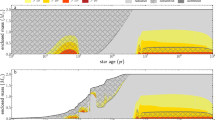
Abstract
White dwarf stars are the final evolutionary stage of the vast majority of stars, including our Sun. Since the coolest white dwarfs are very old objects, the present population of white dwarfs contains a wealth of information on the evolution of stars from birth to death, and on the star formation rate throughout the history of our Galaxy. Thus, the study of white dwarfs has potential applications in different fields of astrophysics. In particular, white dwarfs can be used as independent reliable cosmic clocks, and can also provide valuable information about the fundamental parameters of a wide variety of stellar populations, such as our Galaxy and open and globular clusters. In addition, the high densities and temperatures characterizing white dwarfs allow these stars to be used as cosmic laboratories for studying physical processes under extreme conditions that cannot be achieved in terrestrial laboratories. Last but not least, since many white dwarf stars undergo pulsational instabilities, the study of their properties constitutes a powerful tool for applications beyond stellar astrophysics. In particular, white dwarfs can be used to constrain fundamental properties of elementary particles such as axions and neutrinos and to study problems related to the variation of fundamental constants. These potential applications of white dwarfs have led to renewed interest in the calculation of very detailed evolutionary and pulsational models for these stars. In this work, we review the essentials of the physics of white dwarf stars. We enumerate the reasons that make these stars excellent chronometers, and we describe why white dwarfs provide tools for a wide variety of applications. Special emphasis is placed on the physical processes that lead to the formation of white dwarfs as well as on the different energy sources and processes responsible for chemical abundance changes that occur along their evolution. Moreover, in the course of their lives, white dwarfs cross different pulsational instability strips. The existence of these instability strips provides astronomers with a unique opportunity to peer into their internal structure that would otherwise remain hidden from observers. We will show that this allows one to measure stellar masses with unprecedented precision and to infer their envelope thicknesses, to probe the core chemical stratification, and to detect rotation rates and magnetic fields. Consequently, in this work, we also review the pulsational properties of white dwarfs and the most recent applications of white dwarf asteroseismology.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrikosov AA (1961) Some properties of strongly compressed matter. Soviet Phys JETP 12: 1254–1259
Adams WS (1915) The spectrum of the companion of Sirius. Publ Astronom Soc Pac 27: 236–237
Adams WS (1925) The relativity displacement of the spectral lines in the companion of Sirius. Proc Natl Acad Sci 11: 382–387
Aizenman M, Smeyers P, Weigert A (1977) Avoided crossing of modes of non-radial stellar oscillations. Astron Astrophys 54: 41–46
Alcock C, Allsman RA, Alves D et al (1995) First observation of parallax in a gravitational microlensing event. Astrophys J Lett 454: L125–L128
Alcock C, Allsman RA, Alves D et al (1997) The MACHO project large magellanic cloud microlensing results from the first two years and the nature of the Galactic dark halo. Astrophys J 486: 697–726
Alcock C, Allsman RA, Alves D et al (2000) Binary microlensing events from the MACHO project. Astrophys J 541: 270–297
Althaus LG, Benvenuto OG (2000) Diffusion in helium white dwarf stars. Mon Not R Astron Soc 317: 952–964
Althaus LG, Serenelli AM, Benvenuto OG (2001) Diffusion and the occurrence of hydrogen-shell flashes in helium white dwarf stars. Mon Not R Astron Soc 323: 471–483
Althaus LG, Serenelli AM, Córsico AH, Montgomery MH (2003) New evolutionary models for massive ZZ Ceti stars. I. First results for their pulsational properties. Astron Astrophys 404: 593–609
Althaus LG, Serenelli AM, Panei JA, Córsico AH, García-Berro E, Scóccola CG (2005a) The formation and evolution of hydrogen-deficient post-AGB white dwarfs: the emerging chemical profile and the expectations for the PG 1159-DB-DQ evolutionary connection. Astron Astrophys 435: 631–648
Althaus LG, Miller Bertolami MM, Córsico AH, García-Berro E, Gil-Pons P (2005b) The formation of DA white dwarfs with thin hydrogen envelopes. Astron Astrophys 440: L1–L4
Althaus LG, Córsico AH, Kepler SO, Miller Bertolami MM (2008a) On the systematics of asteroseismological mass determinations of PG 1159 stars. Astron Astrophys 478: 175–180
Althaus LG, Córsico AH, Miller Bertolami MM, García-Berro E, Kepler SO (2008b) Evidence of thin helium envelopes in PG 1159 stars. Astrophys J Lett 677: L35–L38
Althaus LG, Panei JA, Miller Bertolami MM et al (2009a) New evolutionary sequences for hot H-deficient white dwarfs on the basis of a full account of progenitor evolution. Astrophys J 704: 1605–1615
Althaus LG, García-Berro E, Córsico AH, Miller Bertolami MM, Romero AD (2009b) On the formation of hot DQ white dwarfs. Astrophys J Lett 693: L23–L26
Althaus LG, Córsico AH, Torres S, García-Berro E (2009c) On the origin of white dwarfs with carbon-dominated atmospheres: the case of H1504+65. Astron Astrophys 494: 1021–1024
Althaus LG, Córsico AH, Bischoff-Kim A, Romero AD, Renedo I, García-Berro E, Miller Bertolami MM (2010a) New chemical profiles for the asteroseismology of ZZ Ceti stars. Astrophys J 717: 897–907
Althaus LG, García-Berro E, Renedo I, Isern J, Córsico AH, Rohrmann RD (2010b) Evolution of white dwarf stars with high-metallicity progenitors: the role of 22Ne diffusion. Astrophys J 719: 612–621
Anderson W (1929) Gewöhnliche materie und strahlende energie als verschiedene Phasen eines und desselben Grundstoffes. Z Phys 54: 433–444
Baglin A, Schatzman E (1969) Low-luminosity stars. Gordon and Breach Science Publishers, New York, p 385
Barlow BN, Dunlap BH, Rosen R, Clemens JC (2008) Two new variable Hot DQ stars. Astrophys J 688: L95
Barstow MA (2006) The importance of UV observations for the study of white dwarfs and the local interstellar medium. The Ultraviolet Universe. Stars from Birth to Death. IAU Joint Discussion 4 XXVI IAU General Assembly, Prague, 39
