Abstract
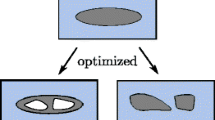
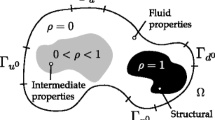
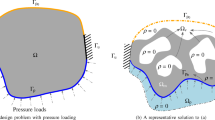
This paper presents an approach to shape and topology optimization of fluid-structure interaction (FSI) problems at steady state. The overall approach builds on an immersed boundary method that couples a Lagrangian formulation of the structure to an Eulerian fluid model, discretized on a deforming mesh. The geometry of the fluid-structure boundary is manipulated by varying the nodal parameters of a discretized level set field. This approach allows for topological changes of the fluid-structure interface, but free-floating volumes of solid material can emerge in the course of the optimization process. The free-floating volumes are tracked and modeled as fluid in the FSI analysis. To sense the isolated solid volumes, an indicator field described by linear, isotropic diffusion is computed prior to analyzing the FSI response of a design. The fluid is modeled with the incompressible Navier-Stokes equations, and the structure is assumed linear elastic. The FSI model is discretized by an extended finite element method, and the fluid-structure coupling conditions are enforced weakly. The resulting nonlinear system of equations is solved monolithically with Newton’s method. The design sensitivities are computed by the adjoint method and the optimization problem is solved by a gradient-based algorithm. The characteristics of this optimization framework are studied with two-dimensional problems at steady state. Numerical results indicate that the proposed treatment of free-floating volumes introduces a discontinuity in the design evolution, yet the method is still successful in converging to meaningful designs.






















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allaire G, Jouve F, Toader A (2002) A level-set method for shape optimization. C.R Math 334 (12):1125–1130
Allaire G, Jouve F, Toader AM (2004) Structural optimization using sensitivity analysis and a level-set method. J Comput Phys 194(1):363–393
Allaire G, Dapogny C, Frey P (2014) Shape optimization with a level set based mesh evolution method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 282:22–53
Allen M, Maute K (2004) Reliability based optimization of aeroelastic structures. Struct Multidiscip Optim 24:228–242
Allen M, Maute K (2005) Reliability-based shape optimization of structures undergoing fluid structure interaction phenomena. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 194:3472–3495
Amestoy P, Duff I, L’Excellent JY (2000) Multifrontal parallel distributed symmetric and unsymmetric solvers. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 184(24):501–520
Annavarapu C, Hautefeuille M, Dolbow JE (2012) A robust nitsches formulation for interface problems. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 225228(0):44–54
Arora D, Behr M, Pasquali M (2004) A tensor-based measure for estimating blood damage. Artif Organs 28:1002–1115
Bazilevs Y, Takizawa K, Tezduyar TE (2013) Computational Fluid-Structure Interaction: Methods and applications Wiley; 1 edition (February 11, 2013)
Bendsøe M (1989) Optimal shape design as a material distribution problem. Struct Multidiscip Optim 1 (4):193–202
Brampton C, Kim HA, Cuningham J (2012) Level set topology optimisation of aircraft wing considering aerostructural interaction. In: 12th AIAA Aviation Technology, Integration, and Opterations (ATIO) Conference and 14th AIAA/ISSM Multidisciplinary Analysis and Optimization Conference, Indianapolis, IN, September 17 - 19
Burger M, Osher SJ (2005) A survey in mathematics for industry a survey on level set methods for inverse problems and optimal design. Euro Jnl of Appl Math 16:263–301
Butler R, Lillico M, Banerjee J, Guo S (1995) Optimum design of high aspect ratio wings subject to aeroelastic constraints. In: Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials and Co-located Conferences, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics
Christiansen AN (2014) Combined shape and topology optimization. PhD thesis, Technical University of Denmark
Coffin P, Maute K (2015) A level-set method for steady-state and transient natural convection problems. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 1–21
Dapogny C (2014) Shape optimization, level set methods on unstructured meshes and mesh evolution. PhD thesis, Thèse de lUniversité Paris VII
van Dijk N, Maute K, Langelaar M, Keulen F (2013) Level-set methods for structural topology optimization: A review. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 1–36
Dillinger J, Abdalla M, Klimmek T, Gurdal Z (2013) Static aeroelastic stiffness optimization and investigation of forward swept composite wings. In: 10th World Congress on Structural and Multidisplinary Optimization. May 19 - 24, Orlando, Florida
