Abstract
Homogeneous turbulence under unstable uniform stratification (N 2 < 0) and vertical shear \((S = \hbox{d}\overline{U}_{1}/\hbox{d}x_3)\) is investigated by using the linear theory (or the so-called rapid distortion theory, RDT) for an initial isotropic turbulence over a range −∞ ≤ R i =N 2/S 2 ≤ 0. The initial potential energy is zero and P r =1 (i.e. the molecular Prandtl number).
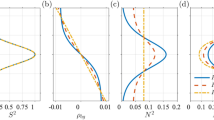
One-dimensional (streamwise) k 1−spectra, especially Θ33(k 1) (i.e., that of the vertical kinetic energy, \(\overline{v_{3}v_{3}}/2)\) are investigated. In agreement with previous experiments, it is found that the unstable stratification affects the turbulence quantities at all scales. A significant increase of the vertical kinetic energy is observed at low wavenumbers k 1 (i.e. large scales) due to an increase of the stratification \(\left(\sqrt{-N^{2}}\right)\). The effect of the shear (S) is appreciable only at high wavenumbers k 1 (i.e. small scales).
Based on the importance of the spectral components with k 1 = 0, the asymptotic forms of Θ ij (k 1 = 0) or equivalently the so-called “two-dimensional” energy components (2DEC) are analyzed in detail. The asymptotic form for the ratio of 2DEC is compared to the long-time limit of the ratio of real energies. In the unstable stratified shearless case (S=0,N 2 ≠ 0) the variances and the covariances of the velocity and the density are derived analytically in terms of the Weber functions, while when S ≠ 0 and N 2 ≠ 0 they are obtained numerically (−100 ≤ R i <0 and \(t^{+} = \sqrt{S^{2}-N^{2}} t = 100)\). The results are discussed in connection to previous experimental results in unstable stratified open channel flows cooled from above by Komori et al. Phy Fluids 25, 1539–1546 (1982).
It is shown that the Richardson number dependence of the long-time limit of the ratios of real energies is well described by this “simple” model (i.e. the dependence of the long-time limit of 2DEC on R i ). For example, the ratio of the potential energy to the kinetic energy (q 2/2), approaches −R i /(1−R i ), the ratio of turbulent energy production by buoyancy forces to production by shearing forces (i.e. the flux Richardson number, R if ), approaches R i . Also, the Richardson number dependence of the principal angle (β) of the Reynolds stress tensor and the angle (βρ) of the scalar flux vector is fairly predicted by this model \(\beta ,\beta_{\rho} \rightarrow 1/2\tan^{-1}\left[2\sqrt{-R_{i}}/(1+R_i)\right]\).
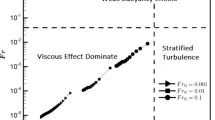
On the other hand, it is found that the above ratios are insensitive to viscosity, while the ratios ɛ /q 2 and \(\varepsilon_{\rho}\left/(2PE)\right.\), depend on the viscosity and they evolve asymptotically like t −1. The turbulent Froude number, F rt =(L Oz /L E )2/3, where L Oz and L E are the Ozmidov length scale and the Ellison length scale, respectively, evolves asymptotically like t −1/3.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Batchelor G.K., Proudman I. (1954). The effect of rapid distortion of a fluid in turbulent motion. Quart. J. Mech. Appl. Math. 7: 83–103
Bradshaw P. (1969). The analogy between streamline curvature and buoyancy in turbulent shear flow. J. Fluid Mech. 36: 177–191
Brethouwer G. (2004). Rotating homogeneous shear flow with passive scalars Advances in turbulence X. In: Andersson H.I., Krogstad P.-A. (eds) Proceeding of the tenth european conference. CiMNE, Barcelona, pp 1–1
Briggs D.A., Ferziger J.H., Koseff J.R., Monismith S.G. (1998). Turbulent mixing in a free-shear stably stratified two-layer fluids. J. Fluid Mech. 354:175–208
Cambon, C.: Contribution to single and double point modelling of homogeneous turbulence. Annual research briefs, Center for Turbulence Research, Stanford University 1990
Cambon C., Scott J.F. (1999). Linear and nonlinear models of anisotropic turbulence. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 31:1–53
Cambon C., Teissèdre C., Jeandel D. (1985). Etude d’effets couplés de déformation et de rotation sur une turbulence homogène. J. Me. Theor. Appli. 4:629–657
Craik A.D.D., Criminale W.O. (1986). Evolution of wavelike disturbances in shear flows: a class of exact solutions of the Navier Stokes equations. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 406:13–26
Craya, A.: Contribution à l’analyse de la turbulence associée à des vitesses moyennes. P.S.T. Ministère de l’Air, 345 1958
Eliassen, A., Hoiland, E., Riis, E.: Two-dimensional perturbation of a flow with constant shear of stratified flow. Institute for Weather and Climate Research, Norwegian Academy of Sciences and Letters, Publication no 1 1953
Erdelyi A., Magnus W., Oberhettinger F., Tricomi F.G. (1953). Higher transcendental functions, vols 1–3. McGraw-Hill, New York
Godfered F.S., Cambon C., Leblanc S. (2001). Zonal approach to centrifugal, elliptic and hyperbolic instabilities in Stuart vortices with external rotation. J. Fluid Mech. 449:1–37
Goldstein M.E., Durbin P.A. (1980). The effect of finite turbulence spatial scale on the amplification of turbulence by a contracting stream. J Fluid Mech. 98:473–508
Gradshteyn I.S., Ryzhik I.M. (1965). Table of integrals, series, and products. Academic, Dublin