Beauchamp A, Wesemael F, Bergeron P, Fontaine G, Saffer RA, Liebert J, Brassard P (1999) Spectroscopic studies of DB white dwarfs: the instability strip of the pulsating DB (V777 Herculis) stars. Astrophys J 516: 887–891
Becker AC, Rest A, Stubbs C et al (2005) The SuperMACHO microlensing survey. IAU Symp 225: 357–362
Bedin LR, King IR, Anderson J, Piotto G, Salaris M, Cassisi S, Serenelli AM (2008) Reaching the end of the white dwarf cooling sequence in NGC 6791. Astrophys J 678: 1279–1291
Benvenuto OG, De Vito MA (2005) The formation of helium white dwarfs in close binary systems-II. Mon Not R Astron Soc 362: 891–905
Benvenuto OG, Córsico AH, Althaus LG, Serenelli AM (2002) Time-dependent diffusion in pulsating white dwarf stars: asteroseismology of G117-B15A. Mon Not R Astron Soc 332: 399–408
Bergeron P, Wesemael F, Fontaine G (1991) Synthetic spectra and atmospheric properties of cool DA white dwarfs. Astrophys J 367: 253–269
Bergeron P, Wesemael F, Lamontagne R, Fontaine G, Saffer RA, Allard NF (1995) Optical and ultraviolet analyses of ZZ Ceti stars and study of the atmospheric convective efficiency in DA white dwarfs. Astrophys J 449: 258–279
Bergeron P, Leggett SK, Ruiz M-T (2001) Photometric and spectroscopic analysis of cool white dwarfs with trigonometric parallax measurements. Astrophys J Suppl 133: 413–449
Bergeron P, Fontaine G, Billères M, Boudreault S, Green EM (2004) On the purity of the ZZ Ceti instability strip: discovery of more pulsating DA dhite dwarfs on the basis of optical spectroscopy. Astrophys J 600: 404–408
Bischoff-Kim A (2009) Asteroseismological Analysis of rich pulsating white dwarfs. Am Inst Phys Conf Ser 1170: 621
Bischoff-Kim A, Montgomery MH, Winget DE (2008a) Fine grid asteroseismology of G117-B15A and R548. Astrophys J 675: 1505–1511
Bischoff-Kim A, Montgomery MH, Winget DE (2008b) Strong limits on the DFSZ axion mass with G117-B15A. Astrophys J 675: 1512–1517
Bognár Zs, Paparó M, Bradley PA, Bischoff-Kim A (2009) Characterizing the pulsations of the ZZ Ceti star KUV 02464+3239. Mon Not R Astron Soc 399: 1954–1963
Bond HE, Ciardullo R (1993) 403: NATO ASI Series. Kluwer, Dordrecht OSC, p 491
Bond HE, Meakes MG (1990) The pulsating nucleus of the planetary nebula Longmore 4. Astron J 100: 788–792
Bond HE, Kawaler SD, Ciardullo R et al (1996) Asteroseismological observations of the central star of the planetary nebula NGC 1501. Astron J 112: 2699–2711
Bradley PA (1996) Theoretical models for asteroseismology of DA white dwarf stars. Astrophys J 468: 350–368
Bradley PA (1998) Asteroseismological constraints on the structure of the ZZ Ceti stars G117-B15A and R548 . Astrophys J Suppl 116: 307–319
Bradley PA (2001) Asteroseismological constraints on the structure of the ZZ Ceti stars L19-2 and GD 165. Astrophys J 552: 326–339
Bradley PA (2006) Preliminary seismology of the DA white dwarf G 185-32. Mem Soc Astron Italiana 77: 437–438
Bradley PA, Dziembowski WA (1996) A theoretical analysis of pulsation driving in PG 1159 Stars. Astrophys J 462: 376–385
Bradley PA, Kleinman SJ (1997) 214: White dwarfs. Kluwer, Dordrecht OSC, p 445
Bradley PA, Winget DE (1994a) Hot or not? Theoretical blue edges for DA and DB white dwarfs models. Astrophys J 421: 236–244
Bradley PA, Winget DE (1994b) An asteroseismological determination of the structure of the DBV white dwarf GD 358. Astrophys J 430: 850–857
Bradley PA, Winget DE, Wood MA (1993) The potential for asteroseismology of DB white dwarf stars. Astrophys J 406: 661–673
Branch D, Livio M, Yungelson L, Boffi F, Baron E (1995) In search of the progenitors of type IA supernovae. Publ Astron Soc Pac 107: 1019–1029
Brassard P, Fontaine G, Wesemael F, Kawaler SD, Tassoul M (1991) Adiabatic properties of pulsating DA white dwarfs. I - the treatment of the Brunt-Vaisala frequency and the region of period formation. Astrophys J 367: 601–611
Brassard P, Fontaine G, Wesemael F, Hansen CJ (1992a) Adiabatic properties of pulsating DA white dwarfs. II—mode trapping in compositionally stratified models. Astrophys J Suppl 80: 369–401
Brassard P, Pelletier C, Fontaine G, Wesemael F (1992b) Adiabatic properties of pulsating DA white dwarfs. III—a finite-element code for solving nonradial pulsation equations. Astrophys J Suppl 80: 725–752
Brassard P, Fontaine G, Wesemael F, Talon A (1993) 403: White dwarfs: advances in observation and theory. Kluwer, Dordrecht OSC, p 485
Brassard P, Fontaine G, Wesemael F (1995) The modeling of energy distributions and light curves of ZZ Ceti stars. 1: basic theory and semianalytic expressions for the emergent flux. Astrophys J Suppl 96: 545–580
Brickhill AJ (1991) The pulsations of ZZ Ceti stars. III—the driving mechanism. Mon Not R Astron Soc 251: 673–680
Brown TM, Gilliland RL (1994) Asteroseismology. Annu Rev Astron Astrophys 32: 37–82
Camacho J, Torres S, Isern J, Althaus LG, García–Berro E (2007) The contribution of oxygen-neon white dwarfs to the MACHO content of the Galactic halo. Astron Astrophys 471: 151–158
Casewell SL, Dobbie PD, Napiwotzki R, Burleigh MR, Barstow MA, Jameson RF (2009) High-resolution optical spectroscopy of Praesepe white dwarfs. Mon Not R Astron Soc 395: 1795–1804
Castanheira BG, Kepler SO (2008) Seismological studies of ZZ Ceti stars—I. The model grid and the application to individual stars. Mon Not R Astron Soc 385: 430–444
Castanheira BG, Kepler SO (2009) Seismological studies of ZZ Ceti stars—II. Application to the ZZ Ceti class. Mon Not R Astron Soc 396: 1709–1731
Castanheira BG, Kepler SO, Handler G, Koester D (2006) Analysis of IUE spectra of helium-rich white dwarf stars. Astron Astrophys 450: 331–337
Castanheira BG, Kepler SO, Costa AFM et al (2007) Towards a pure ZZ Ceti instability strip. Astron Astrophys 462: 989–993
Catalán S, Isern J, García-Berro E, Ribas I (2008) The initial-final mass relationship of white dwarfs revisited: effect on the luminosity function and mass distribution. Mon Not R Astron Soc 387: 1693–1706
Chandrasekhar S (1931) The maximum mass of ideal white dwarfs. Astrophys J 74: 81–82
Chandrasekhar S (1939) An introduction to the study of stellar structure. University of Cambridge, Cambridge
