2002) Diagnostic value of ultrasonography in epicondylitis. Ann Intern Med 136:781–782
Williams RB, Harkins LS, Hammond CJ, Wood JLN (2001) Racehorse injuries, clinical problems and fatalities recorded on British racecourses from flat racing and National Hunt racing during 1996, 1997 and 1998. Equine Vet J 33:478–486
Zeisig E, Ohberg L, Alfredson H (2006) Sclerosing polidocanol injections in chronic painful tennis elbow-promising results in a pilot study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 14:1218–1224
Acknowledgment
The authors are thankful for the economic support for this study by the OAK Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boesen, M.I., Nanni, S., Langberg, H. et al. Colour Doppler ultrasonography and sclerosing therapy in diagnosis and treatment of tendinopathy in horses—a research model for human medicine. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthr 15, 935–939 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-006-0245-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-006-0245-0