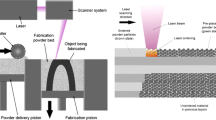
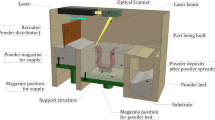
Abstract
This paper addresses the issue of minimizing support material in additive manufacturing (AM) during topology optimization (TO) in order to reduce material and post-processing costs. The TO method developed in this paper utilizes the moving morphable components (MMC) approach, where a structure is composed of several building blocks. This work introduces minimum build angle constraints to eliminate overhanging edges, supplementing these with penalty functions to ensure connectivity between building blocks, such that the TO output is printable. The MMC approach uses explicit geometric entities for the morphable components that are controlled by geometric parameters, such as length, thickness, and angle. These parameters are the design variables. Using this approach enables the formulation of geometric manufacturing constraints and the construction of CAD models, which are important advantages of the MMC method. Examples of a short cantilever beam and an MBB beam demonstrate the capabilities of the TO methods.


























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allaire G, Dapogny C, Estevez R, Faure A, Michailidis G (2017) Structural optimization under overhang constraints imposed by additive manufacturing technologies. J Comput Phys 351:295–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2017.09.041
Bendsøe MP (1989) Optimal shape design as a material distribution problem. Struct Multidiscip Optim 1:193–202
Bendsøe MP, Kikuchi N (1988) Generating optimal topologies in structural design using a homogenization method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 71:197–224
Brackett D, Ashcroft I (2011) Hague R. Topology optimization for additive manufacturing, Austin
Deng S, Suresh K (2016) Multi-constrained 3D topology optimization via augmented topological level-set. Comput Struct 170(1):1–12
Gaynor AT, Guest JK (2016) Topology optimization considering overhang constraints: eliminating sacrificial support material in additive manufacturing through design. Struct Multidiscip Optim, 54:1157–1172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-016-1551-xe
Guo X, Zhang WS, Zhong WL (2014) Doing topology optimization explicitly and geometrically—a new moving morphable components based framework. J Appl Mech 81:081009
Guo X, Zhou J, Zhang WS, Du Z, Liu C, Liu Y (2017) Self-supporting structure design in additive manufacturing through explicit topology optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 323:27–63
Langelaar M (2016) An additive manufacturing filter for topology optimization of print-ready designs. Struct Multidiscip Optim 55:871–883. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-016-1522-2
Leary M, Merli L, Torti F, Mazur M, Brandt M (2014) Optimal topology for additive manufacture: a method for enabling additive manufacture of support-free optimal structures. Mater Des 63:678–690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2014.06.015
Liu J, Ma Y-S (2015) 3D level-set topology optimization: a machining feature-based approach. Struct Multidiscip Optim 52:563–582. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-015-1263-7
Mirzendehdel AM, Suresh K (2016) Support structure constrained topology optimization for additive manufacturing. Comput Aided Des 81:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cad.2016.08.006
Osher SJ, Sethian JA (1988) Fronts propagating with curvature dependent speed: algorithms based on Hamilton-Jacobi formulations. J Comput Phys 79:12–49
Qian X (2017) Undercut and overhang angle control in topology optimization: a density gradient based integral approach. Int J Numer Methods Eng 111:247–272. https://doi.org/10.1002/nme.5461
Svanberg K (1987) The method of moving asymptotes-a new method for structural optimization. Internat. J. Numer. Methods Engrg 24:359–373
Wang MY, Wang XM, Guo DM (2003) A level set method for structural topology optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 192:227–246
Zhang S, Norato JA, Gain AL, Lyu N (2016a) A geometry projection method for the topology optimization of plate structures. Struct Multidiscip Optim 54:1173–1190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-016-1466-6
Zhang WS, Yuan J, Zhang J, Guo X (2016b) A new topology optimization approach based on moving morphable components (MMC) and the ersatz material model. Struct Multidiscip Optim 53:1243–1260
Y. Zhou, W. Zhang, J. Zhu, Z. Xu (2016) Feature-driven topology optimization method with signed distance function, Comput. Methods Appl.Mech Eng 310 1–32.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cma.2016.06.027
Acknowledgements
We would like to show our gratitude to Dr. Krister Svanberg from KTH Royal Institute of Technology who provided the Matlab code GCMMA as the optimization algorithm of this work. We also thank Dr. Xu Guo from Dalian University of Technology for providing an example Matlab code of their MMC framework, although they may not agree with all of the interpretations/conclusions of this paper.
We thank Drs. Oliver Weeger and Narasimha Boddeti, Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD), for sharing their expertise and insightful feedback, and for assistance during the course of this research.
Finally, we acknowledge the International Design Centre, funded by the Singapore Ministry of Education, at SUTD for their partial support of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Replication of results
As comprehensive implementation details are provided, and the software involves other researchers' work, we have decided not to publish the code. Scientists or interested parties are welcome to contact the authors for further explanations.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: YoonYoung Kim
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xian, Y., Rosen, D.W. Morphable components topology optimization for additive manufacturing. Struct Multidisc Optim 62, 19–39 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-019-02466-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-019-02466-6