Chanmugam G (1972) White dwarfs-pulsation periods explained in terms of non-radial oscillations and gravity modes. Nature 236: 83–86
Charpinet S, Fontaine G, Brassard P (2009) Seismic evidence for the loss of stellar angular momentum before the white-dwarf stage. Nature 461: 501–503
Ciardullo R, Bond HE (1996) A survey for pulsations in O VI nuclei of planetary nebulae. Astron J 111: 2332–2348
Clemens JC (1993) The pulsation properties of the DA white dwarf variables. Balt A 2: 407
Clemens JC, van Kerkwijk MH, Wu Y (2000) Mode identification from time-resolved spectroscopy of the pulsating white dwarf G29-38. Mon Not R Astron Soc 314: 220–228
Córsico AH, Althaus LG (2005) Can pulsating PG 1159 stars place constraints on the occurrence of core overshooting? Astron Astrophys 439: L31–L34
Córsico AH, Althaus LG (2006) Asteroseismic inferences on GW Virginis variable stars in the frame of new PG 1159 evolutionary models. Astron Astrophys 458: 863–881
Córsico AH, Althaus LG, Benvenuto OG, Serenelli AM (2001a) New DA white dwarf evolutionary models and their pulsational properties. Astron Astrophys 380: L17–L20
Córsico AH, Benvenuto OG, Althaus LG, Isern J, García-Berro E (2001b) The potential of the variable DA white dwarf G117-B15A as a tool for fundamental physics. New Astron 6: 197–213
Córsico AH, Althaus LG, Benvenuto OG, Serenelli AM (2002a) The mode trapping properties of full DA white dwarf evolutionary models. Astron Astrophys 387: 531–549
Córsico AH, Benvenuto OG, Althaus LG, Serenelli AM (2002b) The effects of element diffusion on the pulsational properties of variable DA white dwarf stars. Mon Not R Astron Soc 332: 392–398
Córsico AH, Althaus LG, Miller Bertolami MM (2006) New nonadiabatic pulsation computations on full PG 1159 evolutionary models: the theoretical GW Virginis instability strip revisited. Astron Astrophys 458: 259–267
Córsico AH, Althaus LG, Miller Bertolami MM, Werner K (2007a) Asteroseismological constraints on the pulsating planetary nebula nucleus (PG 1159-type) RX J2117.1+3412. Astron Astrophys 461: 1095–1102
Córsico AH, Miller Bertolami MM, Althaus LG, Vauclair G, Werner K (2007b) Asteroseismological constraints on the coolest GW Virginis variable star (PG 1159-type) PG 0122+200. Astron Astrophys 475: 619–627
Córsico AH, Althaus LG, Kepler SO, Costa JES, Miller Bertolami MM (2008) Asteroseismological measurements on PG 1159-035, the prototype of the GW Virginis variable stars. Astron Astrophys 478: 869–881
Córsico AH, Althaus LG, Miller Bertolami MM, García-Berro E (2009a) Revisiting the theoretical DBV (V777 Her) instability strip: the MLT theory of convection. J Phys Conf Ser 172: 12075–12079
Córsico AH, Althaus LG, Miller Bertolami MM, García-Berro E (2009b) Asteroseismology of hot pre-white dwarf stars: the case of the DOV stars PG 2131+066é9 and PG 1707+427, and the PNNV star NGC 1501. Astron Astrophys 499: 257–266
Córsico AH, Althaus LG, Miller Bertolami MM, González Pérez JM, Kepler SO (2009c) On the possible existence of short-period g-mode instabilities powered by nuclear-burning shells in post-asymptotic giant branch H-deficient (PG1159-Type) stars. Astrophys J 701: 1008–1014
Córsico AH, Romero AD, Althaus LG, García-Berro E (2009d) Hot C-rich white dwarfs: testing the DB-DQ transition through pulsations. Astron Astrophys 506: 835–843
Costa JES, Kepler SO (2008) The temporal changes of the pulsational periods of the pre-white dwarf PG 1159-035. Astron Astrophys 489: 1225–1232
Costa JES, Kepler SO, Winget DE et al (2008) The pulsation modes of the pre-white dwarf PG 1159-035. Astron Astrophys 477: 627–640
Cowling TG (1941) The non-radial oscillations of polytropic stars. Mon Not R Astron Soc 101: 367–375
Cowling TG, Newing RA (1949) The oscillations of a rotating star. Astrophys J 109: 149–158
Cox JP (1980) Theory of stellar pulsation. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Cox AN (2003) A pulsation mechanism for GW virginis variables. Astrophys J 585: 975–982
D’Antona F, Mazzitelli I (1989) The fastest evolving white dwarfs. Astrophys J 347: 934–949
D’Antona F, Mazzitelli I (1990) Cooling of white dwarfs. Annu Rev Astron Astrophys 28: 139–181
DeGennaro S, von Hippel T, Winget DE, Kepler SO, Nitta A, Koester D, Althaus LG (2008) White dwarf luminosity and mass functions from Sloan digital sky survey spectra. Astron J 135: 1–9
Deloye CJ, Bildsten L (2002) Gravitational settling of 22Ne in liquid white dwarf interiors: cooling and seismological effects. Astrophys J 580: 1077–1090
Díaz–Pinto A, García–Berro E, Hernanz M, Isern J, Mochkovitch R (1994) The luminosity function of massive white dwarfs. Astron Astrophys 282: 86–92
Dolez N, Vauclair G (1981) Gravity modes instability in DA white dwarfs. Astron Astrophys 102: 375–385
Domínguez I, Straniero O, Tornambe A, Isern J (1996) On the formation of massive C-O white dwarfs: the lifting effect of rotation. Astrophys J 472: 783–788
Dreizler S, Heber U (1998) Spectral analyses of PG 1159 star: constraints on the GW Virginis pulsations from HST observations. Astron Astrophys 334: 618–632
Dreizler S, Werner K (1996) Spectral analysis of hot helium-rich white dwarfs. Astron Astrophys 314: 217–232
Dreizler S, Werner K, Heber U, Reid N, Hagen H (1997) The third conference on faint blue stars. L Davis, New York, p 303
Driebe T, Schönberner D, Blöcker T, Herwig F (1998) The evolution of helium white dwarfs. I. The companion of the millisecond pulsar PSR J1012+5307. Astron Astrophys 339: 123–133
Dufour P, Liebert J, Fontaine G, Behara N (2007) White dwarf stars with carbon atmospheres. Nature 450: 522–524
Dufour P, Fontaine G, Liebert J, Schmidt GD, Behara N (2008a) Hot DQ white dwarfs: something different. Astrophys J 683: 978–989
Dufour P, Fontaine G, Liebert J, Williams K, Lai DK (2008b) SDSS J142625.71+575218.3: the first pulsating white dwarf with a large detectable magnetic field. Astrophys J Lett 683: L167–L170
Dufour P et al (2009a) A progress report on the carbon dominated atmosphere white dwarfs. J Phys Conf Ser 172: 12012
Dufour P, Green EM, Fontaine G, Brassard P, Francoeur M, Latour M (2009b) Follow-up observations of the second and third known pulsating hot DQ white dwarfs. Astrophys J 703: 240–251