Hanazaki H. (2002). Linear processes in stably and unstably stratified rotating turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 465:157–190
Hanazaki H., Hunt J.C.R. (1996). Linear processes in unsteady stably stratified turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 318:303–337
Hanazaki H., Hunt J.C.R. (2001). Linear processes in unsteady stably stratified sheared turbulence IUTAM. In: Kambe T., Nakano T., Miyauchi T. (eds) Symposium on geometry and statistics of turbulence. Kluwer, Hayama, pp. 291–296
Hanazaki H., Hunt J.C.R. (2004). Structure of unsteady stably stratified turbulence with mean shear. J. Fluid Mech. 507: 1–42
Herring R.G. (1974). Approach of axisymmetric turbulence to isotropy. Phys. Fluids 17:859–872
Hinch E.J. (1991). Perturbation methods. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Hinze J.O. (1975). Turbulence, 2nd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Holt S.E., Koseff J.R., Ferziger J.H. (1992). A numerical study of the evolution and structure of homogeneous stably stratified sheared turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 237:499–539
Holt S.E., Koseff J.R., Ferziger J.H. (1992). A numerical study of the evolution and structure of homogeneous stably stratified sheared turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 237:499–539
Hunt J.C.R., Carruthers D.J. (1990). Rapid distortion theory and the ‘problem’ of turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 212:497–532
Hunt J.C.R., Stretch D.D., Britter R.E. (1988). Length scales in stably stratified turbulent flows and their use in turbulence models. In: Puttock J.S. (eds) Stably Stratified flow and dense gas dispersion. Clarendon Press, Oxford, pp. 285–321
Iida O., Nagano Y. (1999). Coherent structure and heat transfer in geostrophic flow under density stratification. Phys. Fluids 11:368–377
Ivey G.N., Imberger J. (1991). On the nature of turbulence in a stratified fluid. Part I: the energetics of mixing. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 21:150–658
Jacquin L., Leuchter O., Cambon C., Mathieu J. (1990). Homogeneous turbulence in the presence of rotation. J. Fluid Mech. 220:1–52
Kaltenbach H.J., Gerz T., Schumann U. (1994). Large eddy simulations of homogeneous turbulence and diffusion in stably stratified shear flow. J. Fluid Mech. 280:1–42
Komori S., Ueda H., Ogino F., Mizushina T. (1982). Turbulence structure inunstably-stratified open-channel flow. Phys. Fluids 25:1539–1546
Lee J.M., Kim J., Moin P. (1990). Structure of turbulence at high shear rate. J. Fluid Mech. 216:561–583
Miles J.W. (1961). On the stability of heterogeneous shear flows. J. Fluid Mech. 10:496–508
Moffatt, H.K.: The interaction of turbulence with strong wind shear. In: Yaglom, A.M., Tatarsky, V.I. (eds.) Proceedings of the URSI-IUGG International colloquium on atmospheric turbulence and radio wave propagation. Moscow, June 15–22, 1965, Nauka, Moscow, pp. 139–154, (1967)
Nagata K., Komori S. (2000). The effect of unstable stratification and mean shear on the chemical reaction in grid turbulence.J. Fluid Mech. 408:39–52
Rehmann C.R., Hwang J.H. (2005). Small-scale structure of strongly stratified turbulence. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 35:151–164
Riley, J.J., Metcalfe, R.W., Weissman, M.A.: Direct numerical simulations of homogeneous turbulence in density stratified fluids. In: Nonlinear properties of internal waves. In: AIP Conference Proceedings vol. 76, pp. 79–112. American Institute of Physics (1981)
Rogers M.M. (1991). The structure of a passive scalar field with a uniform mean gradient in rapidly sheared homogeneous turbulent flow. Phys. Fluids A 3:144–154
Rogers M.M., Mansour N.N., Reynolds W.C. (1989). An algebraic model for the turbulent flux of a passive scalar. J. Fluid Mech. 203:77–101
Saffman P.G. (1967). The large-scale structure of homogeneous turbulence. J. Fluid Mech. 27:581–593
Salhi A. (2002). Similarities between rotation and stratification effects on homogeneous shear flow. Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 15:339–352
Salhi A., Cambon C. (1997). An analysis of rotating shear flow using linear theory and DNS and LES results. J. Fluid Mech. 347:171–195
Shih L.H., Koseff J.R., Ferziger J.H., Rehmann C.R. (2000). Scaling parameterization of stratified homogeneous turbulent shear flow. J. Fluid Mech. 412:1–20
Townsend A.A. (1970). Entrainment and the structure of turbulent flow. J .Fluid Mech. 41:13–46
Townsend A.A. (1976). The structure of turbulent shear flow, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Tsujimura, S., Iida, O. Nagano, Y.: Effects of rotation on unstably stratified turbulence. Proc. Int. Conf. on Turbulent Heat Transfer 2, Manchester, UK, vol. 1, pp. 5.58–5.71 (1998)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M.Y. Hussaini
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salhi, A., Bach, A.E. Effects of Large Scales Motion in Unstable Stratified Shear Flows. Theor. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 20, 197–228 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00162-006-0012-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00162-006-0012-3