Abstract
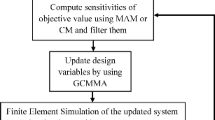
Topology optimization for nonlinear and dynamic problems is expensive because of the necessity to solve the equations of motion at every optimization iteration in order to evaluate the objective function and constraints. In this work, an iterative methodology is developed using the concept of an equivalent linear system for the topology synthesis of structures undergoing nonlinear and dynamic response, using minimal nonlinear response evaluations. The approach uses equivalent loads obtained from nonlinear dynamic analysis to perform optimization iterations, during the course of which the nonlinear and dynamic system is continuously approximated. In this process, the optimization is decoupled from the nonlinear dynamic analysis. Results are presented for various kinds of nonlinear and dynamic problems showing the effectiveness of the developed approach.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arora JS, Kim CH, Mijar AR (1999) Simplified models for automotive crash simulation and design optimization. In: Proc 3rd world congress struct multi optim. Buffalo, New York, USA, vol 1, pp 224–226
Bendsøe MP, Martin P, Kikuchi N (1988) Generating optimal topologies in structural design using a homogenization method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 71:197–224
Cho S, Kwak J (2006) Topology design optimization of geometrically nonlinear structures using meshfree method. Comput Methods Appl Mech and Eng 195:5909–5925
Choi WS, Park GJ (2002) Structural optimization using equivalent static loads at all time intervals. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 191:2077–2094
Dias JP, Pereira MS (2004) Optimization methods for crashworthiness design using multibody models. Comput Struct 82:1371–1380
Gea HC, Luo J (2001) Topology optimization of structures with geometric nonlinearities. Comput Struct 99:1977–1985
Hajela P, Lee E (1997) Topological optimization of rotorcraft subfloor structures for crashworthiness considerations. Comput Struct 64:65–76
Hamza K, Saitou K (2005) Design optimization of vehicle structures for crashworthiness using equivalent mechanism approximations. J Mech Des 127:485–492
Ignatovich CL, Diaz RA (2002) Physical surrogates in design optimization for enhanced crashworthiness. In: 9th AIAA/ISSMO symp multi anal optim. Atlanta, Georgia, USA, pp 1–8
Jog CS (2008) A dual algorithm for the topology optimization of nonlinear elastic structures. Int J Numer Methods Eng 77:502–517
Jung D, Gea HC (2004) Topology optimization of nonlinear structures. Finite Elem Anal Des 40:1417–1427
Jung D, Gea HC (2006) Design of an energy-absorbing structure using topology optimization with a multimaterial model. Struct Multidisc Optim 32:251–257
Kim YI, Park GJ (2010) Nonlinear dynamic response structural optimization using equivalent static loads. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 199:660–676
Mayer RR, Kikuchi N, Scott RA (1996) Applications of topology optimization techniques to structural crashworthiness. Int J Numer Methods Eng 39:1383–1403
Pedersen CB (2004) Crashworthiness design of transient frame structures using topology optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 193:653–678
Ramani A (2009) A pseudo-sensitivity based discrete variable approach to structural topology optimization with multiple materials. Struct Multi Optim 41:913–934
Ramani A (2011) Multi-material topology optimization with strength constraints. Struct Multi Optim 43:597–615
Shin MK, Park KJ, Park GJ (2007) Optimization of structures with nonlinear behavior using equivalent loads. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 196:1154–1167
Wang H, Dong Ma Z, Kikuchi N, Pierre C, Raju B (2004) Multi-domain multi-step topology optimization for vehicle structure crashworthiness design. In: SAE World Congr. Detroit, Michigan 2004–01–1173
Weiss D, Sonntag B, Krumenaker T, Nowottny D, Sprave J, Hipp W (2009) Geometry-based topology optimization – improving head impact performance of an engine hood. In: 7th Eur LS-DYNA Conf
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Dr. Prakash D. Mangalgiri and Dr. Narendran Balan of General Motors, India Science Lab., Bangalore, India, for reviewing the manuscript and providing important suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Motamarri, P., Ramani, A. & Kaushik, A. Structural topology synthesis with dynamics and nonlinearities using equivalent linear systems. Struct Multidisc Optim 45, 545–558 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-011-0713-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-011-0713-0