Dziembowski W (1977) Light and radial velocity variations in a nonradially oscillating star. Acta Astron 27: 203–211
Dziembowski W, Koester D (1981) Excitation of gravity modes in white dwarfs with chemically stratified envelopes. Astron Astrophys 97: 16–26
Eisenstein DJ, Liebert J, Harris HC et al (2006) A catalog of spectroscopically confirmed white dwarfs from the Sloan digital sky survey data release 4. Astrophys J Supp 167: 40–58
Faulkner J, Gribbin JR (1968) Stability and radial vibration periods of the Hamada-Salpeter white dwarf models. Nature 218: 734–736
Fontaine G, Brassard P (1994) White dwarf seismology: modeling of the light curves of ZZ Ceti stars. Astron Soc Pac Conf Ser, San Francisco 57: 195–208
Fontaine G, Brassard P (2008) The pulsating white dwarf stars. Pub Astron Soc Pac 120: 1043–1096
Fontaine G, Brassard P, Bergeron P, Wesemael F (1992) The case of G226-29—evidence for a pulsating DA white dwarf with a thick hydrogen layer? Astrophys J 399: L91–L94
Fontaine G, Brassard P, Bergeron P (2001) The potential of white dwarf cosmochronology. Pub Astron Soc Pac 113: 409–435
Fontaine G, Brassard P, Dufour P (2008) Might carbon-atmosphere white dwarfs harbour a new type of pulsating star? Astron Astrophys 483: L1–L4
Fowler RH (1926) On dense matter. Mon Not R Astron Soc 87: 114–122
Fu J-N, Vauclair G, Solheim J-E et al (2007) Asteroseismology of the PG 1159 star PG 0122+200. Astron Astrophys 467: 237–248
Fujimoto MY (1977) On the origin of R-Type carbon stars: possibility of hydrogen mixing during helium flicker. Pub Astron Soc Pac 29: 331–350
Gänsicke BT, Koester D, Girven J, Marsh TR, Steeghs D (2010) Two white dwarfs with oxygen-rich atmospheres. Science 327: 188–190
García-Berro E, Hernanz M, Isern J, Mochkovitch R (1995) The rate of change of the gravitational constant and the cooling of white dwarfs. Mon Not R Astron Soc 277: 801–810
García-Berro E, Hernanz M, Mochkovitch R, Isern J (1988a) Theoretical white-dwarf luminosity functions for two phase diagrams of the carbon-oxygen dense plasma. Astron Astrophys 193: 141–147
García-Berro E, Hernanz M, Isern J, Mochkovitch R (1988b) Properties of high-density binary mixtures and the age of the universe from white dwarf stars. Nature 333: 642–644
García–Berro E, Torres S, Isern J, Burkert A (1999) Monte Carlo simulations of the disc white dwarf population. Mon Not R Astron Soc 302: 173–188
García–Berro E, Torres S, Isern J, Burkert A (2004) Monte Carlo simulations of the halo white dwarf population. Astron Astrophys 418: 53–65
García-Berro E, Althaus LG, Córsico AH, Isern J (2008) Gravitational settling of 22Ne and white dwarf evolution. Astrophys J 677: 473–482
García-Berro E, Torres S, Althaus LG, Renedo I, Lorén–Aguilar P, Córsico AH, Rohrmann R, Salaris M, Isern J (2010) A white dwarf cooling age of 8Gyr for NGC 6791 from physical separation processes. Nature 465: 194–196
Gautschy A (1997) A further look into the pulsating PG 1159 stars. Astron Astrophys 320: 811–822
Gautschy A, Saio H (1995) Stellar pulsations across the HR diagram: part 1. Annu Rev Astron Astrophys 33: 75–114
Gautschy A, Saio H (1996) Stellar pulsations across the HR diagram: part 2. Annu Rev Astron Astrophys 34: 551–606
Gautschy A, Althaus LG, Saio H (2005) On the excitation of PG 1159-type pulsations. Astron Astrophys 438: 1013–1020
Gianninas A, Bergeron P, Fontaine G (2005) Toward an empirical determination of the ZZ Ceti instability strip. Astrophys J 631: 1100–1112
Gianninas A, Bergeron P, Fontaine G (2006) Mapping the ZZ Ceti instability strip: discovery of six new pulsators. Astron J 132: 831–835
Goldman B, Afonso C, Alard Ch (2002) EROS 2 proper motion survey: constraints on the halo white dwarfs . Astron Astrophys 389: L69–L73
Goldreich P, Wu Y (1999) Gravity modes in ZZ Ceti stars. I. Quasi-adiabatic analysis of overstability. Astrophys J 511: 904–915
González Pérez JM, Solheim J-E, Kamben R (2006) A search for photometric variability of hydrogen-deficient planetary-nebula nuclei. Astron Astrophys 454: 527–536
Grauer AD, Bond HE, Liebert J, Fleming TA, Green RF (1987) A search for pulsating stars similar to PG 1159-035 and K1-16. Astrophys J 323: 271–279
Green EM, Dufour P, Fontaine G, Brassard P (2009) Follow-up studies of the pulsating magnetic white dwarf SDSS J142625.71+575218.3. Astrophys J 702: 1593–1603
Guerrero J, García-Berro E, Isern J (2004) Smoothed particle hydrodynamics simulations of merging white dwarfs. Astron Astrophys 413: 257–272
Hansen BMS (1998) Old and blue white-dwarf stars as a detectable source of microlensing events. Nature 394: 860–862
Hansen BMS, Liebert J (2003) Cool white dwarfs. Annu Rev Astron Astrophys 41: 465–515
Hansen BMS, Phinney ES (1998) Stellar forensics. II—millisecond pulsar binaries. Mon Not R Astron Soc 294: 569–581
Hansen CJ, Cox JP, van Horn HM (1977) The effects of differential rotation on the splitting of nonradial modes of stellar oscillation. Astrophys J 217: 151–159
Hansen BMS, Brewer J, Fahlman GG et al (2002) The white dwarf cooling sequence of the globular cluster Messier 4. Astrophys J Lett 574: L155–158
Hansen BMS, Anderson J, Brewer J et al (2007) The white dwarf cooling sequence of NGC 6397. Astrophys J 671: 380–401
Harper RVR, Rose WK (1970) Nonradial oscillations of white wwarfs, hot white dwarfs, and \({10\, M_{\odot}}\) models. Astrophys J 162: 963–969
Harris HC, Munn JA, Kilic M et al (2006) The white dwarf luminosity function from Sloan digital sky survey imaging data. Astron J 131: 571–581
Hernanz M, García-Berro E, Isern J, Mochkovitch R, Segretain L, Chabrier G (1994) The influence of crystallization on the luminosity function of white dwarfs. Astrophys J 434: 652–661
Herwig F, Blöcker T, Langer N, Driebe T (1999) On the formation of hydrogen-deficient post-AGB stars. Astron Astrophys 349: L5–L8
Hügelmeyer SD, Dreizler S, Homeier D, Krzesiński J, Werner K, Nitta A, Kleinman SJ (2006) Spectral analyses of eighteen hot H-deficient (pre-) white dwarfs from the Sloan digital sky survey data release 4. Astron Astrophys 454: 617–624
Ibata R, Richer HB, Gilliland RL, Scott D (1999) Faint, moving objects in the Hubble deep field: components of the dark halo? Astrophys J Lett 524: L95–L97
