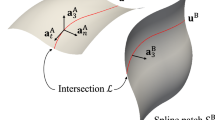
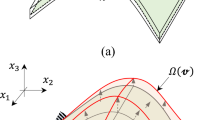
Abstract
In most of structural analyses and optimizations using the conventional isogeometric analysis, handling of trimmed or topologically complex geometries is difficult and awkward. A trimmed or topologically complex geometry is normally modeled with multiple untrimmed patches due to the tensor-product form of a Non-Uniform Rational B-Spline (NURBS) surface, and then the patches are put together for analysis. In the present work, the isogeometric shape optimization of trimmed shell structures using the information of trimmed NURBS surfaces is proposed. To treat the trimmed shell structures efficiently, two-dimensional Trimmed Surface Analysis (TSA) which is the isogeometric approach for treating a topologically complex geometry with a single patch is extended and adopted to the analysis and optimization of shell structures. Not only the coordinates of shell surface control points, but also the coordinates of trimming curve control points are chosen as design variables so that the curvatures of shell surface as well as the trimmed boundaries can be varied during the optimization. The degenerated shell based on Reissner-Mindlin theory is formulated with exact direction vectors and their analytic derivatives. Method of Moving Asymptotes (MMA) is used as the optimization algorithm, and the shape sensitivities with respect to the coordinates of surface control points and trimming curve control points are formulated with exact direction vectors and their analytic derivatives. The developed sensitivity formulations are validated by comparing with the results of Finite Difference Method (FDM), and they show excellent agreements. Numerical examples are treated to confirm the ability of the proposed approach.
























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ansola R, Canales J, Tarrago JA, Rasmussen J (2002) An integrated approach for shape and topology optimization of shell structures. Comput Struct 80(5–6):449–458
Ansola R, Canales J, Tarrago JA, Rasmussen J (2004) Combined shape and reinforcement layout optimization of shell structures. Struct Multidiscip Optim 27(4):219–227
Benson DJ, Bazilevs Y, Hsu MC, Hughes TJR (2010) Isogeometric shell analysis: the Reissner–Mindlin shell. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 199:276–289
Benson DJ, Bazilevs Y, Hsu M-C, Hughes TJR (2011) A large deformation, rotation-free, isogeometric shell. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 200(13–16):1367–1378
Benson DJ, Hartmann S, Bazilevs Y, Hsu M-C, Hughes TJR (2013) Blended isogeometric shells. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 255:133–146
Bletzinger K-U, Ramm E (2001) Structural optimization and form finding of light weight structures. Comput Struct 79:2053–2062
Bletzinger K-U, Wüchner R, Daoud F, Camprubí N (2005) Computational methods for form finding and optimization of shells and membranes. Comput Methods Form Find Optim 194(30–33):3438–3452
Botkin ME (1982) Shape optimization of plate and shell structures. AIAA J 20(2):268–273
Bouclier R, Elguedj T, Combescure A (2013a) Efficient isogeometric NURBS-based solid-shell elements: mixed formulation and B-method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 267:86–110
Bouclier R, Elguedj T, Combescure A (2013b) On the development of NURBS-based isogeometric solid shell elements: 2D problems and preliminary extension to 3D. Comput Mech 52(5):1085–1112
Breitenberger M, Bletzinger K-U, Roland W (2013) isogeometric layout optimization of shell structures using trimmed nurbs surfaces. In: 10th world congress on structural and multidisciplinary optimization. pp 1–10
Choi B, Park YH, Choi KK (2000) Shape design optimization of joining mechanism using doubly curved shell. Comput Struct 77(5):495–507
Dornisch W, Klinkel S (2014) Treatment of Reissner–Mindlin shells with kinks without the need for drilling rotation stabilization in an isogeometric framework. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 276:35–66
Dornisch W, Klinkel S, Simeon B (2013) Isogeometric Reissner–Mindlin shell analysis with exactly calculated director vectors. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 253:491–504
Echter R, Oesterle B, Bischoff M (2013) A hierarchic family of isogeometric shell finite elements. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 254:170–180
Espath LFR, Linn RV, Awruch AM (2011) Shape optimization of shell structures based on NURBS description using automatic differentiation. (March):613–636
Hassani B, Tavakkoli SM, Ghasemnejad H (2013) Simultaneous shape and topology optimization of shell structures. Struct Multidiscip Optim 48(1):221–233
Hosseini S (2013) An isogeometric solid-like shell element for nonlinear analysis. Int J Numer Methods Eng 95(3):238–256
Hosseini S, Remmers JJC, Verhoosel CV, de Borst R (2014) An isogeometric continuum shell element for non-linear analysis. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 271:1–22
