Abstract
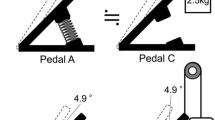
The design optimization of a pedaling mechanism for use by paraplegic persons through functional electric stimulation of paralyzed muscles is described. The objective of the optimization is to enable paraplegics to pedal by use of the limited number of leg muscles accessible to surface stimulation. This is obtained by optimization of a four-bar pedaling mechanism with no “dead points”. As a beneficial side effect of the optimization, an indication of the best stimulation pattern for the muscles is obtained. A prototype of the mechanism is built, and its attractive behavior is explained. It is concluded that the mechanism has indisputable advantages compared with conventional cranks. The next step will be experimental verification with fit people and subsequently with paraplegics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
An, K.N.; Kwak, B.M.; Chao, E.Y.; Morrey, B.F. 1984: Determination of muscle and joint forces: a new technique to solve the indeterminate problem. J. Biomech. Eng. 106, 364–367
Angeli, T.; Gföhler, M.; Eberharter, T.; Lugner, P.; Rinder, L. 2001: Optimiziation of the pedal path for cycling powered by lower extremity muscles activated by functional electrostimulation, FES. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 3, 263–268
Angeli, T.; Gföhler, M.; Eberharter, T.; Rinder, L. 1999: Tricycle for paraplegics using functional electrostimulation. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 37(supp. 2) , 326–327
Bean, J.C.; Chaffin, D.B.; Schultz, A.B. 1988: Biomechanical model calculation of muscle contraction forces: a double linear programming method. J. Biomech. 21, 59–66
Chen, J.J.; Yu, N.Y.; Huang, D.G.; Ann, B.T.; Chang, G.C. 1997: Applying fuzzy logic to control cycling movement induced by functional electrical stimulation. IEEE Trans. Rehabil. Eng. 5, 158–169
Dul, J.; Johnson, G.E.; Shiavi, R.; Townsend, M.A. 1984: Muscular synergism-II. a minimum fatigue criterion for load sharing between synergistic muscles. J. Biomech. 17, 675–684
Durfee, W.K.; Palmer, K.I. 1994: Estimation of force-activation, force-length, and force-velocity properties in isolated, electrically stimulated muscle. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 41, 205–216
Gföhler, M.; Angeli, T.; Eberharter, T.; Lugner, P. 1999: Dynamic simulation of cycling powered by lower extremity muscles activated by functional electrical stimulation. In: Högfors, C. (ed.): Proceedings of the XIIth Biomechanics Seminar (held in Gothenburg). New York, Oxford: Oxford University Press
Gföhler, M.; Angeli, T.; Eberharter, T.; Lugner, P.; Mayr, W.; Hofer, C. 2001: Test bed with force measuring crank for static and dynamic investigations on cycling by means of functional electrical stimulation. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 9, 169–180
Gföhler, M.; Lugner, P. 2000: Cycling by means of functional electrical stimulation. IEEE Trans. Rehab. Eng. TRE 8, 233–243
Glaser, R.M.; Couch, W.P.; Janssen, T.W.J.; Almeyda, J.W.; Pringle, D.D.; Collins, S.R.; Mathews, T. 1996: A development system to enhance FES leg cycle ergometer technology. RESNA ’96 9, 279–281
Haftka, R.T. 1985: Sensitivity calculations for iteratively solved problems. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 21, 1535–1546
Hill, A.V. 1938: The heat of shortening and the dynamics constants of muscle. Proc. Roy. Soc. B. 126, 136–195
Janssen, T.W.J.; Glaser, R.M.; Shuster, D.B. 1998: Clinical efficacy of electrical stimulation exercise training: Effects on health, fitness, and function. Top Spinal Cord Injury Rehabil. 3, 33–49
Malagodi, M.S.; Ferguson-Pell, M.W.; Masiello, R.D. 1993: A functional electrical stimulation exercise system designed to increase bone density in spinal cord injured individuals. IEEE Trans. Rehabil. Eng. 1, 213–219
Ragnarsson, K.T.; Pollack, S.; O’Daniel, W.; Edgar, R.; Petrofsky, J.; Nash, M.S. 1988: Clinical evaluation of computerized functional electrical stimulation after spinal cord injury: a multicenter pilot study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 69, 672–677
Rasmussen, J.; Damsgaard, M.; Christensen, S.T.; Surma, E. 2002: Design optimization with respect to ergonomic properties, structural and multidisciplibary optimization. Struct. Multidisc. Optim. 24(2), 89–97
Rasmussen, J.; Damsgaard, M.; Voigt, M. 2000: Muscle recruitment by the min/max criterion – a comparative numerical study. J. Biomech. 34, 409–415
Schutte, L.M.; Rodgers, M.M.; Zajac, F.E.; Glaser, R.M. 1993: Improving the efficacy of electrical stimulation-induced leg cycle ergometry. An analysis based on a dynamic musculoskeletal model. IEEE Trans. Rehabil. Eng. 1, 109–125
Solomonow, M. 1984: External control of the neuromuscular system. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 31, 752–763
Stein, R.B.; Momose, K.; Bobet, J. 1999: Biomechanics of human quadriceps muscles during electrical stimulation. J. Biomech. 32, 347–357
Stein, R.B.; Peckham, P.H.; Popovic, D.P. (eds.) 1992: Neural prostheses. Replacing motor function after disease or disability. In: Högfors, C. (ed.): Proceedings of the XIIth Biomechanics Seminar (held in Gothenburg). New York, Oxford: Oxford University Press
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rasmussen , J., Christensen , S., Gföhler , M. et al. Design optimization of a pedaling mechanism for paraplegics. Struct Multidisc Optim 26, 132–138 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-003-0324-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-003-0324-5