Iben I Jr, MacDonald J (1985) The effects of diffusion due to gravity and due to composition gradients on the rate of hydrogen burning in a cooling degenerate dwarf. I - the case of a thick helium buffer layer. Astrophys J 296: 540–553
Iben I Jr, MacDonald J (1986) The effects of diffusion due to gravity and due to composition gradients on the rate of hydrogen burning in a cooling degenerate dwarf. II - dependence on initial metallicity and on buffer mass. Astrophys J 301: 164–176
Iben I Jr, Kaler JB, Truran JW, Renzini A (1983) On the evolution of those nuclei of planetary nebulae that experience a final helium shell flash. Astrophys J 264: 605–612
Isern J, Hernanz M, Mochkovitch R, García-Berro E (1991) The role of the minor chemical species in the cooling of white dwarfs. Astron Astrophys 241: L29–L32
Isern J, Hernanz M, García-Berro E (1992) Axion cooling of white dwarfs. Astrophys J Lett 392: L23–L25
Isern J, Mochkovitch R, García-Berro E, Hernanz M (1997) The physics of crystallizing white dwarfs. Astrophys J 485: 308–312
Isern J, García-Berro E, Hernanz M, Mochkovitch R, Torres S (1998) The halo white dwarf population. Astrophys J 503: 239–246
Isern J, García–Berro E, Hernanz M, Chabrier G (2000) The energetics of crystallizing white dwarfs revisited again. Astrophys J 528: 397–400
Isern J, García-Berro E, Torres S, Catalán S (2008) Axions and the cooling of white dwarf stars. Astrophys J Lett 682: L109–L112
Isern J, García-Berro E, Althaus LG, Córsico AH (2010) Axions and the pulsation periods of variable white dwarfs revisited. Astron Astrophys (RN) 512: A86–A89
Itoh N, Hayashi H, Nishikawa A, Kohyama Y (1996) Neutrino energy loss in stellar interiors. VII. Pair, photo-, plasma, Bremsstrahlung, and recombination neutrino processes. Astrophys J Suppl 102: 411–424
Jones PW, Hansen CJ, Pesnell WD, Kawaler SD (1989) On the possibility of detecting weak magnetic fields in variable white dwarfs. Astrophys J 336: 403–408
Kanaan AN (1996) PhD Thesis. Univ Texas, Austin
Kawaler SD (1987) The stellar seismology of hot white dwarfs and planetary nebula nuclei. The second conference on Faint Blue Stars. IAU Colloquium, vol 95. Davis, Schenectady, pp 297–307
Kawaler SD (1988) The hydrogen shell game - pulsational instabilities in hydrogen shell-burning planetary nebula nuclei. Astrophys J 334: 220–228
Kawaler SD (1993) Radial pulsations in DB white dwarfs? Astrophys J 404: 294–304
Kawaler SD, Bradley PA (1994) Precision asteroseismology of pulsating PG 1159 stars. Astrophys J 427: 415–428
Kawaler SD, Weiss P (1990) Mode trapping in pulsating white dwarfs. Lecture notes in physics. Springer, Heidelberg 367:431
Kawaler SD, Winget DE, Iben I Jr, Hansen CJ (1986a) Evolutionary period changes in variable helium-rich white dwarfs. Astrophys J 302: 530–535
Kawaler SD, Winget DE, Hansen CJ, Iben I Jr (1986b) The helium shell game - Nonradial g-mode instabilities in hydrogen-deficient planetary nebula nuclei. Astrophys J 306: L41–L44
Kawaler SD, O’Brien MS, Clemens JC et al (1995) Whole earth telescope observations and seismological analysis of the pre-white dwarf PG 2131+066. Astrophys J 450: 350–363
Kawaler SD, Potter EM, Vuĉković M et al (2004) Whole earth telescope observations of the pulsating hot white dwarf PG 1707 + 427. Astron Astrophys 428: 969–981
Kawka A, Vennes S (2009) A new extremely low-mass white dwarf in the NLTT catalogue. Astron Astrophys 506: L25–L28
Kepler SO (2009) New advances in helio- and asteroseismology. IAU Joint Discussion 11 XXVII IAU General Assembly, Rio de Janeiro
Kepler SO, Nather RE, McGraw JT, Robinson EL (1982) The pulsation periods of the pulsating white dwarf G117-B15A. Astrophys J 254: 676–682
Kepler SO, Robinson EL, Koester D, Clemens JC, Nather RE, Jiang XJ (2000) Mode identification of pulsating white dwarfs using the Hubble space telescope. Astrophys J 539: 379–391
Kepler SO, Costa JES, Castanheira BG et al (2005) Measuring the evolution of the most stable optical clock G 117-B15A. Astrophys J 634: 1311–1318
Kepler SO, Kleinman SJ, Nitta A, Koester D, Castanheira BG, Giovannini O, Costa AFM, Althaus LG (2007) White dwarf mass distribution in the SDSS. Mon Not R Astron Soc 375: 1315–1324
Kilic M, Mendez RA, von Hippel T, Winget DE (2005) Faint blue objects in the Hubble deep field-south revealed: white dwarfs, subdwarfs, and quasars. Astrophys J 633: 1126–1141
Kilkenny D, O’Donoghue D, Crause LA, Hambly N, MacGillivray H (2009) Two new pulsating DB Stars from the EC survey, EC 04207-4748 and EC 05221-4725. Mon Not R Astron Soc 397: 453–457
Kippenhahn R, Weigert A (1990) Stellar structure and evolution. Springer, Berlin
Kirshnitz DA (1960) Soviet Phys JETP 11: 365
Kleinman SJ, Harris HC, Eisenstein DJ et al (2004) A catalog of spectroscopically identified white dwarf stars in the first data release of the Sloan digital sky survey. Astrophys J 607: 426–444
Koester D (1972) Outer envelopes and cooling of white dwarfs. Astron Astrophys 16: 459–470
Koester D (1978) Virial theorem, energy content, and mass-radius-relation for white dwarfs. Astron Astrophys 64: 289–294
Koester D (2002) White dwarfs: recent developments. Astron Astrophys Rev 11: 33–66
Koester D, Allard NF (2000) The ZZ Ceti instability strip revisited. Balt Astron 9: 119–124
Koester D, Chanmugam G (1990) Physics of white dwarf stars. Rep Prog Phys 53: 837–915
Koester D, Voss B, Napiwotzki R et al (2009) High-resolution UVES/VLT spectra of white dwarfs observed for the ESO SNIa progenitor survey. III. DA white dwarfs. Astron Astrophys 505: 441–462
Koesterke L, Dreizler S, Rauch T (1998) On the mass-loss of PG1159 stars. Astron Astrophys 330: 1041–1046
Kotak R (2008) Progenitors of type Ia supernovae. Astron Soc Pac Conf Ser 401: 150
Kotak R, van Kerkwijk MH, Clemens JC (2002a) Time-resolved optical spectroscopy of the pulsating DA white dwarf HS 0507 + 0434B. New constraints on mode identification and pulsation properties. Astron Astrophys 388: 219–234
Kotak R, van Kerkwijk MH, Clemens JC, Bida TA (2002b) Pulsating or not? A search for hidden pulsations below the red edge of the ZZ Ceti instability strip. Astron Astrophys 391: 1005–1012
Kotak R, van Kerkwijk MH, Clemens JC, Koester D (2003) A new look at the pulsating DB white dwarf GD 358: Line-of-sight velocity measurements and constraints on model atmospheres. Astron Astrophys 397: 1043–1055