Hughes TJR, Cottrell JA, Bazilevs Y (2005) Isogeometric analysis CAD, finite elements, NURBS, exact geometry and mesh refinement. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 194(39–41):4135–4195
Kang P, Youn SK (2015) Isogeometric analysis of topologically complex shell structures. Finite Elem Anal Des 99:68–81
Kegl M, Brank B (2006) Shape optimization of truss-stiffened shell structures with variable thickness. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 195(19–22):2611–2634
Kiendl J, Bletzinger K-U (2009) Isogeometric shell analysis with Kirchhoff–Love elements. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 198(49–52):3902–3914
Kiendl J, Bazilevs Y, Hsu M (2010) The bending strip method for isogeometric analysis of Kirchhoff–Love shell structures comprised of multiple patches. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 199(37–40):2403–2416
Kiendl J, Schmidt R, Wüchner R, Bletzinger K-U (2014) Isogeometric shape optimization of shells using semi-analytical sensitivity analysis and sensitivity weighting. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 274:148–167
Kim HJ, Youn SK (2012) Spline-based meshfree method. Int J Numer Methods Eng 92(9):802–834
Kim HJ, Seo YD, Youn SK (2009) Isogeometric analysis for trimmed CAD surfaces. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 198(37–40):2982–2995
Kim SY, Mechefske CK, Kim IY (2013) Optimal damping layout in a shell structure using topology optimization. J Sound Vib 332(12):2873–2883
Kim HJ, Seo YD, Youn SK (2010) Isogeometric analysis with trimming technique for problems of arbitrary complex topology. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 199(45–48):2796–2812
Lee BY (1993) Shape sensitivity formulation for axisymmetric thermal conducting solids. In: Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C: Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science. pp 209–216
Lee SJ, Bae JE, Hinton E (2000) Shell topology optimization using the layered artifcial material model. 867(February 1998):843–867
Linn RV, Espath LFR, Awruch AM (2014) Optimal shape of axisymmetric solids using NURBS and automatic differentiation. Appl Math Model 38(4):1385–1402
Maute K, Ramm E (1997) Adaptive topology optimization of shell structures. AIAA J 35(11):1767–1773
Nagy AP, IJsselmuiden ST, Abdalla MM (2013) Isogeometric design of anisotropic shells: optimal form and material distribution. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 264:145–162
Nguyen-Thanh N, Kiendl J, Nguyen-Xuan H, Wüchner R, Bletzinger KU, Bazilevs Y, Rabczuk T (2011) Rotation free isogeometric thin shell analysis using PHT-splines. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 200(47–48):3410–3424
Ramm E, Bletzinger KU, Reitinger R (1993) Shape optimization of shell structures. Rev Eur Éléments Finis 2(3):377–398
Seo YD, Kim HJ, Youn SK (2010a) Isogeometric topology optimization using trimmed spline surfaces. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 199:3270–3296
Seo YD, Kim HJ, Youn SK (2010b) Shape optimization and its extension to topological design based on isogeometric analysis. Int J Solids Struct 47(11–12):1618–1640
Stegmann J, Lund E (2004) Nonlinear topology optimization of layered shell structures. Struct Multidiscip Optim 29(5):349–360
Svanberg K (1987) The method of moving asymptotes- a new method for structural optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 24(2):359–373
Svanberg K (2002) A class of globally convergent optimization methods based on conservative convex separable approximations. SIAM J Optim 12(2):555–573
Uhm TK, Youn SK (2009) T-spline finite element method for the analysis of shell structures. Int J Numer Methods Eng 80(4):507–536
Uysal H, Gul R, Uzman U (2007) Optimum shape design of shell structures. Eng Struct 29(1):80–87
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIP) (No. 20100028680) and the NRF grant funded by the Korea government (MSIP) (No. 20110015469).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Highlights
• The methodology for isogeometric shape optimization of trimmed shell structures is presented.
• To treat trimmed shell structures effectively, two-dimensional Trimmed Surface Analysis (TSA) is adopted and appropriately extended to shell structures.
• The shell formulation and the sensitivity formulation are developed with the exact direction vectors and their analytic derivatives which are directly calculated from the NURBS surface expression.
• To adopt two-dimensional TSA to shell structures, the shell formulation and the sensitivity formulation for trimmed shell elements are developed.
• Using the gradient-based optimizer Method of Moving Asymptotes (MMA), isogeometric shape optimization of trimmed shell structures is conducted.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, P., Youn, SK. Isogeometric shape optimization of trimmed shell structures. Struct Multidisc Optim 53, 825–845 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-015-1361-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-015-1361-6