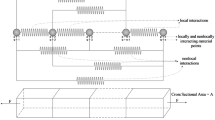
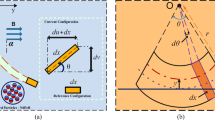
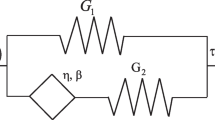
Abstract
A methodology is proposed to define an equivalent geometry allowing the use of an uncoupled algorithm to solve thermomechanical problems when cyclic large strain occurs. This methodology is set up on the case of a simple bar and is then challenged on a structural sample for cyclic loadings. It is shown that the definition of the equivalent geometry is dependent on the thermal boundary conditions, which are usually unknowns of the thermal problem. The proposed approach is finally applied to the identification of cyclic dissipation from infrared thermography measurements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Behnke, R., Kaliske, M., Klüppel, M.: Thermo-mechanical analysis of cyclically loaded particle-reinforced elastomer components: experiment and finite element simulation. Rubber Chem. Technol. 89, 154–176 (2016)
Bergstrom, J., Boyce, M.: Constitutive modelling of the large-strain time-dependent behaviour of elastomers. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 46, 931–954 (1998)
Biot, M.: Thermoelasticity and irreversible thermodynamics. J. Appl. Phys. 27, 240–253 (1956)
Boulanger, T., Chrysochoos, A., Mabru, A., Galtier, A.: Calorimetric analysis of dissipative and thermoelastic effects associated with the fatigue behaviour of steels. Int. J. Fatigue 26, 221–229 (2004)
Chrysochoos, A., Louche, H.: An infrared image processing to analyse the calorific effects accompanying strain localisation. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 38, 1759–1788 (2000)
Connesson, N., Maquin, F., Pierron, F.: Experimental energy balance during the first cycles of cyclically loaded specimens under the conventional yield stress. Exp. Mech. 51, 23–44 (2011)
Delpuyo, D., Balandraud, X., Grédiac, M.: Applying infrared thermography to analyze martensitic microstructures in a Cu–Al–Be shape memory alloy subjected to cyclic loading. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 528, 8249–8258 (2011)
Delpuyo, D., Balandraud, X., Grédiac, M.: Heat source reconstruction from noisy temperature fields using an optimized derivative Gaussian filter. Infrared Phys. Technol. 60, 312–322 (2013)
Doudard, C., Calloch, S., Hild, F., Cugy, P., Galtier, A.: Identification of scatter in high cycle fatigue from temperature measurements. Comptes Rendus Mécanique 10, 795–801 (2004)
Doudard, C., Calloch, S., Hild, F., Roux, S.: Identification of heat source fields from infrared thermography: determination of self-heating in a dual-phase steel by using a dog bone sample. Mech. Mater. 42, 55–62 (2010)
Dulieu Barton, J., Stanley, P.: Applications of thermoelastic stress analysis to composites materials. Strain 35, 41–48 (1999)
Florin, P., Doudard, C., Fachinetti, M., Calloch, S.: Determination of the first stress tensor invariant of a complex steel sheet structure from thermoelastic stress analysis. Procedia Eng. 133, 736–745 (2015)
Harwood, N., Cummings, W.: Thermoelastic Stress Analysis. CRC Press, Boca Raton (1991)
Jégou, L., Marco, Y., Le Saux, V., Calloch, S.: Fast prediction of the wöhler curve from heat build-up measurements on short fiber reinforced thermoplastics. Int. J. Fatigue 47, 259–267 (2012)
Le Chenadec, Y.: Autoéchauffement, fatigue thermomécanique des élastomères. Ph.D. thesis, Ecole Polytechnique (2008)
Le Chenadec, Y., Raoult, I., Stolz, C., Nguyen-Tajan, M.: Cyclic approximation of the heat equation in finite strains for the heat build-up problem of rubber. J. Mech. Mater. Struct. 4, 309–318 (2009)
Le Saux, V., Doudard, C.: Proposition of a compensated pixelwise calibration for photonic infrared cameras and comparison to classic calibration procedures: case of thermoelastic stress analysis. Infrared Phys. Technol. 80, 83–92 (2017)
Le Saux, V., Marco, Y., Calloch, S., Charrier, P.: Contribution of accurate thermal measurements to the characterization of the thermomechanical properties of rubber-like materials. Plast. Rubbers Compos.: Macromol. Eng. 41, 277–284 (2012)
Le Saux, V., Marco, Y., Calloch, S., Charrier, P., Taveau, D.: Heat build-up of rubber under cyclic loadings: validation of an efficient demarch to predict the temperature fields. Rubber Chem. Technol. 86, 38–56 (2013)
Le Saux, V., Marco, Y., Doudard, C., Calloch, S., Charrier, P.: Fast evaluation of the fatigue lifetime of rubber-like materials based on a heat build-up protocol and micro-tomography measurements. Int. J. Fatigue 32, 1582–1590 (2010)
Lemaitre, J., Chaboche, J.: Mechanics of Solid Materials. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1990)
Lion, A.: A physically based method to represent the thermo-mechanical behaviour or elastomers. Acta Mech. 123, 1–25 (1997)
Marco, Y., Huneau, B., Masquelier, I., Le Saux, V., Charrier, P.: Prediction of the fatigue properties of natural rubber based on the description of the cracks population and of the dissipated energy. Polym. Test. 59, 67–74 (2017)
Marco, Y., Le Saux, V., Jégou, L., Launay, A., Serrano, L., Raoult, I., Calloch, S.: Dissipation analysis in sfrp structural samples: thermomechanical analysis and comparison to numerical simulations. Int. J. Fatigue 67, 142–150 (2014)
Marco, Y., Masquelier, I., Le Saux, V., Charrier, P.: Fast prediction of the wöhler curve from thermal measurements for a wide range of nr and sbr compounds. Rubber Chem. Technol. (2017). doi:10.5254/rct.16.83755
Masquelier, I., Marco, Y., Le Saux, V., Calloch, S., Charrier, P.: Determination of dissipated energy fields from temperature mappings on a rubber-like structural sample: experiments and comparison to numerical simulations. Mech. Mater. 80, 113–123 (2015)
Mooney, M.: A theory of large elastic deformation. J. Appl. Phys. 11, 582–592 (1940)
Munier, R., Doudard, C., Calloch, S., Weber, B.: Determination of high cycle fatigue properties of a wide range of steel sheet grades from self-heating measurements. Int. J. Fatigue 63, 46–61 (2014)
Munier, R., Doudard, C., Calloch, S., Weber, B., Fachinetti, M.: Contribution of kinematical and thermal measurements for mechanical properties identification: application to high cycle fatigue. Exp. Mech. 52, 743–756 (2012)
Reese, S., Govindjee, S.: Theoretical and numerical aspects in the thermo-viscoelastic material behaviour of rubber-like materials. Mech. Time-Depend. Mater. 1, 357–369 (1998)
Rittel, D.: An investigation of the heat generated during cyclic loading of two glassy polymers. Part I. Experiments. Mech. Mater. 32, 131–147 (2000)
Rivlin, R.: Large elastic deformations of isotropic materials. iv. Further developments of the general theory. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 241, 379–397 (1948)
Stanley, P.: Beginnings and early development of thermoelastic stress analysis. Strain 44, 285–297 (2008)
Treloar, L.: The Physics of Rubber Elasticity. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Andreas Öchsner.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Glanowski, T., Le Saux, V., Doudard, C. et al. Proposition of an uncoupled approach for the identification of cyclic heat sources from temperature fields in the presence of large strains. Continuum Mech. Thermodyn. 29, 1163–1179 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00161-017-0572-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00161-017-0572-z