Kotak R, van Kerkwijk MH, Clemens JC (2004) A puzzling periodicity in the pulsating DA white dwarf G 117-B15A. Astron Astrophys 413: 301–308
Lamb DQ, Van Horn HM (1975) Evolution of crystallizing pure C-12 white dwarfs. Astrophys J 200: 306–323
Landolt AU (1968) A new short-period blue variable. Astrophys J 153: 151–164
Lasker BM, Hesser JE (1969) High-frequency stellar oscillations. II. G44-32: a new short-period blue variable star. Astrophys J Lett 158: L171–L173
Lasker BM, Hesser JE (1971) High-frequency stellar oscillations.VI. R548, a periodically variable white dwarf. Astrophys J Lett 163: L89–L93
Lasserre T, Afonso C, Albert JN et al (2000) Not enough stellar mass Machos in the Galactic halo. Astron Astrophys 355: L39–L42
Ledoux PJ (1951) The nonradial oscillations of gaseous stars and the problem of Beta Canis Majoris. Astrophys J 114: 373–384
Ledoux PJ, Sauvenier-Goffin E (1950) The vibrational stability of white dwarfs. Astrophys J 111: 611–624
Liebert J, Bergeron P, Holberg J (2005) The Formation rate and mass and luminosity functions of DA white dwarfs from the Palomar green survey. Astrophys J Supp 156: 47–68
Lorén-Aguilar P, Isern J, García-Berro E (2009) High-resolution smoothed particle hydrodynamics simulations of the merger of binary white dwarfs. Astron Astrophys 500: 1193–1205
Luyten WM (1922) The mean parallax of early-type stars of determined proper motion and apparent magnitude. Pub Astron Soc Pac 34: 156–160
Madej J, Nalezyty M, Althaus LG (2004) Mass distribution of DA white dwarfs in the first data release of the Sloan digital sky survey. Astron Astrophys 419: L5–L8
Marsh TR, Dhillon VS, Duck SR (1995) Low-mass white dwarfs need friends - five new double-degenerate close binary stars. Mon Not R Astron Soc 275: 828–840
McGraw JT (1979) The physical properties of the ZZ Ceti stars and their pulsations. Astrophys J 229: 203–211
McGraw JT, Robinson EL (1976) High-speed photometry of luminosity-variable DA dwarfs: R808, GD 99, and G 117-B15A. Astrophys J Lett 205: L155–L158
McGraw JT, Liebert J, Starrfield SG, Green R (1979) A new, hot, non-DA pulsating degenerate. White dwarfs and variable degenerate stars. University of Rochester, Rochester, pp 377–381
Méndez RA, Minniti D (2000) Faint blue objects on the Hubble deep field north and south as possible nearby old halo white dwarfs. Astrophys J 529: 911–916
Méndez RA, Ruiz MT (2001) The luminosity function of magnitude and proper-motion-selected samples: the case of white dwarfs. Astrophys J 547: 252–262
Mestel L (1952) On the theory of white dwarf stars. I. The energy sources of white dwarfs. Mon Not R Astron Soc 112: 583–597
Metcalfe TS (2005) Lessons for asteroseismology from white dwarf stars. Astrophys J 26: 273–281
Metcalfe TS, Nather RE, Winget DE (2000) Genetic-algorithm-based asteroseismological analysis of the DBV white dwarf GD 358. Astrophys J 545: 974–981
Metcalfe TS, Winget DE, Charbonneau P (2001) Preliminary constraints on 12C(α, γ)16O from white dwarf seismology. Astrophys J 557: 1021–1027
Metcalfe TS, Salaris ME, Winget DE (2002) Measuring 12C(α, γ)16O from white dwarf asteroseismology. Astrophys J 573: 803–811
Miller Bertolami MM, Althaus LG (2006) Full evolutionary models for PG 1159 stars. Implications for the helium-rich O(He) stars. Astron Astrophys 454: 845–854
Miller Bertolami MM, Althaus LG, Córsico AH (2005) The formation of DA white dwarfs with thin hydrogen envelopes through a late thermal pulse. Bol Asoc Arg Astron 48: 185–191
Miller Bertolami MM, Althaus LG, Serenelli AM, Panei JA (2006) New evolutionary calculations for the born again scenario. Astron Astrophys 449: 313–326
Mochkovitch R (1983) Freezing of a carbon-oxygen white dwarf. Astron Astrophys 122: 212–218
Montgomery MH (2005) A new technique for probing convection in pulsating white dwarf stars. Astrophys J 633: 1142–1149
Montgomery MH (2008) What we can learn from the light curves of GD 358 and PG 1351+489. Commun Asteroseismol 154: 38–48
Montgomery MH, Metcalfe TS, Winget DE (2003) The core/envelope symmetry in pulsating stars. Mon Not R Astron Soc 344: 657–664
Montgomery MH, Williams KA, Winget DE, Dufour P, DeGennaro S, Liebert J (2008) SDSS J142625.71+575218.3: a prototype for a new class of variable white dwarf. Astrophys J Lett 678: L51–L54
Mukadam AS, Mullally F, Nather RE et al (2004) Thirty-five new pulsating DA white dwarf stars. Astrophys J 607: 982–998
Mukadam AS, Montgomery MH, Winget DE, Kepler SO, Clemens JC (2006) Ensemble characteristics of the ZZ Ceti stars. Astrophys J 640: 956–965
Mullally F, Winget DE, DeGennaro S, Jeffery E, Thompson SE, Chandler D, Kepler SO (2008) Limits on planets around pulsating white dwarf stars. Astrophys J 676: 573–583
Muraki Y, Sumi T, Abe F et al (1999) Search for Machos by the MOA collaboration. Prog Theor Phys Suppl 133: 233–246
Nagel T, Werner K (2004) Detection of non-radial g-mode pulsations in the newly discovered PG 1159 star HE 1429-1209. Astron Astrophys 426: L45–L48
Nather RE, Winget DE, Clemens JC, Hansen CJ, Hine BP (1990) The whole earth telescope - a new astronomical instrument. Astrophys J 361: 309–317
Nitta A, Kepler SO, Winget DE et al (1998) HST observation of GD 358. Balt Astron 7: 203–209
Nitta A, Kleinman SJ, Krzesinski J et al (2009) New pulsating DB white dwarf stars from the Sloan digital sky survey. Astrophys J 690: 560–565
O’Brien MS (2003) Old pulsators: white dwarfs and their immediate precursors. Astrophys Space Sci 284: 45–52
O’Brien MS, Kawaler SD (2000) The predicted signature of neutrino emission in observations of pulsating pre-white dwarf stars. Astrophys J 539: 372–378
Ostriker JP, Tassoul J-L (1968) Pulsation periods of rotating white dwarf models. Nature 219: 577–579
Pekeris CL (1938) Nonradial oscillations of stars. Astrophys J 88: 189–199
Pfeiffer B, Vauclair G, Dolez N et al (1996) Whole earth telescope observations and seismological analysis of the cool ZZ Ceti star GD 154. Astron Astrophys 314: 182–190
Prada Moroni PG, Straniero O (2009) Very low-mass white dwarfs with a C-O core. Astron Astrophys 507: 1575–1583
