Abstract
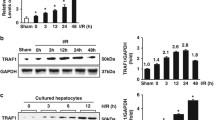
The pathway leading to cell death in clinical liver transplantation is not known. Eight liver transplant recipients and eight donors were enrolled in this study. Postoperative serum levels of alanine transferase had significantly increased in the recipients compared with those in the donors. Mild centri-lobular necrosis was observed in only liver tissues taken from the recipients. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-R1 and death receptor 5 expression levels had increased in liver tissues taken from the recipients. There were no changes in the levels of Fas/Fas ligand expression in liver tissues from either the donors or recipients. Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) expression was down-regulated in donor liver after hepatectomy and liver allograft after implantation. The results suggest that, although ischemic liver injury was not serious, due to the short ischemia time, TNF and TRAIL signals are associated with liver ischemic injury in live-donor liver transplantation but Fas signal is not




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grace P. Ischemia–reperfusion injury. Br J Surg 1994; 81:637.
Serizawa A, Nakamura S, Suzuku S, Baba S, Nakano M. Involvement of platelet-activating factor in cytokine production and neutrophil activation after hepatic ischemia/reperfusion. Hepatology 1996; 23:1656.
Mutoy Y, Nouri-Aria KT, Meager A, Alexander GJ, Eddleston AL, Williams R. Enhanced tumor necrosis factor and interleukine-1 in fulminant hepatic failure. Lancet 1998; 8602:72.
Bradham CA, Plumpe J, Manns MP, Brenner DA, Trautwein C. Mechanisms of hepatic toxicity: TNF-induced liver injury. Am Phys Soc 1998; G387.
Alex B. Lentsch. Inflammatory mechanisms and therapeutic strategies for warm hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. Hepatology 2000; 32:169.
Faubion WA, Gores GJ. Death receptors in liver biology and pathology. Hepatology 1999; 29:1.
Colletti L, Burtch G, Remick D, et al. The production of tumor necrosis factor alpha and the development of a pulmonary capillary injury following hepatic ischemia/reperfusion. Transplantation 1990; 49:268.
Colletti L, Remick D, Burtch G, Kunkel S, Strieter R, Campbel D. Role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in the pathophysiologic alterations after hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in the rat. J Clin Invest 1990; 85:1936.
Bazzoni F, Beutler B. The tumor necrosis factor ligand and receptor families. N Engl J Med 1996; 334:1717.
Ashkenazi A, Dixit V. Death receptors: signaling and modulation. Science 1998; 281:13058.
Ogasawara J, Watanabe-Fukunaga R, Adachi M, et al. Lethal effect of the anti-Fas antibody in mice. Nature 1993; 364:806.
Mochizuki K, Hayashi N, Hiramatsu N, et al. Fas antigen expression in liver tissues of patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol 1996; 24:1.
Thomas S Griffith. TRAIL: a molecule with multiple receptors and control mechanisms. Curr Opin Immunol 1998; 10:559.
Walczak H, Miller RE, Ariail K, et al. Tumoricidal activity of tumor necrosis-factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in vivo. Nat Med 1999; 5:157.
Jo M, Kim TH, Seol DW, et al. Apoptosis induced in normal human hepatocytes by tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. Nat Med 2000; 6:564.
Gores GJ, Kaufmann SH. Is TRAIL hepatotoxic? Hepatology 2001; 34:3.
Pan G, Orourke K, Chinnaiyan AM, et al. The receptor for the cytotoxic ligand TRAIL. Science 1997; 276:111.
Sheridan JP, Marsters SA, Pitti RM, Gurney A, Skubatch M, Baldwin D, Ramakrishnan L, Gray Cl, et al. Control of TRAIL-induced apoptosis by a family of signaling and decoy receptors. Science 1997; 277:818.
Chaudhary PM, Eby M, Jasmin A, Bookwalter A, Murray J, Hood L. Death receptor 5, a new member of the TNFR family, and DR4 induce FADD-dependent apoptosis and activate the NF-kappaB pathway. Immunity 1997; 7:821.
Chomczynski P, Sacchi A. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidium thiocyanate–chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 1987; 162:156.
Gao W, Bentley R, madden JF, Clavien PA. Apoptosis of sinusoidal endothelial cells is a critical mechanism of preservation injury in rat liver transplantation. Hepatology 1998; 27:1652.
Clavien PA. Sinusoidal endothelial cell injury during hepatic preservation and reperfusion. Hepatology 1998; 28:281.
Kohli V, Seizner M, Madden J, Bentley RC, Clavien PA. Endothelial cell and hepatocyte deaths occur by apoptosis after ischemia–reperfusion injury in the rat liver. Transplantation 1999; 67:1099.
Gujral J, Bucci T, Farhood A, Jaeschke H. Mechanism of cell death during warm hepatic ischemia–reperfusion in rats: apoptosis or necrosis? Hepatology 2001; 33:397.
Clavien PA. Protective effects of ischemic preconditioning for liver resection performed under inflow occlusion in humans. Ann Surg 2000; 232:155.
Rudiger HA, Clavien PA. Tumor necrosis factor α, but not Fas, mediates hepatocellular apoptosis in the murine ischemic liver. Gastroenterology 2002; 122:202.
Iwata S, Taki Y, Kawai Y, Kanai M, Takabayashi A. Mitochondrial membrane potential is reduced in peripheral natural killer cells following partial hepatectomy. Immunol Lett 2002; 82:225.
Vujanovic NL, Polimeno L, Azzarone A, et al. Changes of liver-resident NK cells during liver regeneration in rats. J Immunol 1995; 154:6324.
Matsushita T, Ando K, Kimura K, et al. IL-12 induces specific cytotoxicity against regenerating hepatocytes in vivo. Int Immunol 1999; 11:657.
Zhang HG, Xie J, Xu L, et al. Hepatic DR5 induces apoptosis and limits adenovirus gene therapy products expression in the liver. J Virol 2002; 76:5692.
Ichikawa K, Liu W, Zhao L, et al. Tumoricidal activity of a novel anti-human DR5 monoclonal antibody without hepatocyte cytotoxicity. Nat Med 2001; 7:954.
Higuchi H, Bronk SF, Taniai M, Canbay A, Gores GJ. Cholestasis increases tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis- inducing ligand (TRAIL)-R2/DR5 expression and sensitizes the liver TRAIL-mediated cytotoxicity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2002; 303:461.
Guicciardi ME, Miyoshi H, Bronk SF, Gores GJ. Cathepsin B. Knockout mice are resistant to tumor necrosis factor-a-mediated hepatocyte apoptosis and liver injury: implications for therapeutic applications. Am J Path 2001; 159:2045.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Yuka Tanaka for expert secretarial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Tashiro, H., Itamoto, T., Ohdan, H. et al. Involvement of tumor necrosis factor-α receptor 1 and tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-(TRAIL) receptor-2/DR-5, but not Fas, in graft injury in live-donor liver transplantation. Transpl Int 17, 626–633 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00147-004-0762-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00147-004-0762-z