Abstract
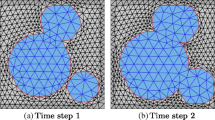
We introduce the Deformable Simplicial Complex method to topology optimization as a way to represent the interface explicitly yet being able to handle topology changes. Topology changes are handled by a series of mesh operations, which also ensures a well-formed mesh. The same mesh is therefore used for both finite element calculations and shape representation. In addition, the approach unifies shape and topology optimization in a complementary optimization strategy. The shape is optimized on the basis of the gradient-based optimization algorithm MMA whereas holes are introduced using topological derivatives. The presented method is tested on two standard minimum compliance problems which demonstrates that it is both simple to apply, robust and efficient.













Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Presented at the 10th World Congress on Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization in 2013.
CHOLMOD is the default solver for sparse symmetric positive definite linear systems in MATLAB.
References
Allaire G, Jouve F, Toader AM (2004) Structural optimization using sensitivity analysis and a level-set method. J Comput Phys 194(1):363–393
Allaire G, Dapogny C, Frey P (2011) Topology and geometry optimization of elastic structures by exact deformation of simplicial mesh. Compt Rendus Math 349(17–18):999–1003
Allaire G, Dapogny C, Frey P (2013) A mesh evolution algorithm based on the level set method for geometry and topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 1–5
Ambrosio L, Buttazzo G (1993) An optimal design problem with perimeter penalization. Calc Var 1(1):55–69
Amstutz S (2010) A penalty method for topology optimization subject to a pointwise state constraint. ESAIM: Control Optim Calc Var 16:523–544
Arnout S, Firl M, Bletzinger KU (2012) Parameter free shape and thickness optimisation considering stress response. Struct Multidiscip Optim 45(6):801–814
Bærentzen JA, Gravesen J, Anton F, Aanæs H (2012) Guide to computational geometry processing: foundations, algorithms, and methods. Springer, London
Bærentzen JA, Revall Frisvad J, Aanæs H (2013) Geometry and linear algebra (GEL) library. http://www2.imm.dtu.dk/projects/GEL/
Bendsøe MP, Sigmund O (1999) Material interpolation schemes in topology optimization. Arch Appl Mech 69(9–10):635–654
Bletzinger KU, Maute K (1997) Towards generalized shape and topology optimization. Eng Optim 29(1–4):201–216
Céa J, Garreau S, Guillaume P, Masmoudi M (2000) The shape and topological optimizations connection. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 188(4):713–726
Chen Y, Davis TA, Hager WW, Rajamanickam S (2008) Algorithm 887: cholmod, supernodal sparse cholesky factorization and upyear/downyear. ACM Trans Math Softw 35(3):22:1–22:14
Cheng S, Dey T, Shewchuk J (2012) Delaunay mesh generation. Chapman & Hall/CRC Computer and Information Science. CRC Press INC, Boca Raton
Davis TA, Hager WW, Duff IS (2013) Suite sparse. http://www.cise.ufl.edu/research/sparse/SuiteSparse/
Ding Y (1986) Shape optimization of structures: a literature survey. Comput Struct 24(6):985–1004
Eschenauer HA, Kobelev VV, Schumacher A (1994) Bubble method for topology and shape optimization of structures. Struct Multidiscip Optim 8:42–51
Feijóo RA, Novotny AA, Taroco E, Padra C (2003) The topological derivative for the poisson’s problem. Math Model Methods Appl Sci 13(12):1825–1844
Ha SH, Cho S (2008) Level set based topological shape optimization of geometrically nonlinear structures using unstructured mesh. Comput Struct 86(13–14):1447–1455
Kim DH, Lee SB, Kwank BM, Kim HG, Lowther D (2008) Smooth boundary topology optimization for electrostatic problems through the combination of shape and topological design sensitivities. IEEE Trans Magn 44(6):1002–1005
Le C, Bruns T, Tortorelli D (2011) A gradient-based, parameter-free approach to shape optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 200(9–12):985–996
Maute K, Ramm E (1995) Adaptive topology optimization. Struct Optim 10:100–112
Misztal MK, Bærentzen JA (2012) Topology adaptive interface tracking using the deformable simplicial complex. ACM Trans Graph 31(3):24
Misztal MK, Bridson R, Erleben K, Bærentzen JA, Anton F (2010) Optimization-based fluid simulation on unstructured meshes. In: 7th workshop on virtual reality interaction and physical simulation VRIPHYS, p 10
Misztal MK, Erleben K, Bargtei A, Fursund J, Christensen BB, Bærentzen JA, Bridson R (2012) Multiphase flow of immiscible fluids on unstructured moving meshes. In: Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symposium on Computer Animation, Eurographics Association, Aire-la-Ville, Switzerland, SCA ’12, pp 97–106
Mohammadi B, Pironneau FO (2001) Applied shape optimization for fluids. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Osher SJ, Fedkiw RP (2002) Level set methods and dynamic implicit surfaces, 1st edn. Springer, New York
Sokolowski J, Zochowski A (1999) On the topological derivative in shape optimization. SIAM J Control Optim 37(4):1251–1272
Sokołowski J, Zolésio J (1992) Introduction to shape optimization: shape sensitivity analysis. Springer series in computational mathematics. Springer-Verlag, New York
Svanberg K (1987) The method of moving asymptotes—a new method for structural optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 24(2):359–373
Wang M, Wang X, Guo D (2003) A level set method for structural topology optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 192(1):227–246
Xia Q, Shi T, Liu S, Wang MY (2012) A level set solution to the stress-based structural shape and topology optimization. Comput Struct 90–91:55–64
Yamasaki S, Nomura T, Kawamoto A, Sato K, Nishiwaki S (2011) A level set-based topology optimization method targeting metallic waveguide design problems. Int J Numer Methods Eng 87(9):844–868
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate the support from the Villum Foundation through the grant: “NextTop”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Christiansen, A.N., Nobel-Jørgensen, M., Aage, N. et al. Topology optimization using an explicit interface representation. Struct Multidisc Optim 49, 387–399 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-013-0983-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-013-0983-9