Quirion P-O, Fontaine G, Brassard P (2004) On the driving mechanism and the coexistence of variable and nonvariable stars in the domain of the pulsating PG 1159 stars. Astrophys J 610: 436–441
Quirion P-O, Fontaine G, Brassard P (2007) Mapping the instability domains of GW Vir stars in the effective temperature-surface gravity diagram. Astrophys J Suppl 171: 219–248
Raffelt GG (1996) Stars as laboratories for fundamental physics: the astrophysics of neutrinos, axions, and other weakly interacting particles. University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Rauch T, Reiff E, Werner K, Herwig F, Koesterke L, Kruk JW (2006) On the Evolutionary status of extremely hot helium stars—are O(He) stars successors of RCrB stars? Astron Soc Pac Conf Ser, San Francisco 348: 194–196
Reed MD, Kawaler SD, O’Brien MS (2000) PG 2131+066: a test of pre-white dwarf asteroseismology. Astrophys J 545: 429–434
Renedo I, Althaus LG, Miller Bertolami MM, Romero AD, Córsico AH, Rohrmann RD, García-Berro E (2010) New cooling sequences for old white dwarfs. Astrophys J 717: 183–195
Richer HB, Fahlman GG, Ibata RA et al (1997) White dwarfs in globular clusters: Hubble space telescope observations of M4. Astrophys J 484: 741–760
Richer HB, Anderson J, Brewer J, Davis S, Fahlman GG (2006) Probing the faintest stars in a globular star cluster. Science 313: 936–940
Ritossa C, García-Berro E, Iben I Jr (1996) n the evolution of stars that form electron-degenerate cores processed by carbon burning. II. Isotope abundances and thermal pulses in a \({10 M_{\odot}}\) model with an ONe core and applications to long-period variables, classical novae, and accretion-induced collapse. Astrophys J 460: 489–505
Ritossa C, García-Berro E, Iben I Jr (1999) On the evolution of stars that form electron-degenerate cores processed by carbon burning. V. Shell convection sustained by helium burning, transient neon burning, dredge-out, URCA cooling, and other properties of an \({11 M_{\odot}}\) population I model star. Astrophys J 515: 381–397
Robinson EL, Nather RE, McGraw JT (1976) The photometric properties of the pulsating white dwarf R548. Astrophys J 210: 211–219
Robinson EL, Kepler SO, Nather RE (1982) Multicolor variations of the ZZ Ceti stars. Astrophys J 259: 219–231
Robinson EL, Mailloux TM, Zhang E, Koester D, Stiening RF et al (1995) The pulsation index, effective temperature, and thickness of the hydrogen layer in the pulsating DA white dwarf G117-B15A. Astrophys J 438: 908–916
Rohrmann RD (2001) Hydrogen-model atmospheres for white dwarf stars. Mon Not R Astron Soc 323: 699–712
Rohrmann RD, Serenelli AM, Althaus LG, Benvenuto OG (2002) Improved synthetic spectra of helium-core white dwarf stars. Mon Not R Astron Soc 335: 499–511
Russell HN (1914) Relations between the spectra and other characteristics of the stars. Pop Astron 22: 275–294
Saio H (1996) Linear models for hydrogen-deficient star pulsations. Astron Soc Pac Conf Ser, San Francisco 96: 361–373
Saio H, Jeffery CS (2000) The evolution of a rapidly accreting helium white dwarf to become a low-luminosity helium star. Mon Not R Astron Soc 313: 671–677
Saio H, Winget DE, Robinson EL (1983) Pulsation properties of DA white dwarfs - radial mode instabilities. Astrophys J 265: 982–995
Salaris M, Serenelli AM, Weiss A, Miller Bertolami MM (2009) Semi-empirical white dwarf initial-final mass relationships: a thorough analysis of systematic uncertainties due to stellar evolution models. Astrophys J 692: 1013–1032
Salaris M, Domínguez I, García-Berro E, Hernanz M, Isern J, Mochkovitch R (1997) The cooling of CO white dwarfs: influence of the internal chemical distribution. Astrophys J 486: 413–419
Salpeter EE (1961) Energy and pressure of a zero-temperature plasma. Astrophys J 134: 669–682
Sarna MJ, Antipova J, Ergma E (1999) Cooling curves and initial models for low-mass white dwarfs ( < \({0.25 M_{\odot}}\)) with helium core. Astron Soc Pac Conf Ser, San Franciso 169: 400–407
Saumon D, Jacoboson SB (1999) Pure hydrogen model atmospheres for very cool white dwarfs. Astrophys J 511: L107–L110
Saumon D, Bergeron P, Lunine JI, Hubbard WB, Burrows A (1994) Cool zero-metallicity stellar atmospheres. Astrophys J 424: 333–344
Sauvenier-Goffin E (1949) La stabilité dynamique des Naines blanches. Annales d’Astrophysique 12: 39–51
Schmidt M (1959) The rate of star formation. Astrophys J 129: 243–258
Schönberner D (1979) Asymptotic giant branch evolution with steady mass loss. Astrons Astrophys 79: 108–114
Segretain L, Chabrier G, Hernanz M, García-Berro E, Isern J, Mochkovitch R (1994) Cooling theory of crystallized white dwarfs. Astrophys J 434: 641–651
Shaviv G, Kovetz A (1976) The cooling of carbon-oxygen white dwarfs. Astron Astrophys 51: 383–391
Siess L (2007) Evolution of massive AGB stars. II. Model properties at non-solar metallicity and the fate of Super-AGB stars. Astron Astrophys 476: 893–909
Silvotti R, Dreizler S, Handler G, Jiang XJ (1999) The photometric behaviour of the peculiar PG 1159 star HS 2324+3944 at high frequency resolution. Astron Astrophys 342: 745–755
Silvotti R, Fontaine G, Pavlov M, Marsh TR, Dhillon VS, Littlefair SP (2007) Search for p-mode pulsations in DA white dwarfs with VLT-ULTRACAM. Astron Soc Pac Conf Ser, San Francisco 372: 593
Solheim J-E, Vauclair G, Mukadam AS, Janulis R, Dobrovolskas V (2007) Abell 43: longest period planetary nebula nucleus variable. Astron Astrophys 468: 1057–1061
Stanghellini L, Cox AN, Starrfield S (1991) Post-asymptotic giant branch nonradial instability strips. Astrophys J 383: 766–778
Starrfield S, Cox AN, Hodson SW, Pesnell WD (1983) The discovery of nonradial instability strips for hot, evolved stars. 268:L27–L32
Starrfield S, Cox AN, Kidman RB, Pesnell WD (1984) Nonradial instability strips based on carbon and oxygen partial ionization in hot, evolved stars. Astrophys J 281: 800–810
Starrfield S, Cox AN, Kidman RB, Pesnell WD (1985) An analysis of nonradial pulsations of the central star of the planetary nebula K1-16. Astrophys J Lett 293: L23–L27
Stevenson DJ (1980) A eutectic in carbon-oxygen white dwarfs? J Phys Colloq 41: C2/61–64
Stoner EC (1930) The equilibrium of dense stars. Philos Mag 9: 944–963