Dunning P, Stanford B, Kim H (2014) Coupled aerostructural topology optimization using a level set method for 3d aircraft wings. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 1–20
Dunning P, Stanford B, Kim HA (2015) Coupled aerostructural topology optimization using level set method for 3d aircraft wings. Struct Multidiscip Optim 51:1113–1132
Gasbarri P, Chiwiacowsky LD, de Campos Velho H (2009) A hybrid multilevel approach for aeroelastic optimization of composite wing-box. Struct Multidiscip Optim 39(6):607–624
Gern FH, Gundlach JF, Ko A, Naghshineh-Pour A, Sulaeman E, Tetrault PA, Grossman B, Kapania RK, Mason WH, Schetz JA, Haftka R (1999). In: Multidisciplinary design optimization of a transonic commercial transport with a strut-braced wing 1999 World Aviation Congress, San Franciso, CA, October 19 - 21
Ghazlane I, Carrier G, Dumont A, Marcelet M, Désidéri JA (2011) Aerostructural optimization with the adjoint method. In: EUROGEN 2011, Capua, Italy, September 14 - 15
Gomes AA, Suleman A (2008) Topology optimization of a reinforced wing box for enhanced roll maneuvers. AIAA J 46:548–556
Griffith BE (2012) Immersed boundary model of aortic heart valve dynamics with physiological driving and loading conditions. Int J Numer Methods Biomed Eng 28(3):317–345
Gumbert CR, Hou GJW, Newman PA (2001) Simultaneous aerodynamic analysis and design optimization (saado) for a 3-d flexible wing. In: Proceedngs of the 39th Aerospace Science Meeting and Exhibit, January 8-11, 2001, Reno, NV, AIAA 2001- 1107
Guo S (2007) Aeroelastic optimization of an aerobatic aircraft wing structure. Aerosp Sci Technol 11(5):396–404
Guo S, Cheng W, Cui D (2005) Optimization of composite wing structures for maximum flutter speed. In: 46th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics & Materials Conference, Austin, TX, April 21 - 25
Hansbo P, Hermansson J, Svedberg T (2004) Nitsches method combined with space-time finite elements for ale fluid-structure interaction problems. Comput Methods Appl Mech Engrg 193:4195–4206
Hart JD (2002) Fluid-structure interaction in the aortic heart valve a three-dimensional computational analysis. PhD thesis, Technische Universiteit Eindhoven
Hsu MC, Kamensky D, Bazilevs Y, Sacks M, Hughes T (2014) Fluidstructure interaction analysis of bioprosthetic heart valves: significance of arterial wall deformation. Comput Mech 54(4):1055–1071
James K, Martins J (2010) Topology optimization using a level set method with an arbitrary structured mesh. In: 51st AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference, Orlando, FL, April 12 - 16
Jenkins N, Maute K (2015) Level set topology optimization of stationary fluid-structure interaction problems. Struct Multidiscip Optim 52:179–195
Kamensky D, Hsu MC, Schillinger D, Evans JA, Aggarwal A, Bazilevs Y, Sacks MS, Hughes TJ (2015) An immersogeometric variational framework for fluidstructure interaction: Application to bioprosthetic heart valves. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 284(0):1005–1053
Kreissl S, Maute K (2011) Topology optimization for unsteady flow. Int J Numer Methods Eng 87:1229–1253
Krog L, Tucker A, Rollema G (2002) Application of topology, sizing and shape optimization methods to optimal design of aircraft components. In: 3 rd Altair UK HyperWorks Users Conference
Krog L, Tucker A, Kemp M, Boyd R (2004) Topology optimization of aircraft wing box ribs. In: 10th AIAA/ISSMO Multidisciplinary Analysis and Optimization Conference, August 30 - September 1, Albany, New York
Liu S, Li Q, Chen W, Tong L, Cheng G (2015) An identification method for enclosed voids restriction in manufacturability design for additive manufacturing structures. Front Mech Eng 10(2):126–137
Lund E, Moller H, Jakobsen LA (2001) Shape design optimization of steady fluid-structure interaction problems with large displacements. In: 42cd AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference and Exhibit. April 16-19
Luo Z, Tong L, Wang MY, Wang S (2007) Shape and topology optimization of compliant mechanisms using a parameterization level set method. J Comput Phys 227(1):680–705
Makhija D, Maute K (2014) Numerical instabilities in level set topology optimization with the extended finite element method. Struct Multidiscip Optim 49(2):185–197
Martins J, Alonso J, Reuther J (2005) A coupled-adjoint sensitivity analysis method for high-fidelity aero-structural design. Optim Eng 6(1):33–62
Martins J RRA, Alonso JJ, Reuther JJ (2004) High-fidelity aerostructural design optimization of a supersonic business jet. J Aircr 41(3)
Maute K, Reich G (2006) Integrated multidisciplinary topology optimization approach to adaptive wing design. AIAA J Aircr 43(1):253–263
Maute K, Nikbay M, Farhat C (2001) Coupled analytical sensitivity analysis and optimization of three-dimensional nonlinear aeroelastic systems. AIAA J 39(11):2051–2061