Straniero O, Domínguez I, Imbriani G, Piersanti L (2003) The chemical composition of white dwarfs as a test of convective efficiency during core helium burning. Astrophys J 583: 878–884
Tassoul M (1980) Asymptotic approximations for stellar nonradial pulsations. Astrophys J Suppl 43: 469–490
Tassoul M, Fontaine G, Winget DE (1990) Evolutionary models for pulsation studies of white dwarfs. Astrophys J Suppl 72: 335–386
Thompson SE, van Kerkwijk MH, Clemens JC (2008) Deciphering the pulsations of G 29-38 with optical time series spectroscopy. Mon Not R Astron Soc 389: 93–101
Tisserand P, Le Guillou L, Afonso C et al (2007) Limits on the Macho content of the Galactic Halo from the EROS-2 Survey of the Magellanic Clouds. Astron Astrophys 469: 387–404
Torres S, García–Berro E, Isern J (1998) Neural network identification of halo white dwarfs. Astrophys J Lett 508: L71–L74
Torres S, García–Berro E, Burkert A, Isern J (2001) The impact of a merger episode in the galactic disc white dwarf population. Mon Not R Astron Soc 328: 492–500
Torres S, García–Berro E, Burkert A, Isern J (2002) High-proper-motion white dwarfs and halo dark matter. Mon Not R Astron Soc 336: 971–978
Torres S, Camacho J, Isern J, García–Berro E (2008) The contribution of red dwarfs and white dwarfs to the halo dark matter. Astron Astrophys 486: 427–435
Udalski A, Szymanski M, Kaluzny J, Kubiak M (1994) The optical gravitational lensing experiment. Journal of the 1993 Season Observatioin. Acta Astron 44: 1–20
Unglaub K, Bues I (2000) The chemical evolution of hot white dwarfs in the presence of diffusion and mass loss. Astron Astrophys 359: 1042–1058
Unno W, Osaki Y, Ando H, Saio H, Shibahashi H (1989) Non-radial oscillations of stars. University of Tokyo Press, Tokyo
van Horn HM (1968) Crystallization of white dwarfs. Astrophy J 151: 227–238
van Kerkwijk MH, Clemens JC, Wu Y (2000) Surface motion in the pulsating DA white dwarf G29-38. Mon Not R Astron Soc 314: 209–219
van Kerkwijk MH et al (2005) Optical studies of companions to millisecond pulsars. Astron Soc Pac Conf Ser, San Franciso 328: 357–370
Vauclair G (1971) Vibrational stability of DA white dwarfs. Astrophys Lett 9: 161–164
Vauclair G, Moskalik P, Pfeiffer B et al (2002) Asteroseismology of RXJ 2117+3412, the hottest pulsating PG 1159 star. Astron Astrophys 381: 122–150
Vauclair G, Solheim J-E, Østensen RH (2005) Abell 43, a second pulsating “hybrid-PG 1159” star. Astron Astrophys 433: 1097–1100
Von Hippel T, Gilmore G (2000) The white dwarf cooling age of the open cluster NGC 2420. Astron J 120: 1384–1395
Von Hippel T, Jefferys WH, Scott J et al (2006) Inverting color-magnitude diagrams to access precise star cluster parameters: a Bayesian approach. Astrophys J 645: 1436–1447
Voss B, Koester D, Napiwotzki R, Christlieb N, Reimers D (2007) High-resolution UVES/VLT spectra of white dwarfs observed for the ESO SN Ia progenitor survey. II. DB and DBA stars. Astron Astrophys 470: 1079–1088
Vuille F (1998) PhD Thesis, Univ Capetown
Warner B, Robinson EL (1972) White dwarfs-more rapid variables. Nature 239: 2–7
Weidemann V (2000) Revision of the initial-to-final mass relation. Astron Astrophys 363: 647–656
Werner K (2001) Properties of atmospheres and winds of H-deficient central stars and related objects. Astrophys Space Sci 275: 27–39
Werner K, Herwig F (2006) The elemental abundances in bare planetary nebula central stars and the shell burning in AGB stars. Publ Astron Soc Pac 118: 183–204
Werner K, Rauch T, Kruk JW (2008a) KPD0005+5106: hottest DO white dwarf much hotter than assumed. Astron Soc Pac Conf Ser, San Franciso 391: 239–240
Werner K, Rauch T, Kruk JW (2008b) Discovery of photospheric Ca X emission lines in the far-UV spectrum of the hottest known white dwarf (KPD 0005+5106). Astron Astrophys 492: L43–L47
Winget DE (1988) Seismological investigations of compact stars. Advances in Helio- and Asteroseismology. Adv Helio-Asteroseismol IAU Symp 123: 305–324
Winget DE, Kepler SO (2008) Pulsating white dwarf stars and precision asteroseismology. Annu Rev Astron Astrophys 46: 157–199
Winget DE, van Horn HM, Hansen CJ (1981) The nature of the ZZ Ceti oscillations - trapped modes in compositionally stratified white dwarfs. Astrophys J Lett 245: L33–L36
Winget DE, van Horn HM, Tassoul M, Fontaine G, Hansen CJ, Carroll BW (1982a) Hydrogen-driving and the blue edge of compositionally stratified ZZ Ceti star models. Astrophys J Lett 252: L65–L68
Winget DE, Robinson EL, Nather RD, Fontaine G (1982b) Photometric observations of GD 358 - DB white dwarfs do pulsate. Astrophys J Lett 262: L11–L15
Winget DE, Hansen CJ, van Horn HM (1983) Do pulsating PG1159-035 stars put constraints on stellar evolution? Nature 303: 781–782
Winget DE, Hansen CJ, Liebert J, Van Horn HM, Fontaine G, Nather RE, Kepler SO, Lamb DQ (1987) An independent method for determining the age of the universe. Astrophys J Lett 315: L77–L81
Winget DE, Nather RE, Clemens JC et al (1991) Asteroseismology of the DOV star PG 1159 - 035 with the whole earth telescope. Astrophys J 378: 326–346
Winget DE, Nather RE, Clemens JC et al (1994) Whole earth telescope observations of the DBV white dwarf GD 358. Astrophys J 430: 839–849
Winget DE, Sullivan DJ, Metcalfe TS, Kawaler SD, Montgomery MH (2004) A strong test of electroweak theory using pulsating DB white dwarf stars as plasmon neutrino detectors. Astrophys J Lett 602: L109–L112
Winget DE, Kepler SO, Campos F, Montgomery MH, Girardi L, Bergeron P, Williams K (2009) The physics of crystallization from globular cluster white dwarf stars in NGC 6397. Astrophys J Lett 693: L6–L10
Xu ZW, Van Horn HM (1992) Effects of Fe/C phase separation on the ages of white dwarfs. Astrophys J 387: 662–672
Yoo J, Chanamé J, Gould A (2004) The end of the MACHO era: limits on halo dark matter from stellar halo wide binaries. Astrophys J 601: 311–318
York DG, Adelman J, Anderson JE Jr et al (2000) The Sloan digital sky survey: technical summary. Astron J 120: 1579–1587
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Althaus, L.G., Córsico, A.H., Isern, J. et al. Evolutionary and pulsational properties of white dwarf stars. Astron Astrophys Rev 18, 471–566 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00159-010-0033-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00159-010-0033-1