Maute K, Nikbay M, Farhat C (2003) Sensitivity analysis and design optimization of three-dimensional nonlinear aeroelastic systems by the adjoint method. Int J Numer Methods Eng 56(6):911–933
Mayer U, Popp A, Gerstenberger A, Wall W (2010) 3d fluidstructure-contact interaction based on a combined xfem fsi and dual mortar contact approach. Comput Mech 46(1):53–67
Morbiducci U, Ponzini R, Nobili M, Massai D, Montevecchi FM, Bluestein D, Redaelli A (2015) Blood damage safety of prosthetic heart valves. shear-induced platelet activation and local flow dynamics: A fluidstructure interaction approach. J Biomech 42:1952–1960
Munk D, Vio G, Steven G (2015) Aerothermoelastic structural topology optimisation for a hypersonic transport aircraft wing. In: 11th World Congress on Structural and Mutlidisciplinary Optimization. June 7 - 12, Sydney, Australia
Osher SJ, Sethian JA (1988) Fronts propagating with curvature dependent speed: algorithms based on Hamilton-Jacobi formulations. J Comput Phys 79:12—49
Picelli R, Vicente WM, Pavanello R, van Keulan F (2015) Topology optimization considering design-dependent stokes flow loads. In: 11th World Congress on Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization. Sydney Australia, June 7 - 12
Pingen G, Waidmann M, Evgrafov A, Maute K (2010) A parametric level-set approach for topology optimization of flow domains. Struct Multidiscip Optim 41(1):117–131
Sala M, Stanley KS, Heroux MA (2008) On the design of interfaces to sparse direct solvers. ACM Trans Math Softw 34(2):9:1–9:22
Schleupen A, Maute K, Ramm E (2000) Adaptive fe-procedures in shape optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 19:282–302
Sigmund O, Maute K (2013) Topology optimization approaches: A comparative review. Struct Multidiscip Optim 48(6):1031–1055
Sobieszczanski-Sobieski J, Haftka R (1997) Multidisciplinary aerospace design optimization: survey of recent developments. Struct Optim 14(1):1–23
Stanford B (2008) Aeroelastic analysis and optimization of membrane micro air vehicle wings. PhD thesis, University of Florida
Stanford B, Beran P (2013) Aerothermoelastic topology optimization with flutter and buckling metrics. Struct Multidiscip Optim 48(1):149–171
Stanford B, Ifju P (2009) Aeroelastic topology optimization of membrane structures for micro air vehicles. Struct Multidiscip Optim 38(3):301–316
Svanberg K (2002) A class of globally convergent optimization methods based on conservative convex separable approximations. SIAM J on Optim 12(2):555–573
Terada K, Asai M, Yamagishi M (2003) Finite cover method for linear and non-linear analyses of heterogeneous solids. Int J Numer Methods Eng 58(9):1321–1346
Tezduyar TE, Mittal S, Ray SE, Shih R (1992) Incompressible flow computations with stabilized bilinear and linear equal-order-interpolation velocity-pressure elements. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 95:221–242
Tran AB, Yvonnet J, He QC, Toulemonde C, Sanahuja J (2011) A multiple level set approach to prevent numerical artifacts in complex microstructures with nearby inclusions within xfem. Int J Numer Methods Eng 85(11):1436–1459
Vasava P, Jalali P, Dabagh M, Kolari PJ (2012) Finite element modelling of pulsatile blood flow in idealized model of human aortic arch: Study of hypotension and hypertension. Comput Math Methods Med 861837:1748–6718
Villanueva CH, Maute K (2014) Density and level set-xfem schemes for topology optimization of 3-d structures. Comput Mech 54(1):133–150
Wang MY, Wang X, Guo D (2003) A level set method for structural topology optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 192(1–2):227–246
Wang S, Wang M (2006) Radial basis functions and level set method for structural topology optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 65(12):2060–2090
Yoon GH (2010) Topology optimization for stationary fluid–structure interaction problems using a new monolithic formulation. Int J Numer Methods Eng 82(5):591–616
Yoon GH (2014) Stress-based topology optimization method for steady-state fluidstructure interaction problems. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 278(0):499–523
Zhou M, Rozvany GIN (1991) The COC algorithm, part II: Topological, geometrical and generalized shape optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 89(1–3):309–336
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the support of the National Science Foundation under grant CMMI 1235532. The opinions and conclusions presented in this paper are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the sponsoring organization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jenkins, N., Maute, K. An immersed boundary approach for shape and topology optimization of stationary fluid-structure interaction problems. Struct Multidisc Optim 54, 1191–1208 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-016-1467-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-016-1467-5