Abstract
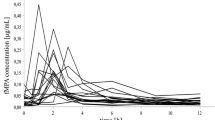
In order to allow a similar algorithm to be used for both adults and children on tacrolimus-based and mycophenolate mofetil [MMF, a pro-drug for mycophenolic acid (MPA)]-based immunosuppression, a limited sampling technique from the trough level (C0) and the levels 30 min (C0.5) and 2 h (C2) after intake was to be developed from MPA area under the time–concentration curves (AUC). We retrospectively analyzed 49 full ten-point pharmacokinetic (PK) profiles from 29 pediatric patients on MMF and tacrolimus. We used stepwise multiple regression analysis to calculate limited sampling approaches. Agreement with the AUC was tested by means of Bland and Altman analysis. The correlation between AUC and pre-dose trough concentration was r 2=0.5188 (P<0.0001) and between AUC and post-dose trough concentration r 2=0.6924 (P<0.0001). The next best correlations were with 2 h (C2, r 2=0.6711, P<0.0001), 4 h (C4, r 2=0.6411, P<0.0001), 1.5 h (C1.5, r 2=0.6344, P<0.0001), and 6 h (C6, r 2=0.6219, P<0.0001). Three-point estimates at C0, C0.5, and C2 resulted in an acceptable correlation between predicted AUC and AUC from the full profile when we used the formula AUC = 10.01391+3.94791×C0+3.24253×C0.5+1.0108×C2, Pearson’s r=0.8996, 95% confidence interval 0.8277–0.9424. However, even better results could be obtained when we used AUC = 8.217+3.163×C0+0.994×C1+1.334×C2+4.183×C4, Pearson’s r=0.9456, 95% confidence interval 0.9051–0.9691. Bland and Altman analysis revealed good agreement between AUC predicted from C0, C0.5, and C2 and AUC from the full profile, but was inferior to the four-point approach. Also, the previously reported formula derived for adults was not usable in these patients. A special formula must be used for children. The AUC of MPA can be predicted by limited sampling including C0, C0.5, and C2, while an approach using C0, C1, C2, and C4 is preferable.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jensen CW, Jordan ML, Schneck FX, et al. Pediatric renal transplantation under FK 506 immunosuppression. Transplant Proc 1991; 23:3075.
Woude FJ van der. Mycophenolate mofetil (RS 61443): nothing new under the sun or an important break-through in the field of transplantation? Nephrol Dial Transplant 1995; 10:1112.
Allison AC, Eugui EM. Immunosuppressive and other effects of mycophenolic acid and an ester prodrug, mycophenolate mofetil. Immunol Rev 1993; 136:5.
Filler G, Grygas R, Mai I, et al. Pharmacokinetics of tacrolimus (FK 506) in children and adolescents with renal transplants. Nephrol Dial Transplant 1997; 12:1668.
European Mycophenolate Mofetil Cooperative Study Group. Placebo-controlled study of mycophenolate mofetil combined with cyclosporine and corticosteroids for prevention of acute rejection. Lancet 1995; 345:1321.
Ettenger R, Menster B, Warshaw B, Potter D, Nichols A. Mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) in pediatric (ped) renal transplantation (TX): final report of the pediatric MMF study group (PMMFSG). 16th Annual Meeting of the American Society of Transplant Physicians, 1997: abstract 287.
Weber LT, Shipkova M, Lamersdorf T, et al. Pharmacokinetics of mycophenolic acid (MPA) and determinants of MPA free fraction in pediatric and adult renal transplant recipients. German Study Group on Mycophenolate Mofetil Therapy in Pediatric Renal Transplant Recipients. J Am Soc Nephrol 1998; 9:1511.
Jacqz-Aigrain E, Khan-Shaghaghi E, Baudouin V, et al. Pharmacokinetics and tolerance of mycophenolate mofetil in renal transplant children. Pediatr Nephrol 2000; 14:95.
Filler G, Lampe D, Mai I, Strehlau J, Ehrich JHH. Reduced dosing of MMF in combination with tacrolimus for steroid-resistant, vascular rejection in renal allografts. Transpl Int 1998; 11 (Suppl 1): 82.
Zucker K, Rosen A, Tsaroucha A, et al. Unexpected augmentation of mycophenolic acid pharmacokinetics in renal transplant patients receiving tacrolimus and mycophenolate mofetil in combination therapy, and analogous in vitro findings. Transpl Immunol 1997; 5:225.
Cox VC, Ensom MH. Mycophenolate mofetil for solid organ transplantation: does the evidence support the need for clinical pharmacokinetic monitoring? Ther Drug Monit 2003; 25:137.
Shaw LM, Kaplan B, Kaufman D. Toxic effects of immunosuppressive drugs: mechanisms and strategies for controlling them. Clin Chem 1996:42; 1316.
Filler G, Mai I. Limited sampling strategy for mycophenolic acid area under the curve. Ther Drug Monit 2000; 22:169.
Filler G, Feber J, Lepage N, Weiler G, Mai I. Universal approach to pharmacokinetic monitoring of immunosuppressive agents in children. Pediatr Transplant 2002; 6:411.
Shaw LM, Holt DW, Keown P, Venkataramanan R, Yatscoff RW. Current opinions on therapeutic drug monitoring of immunosuppressive drugs. Clin Ther 1999; 10:1632.
Schütz E, Shipkova M, Armstrong VW, et al. Therapeutic drug monitoring of mycophenolic acid: comparison of HPLC and immunoassay reveals new MPA metabolites. Transplant Proc 1998; 30:1185.
Krouwer JS, Monti KL. A simple, graphical method to evaluate laboratory assays. Eur J Clin Chem Clin Biochem 1995; 33:525.
Pawinski T, Hale M, Korecka M, Fitzsimmons WE, Shaw LM. Limited sampling strategy for the estimation of mycophenolic acid area under the curve in adult renal transplant patients treated with concomitant tacrolimus. Clin Chem 2002; 48:1497.
Langman LJ, LeGatt DF, Halloran PF, Yatscoff RW. Pharmacodynamic assessment of mycophenolic acid-induced immunosuppression in renal transplant recipients. Transplantation 1996; 62:666.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Filler, G. Abbreviated mycophenolic acid AUC from C0, C1, C2, and C4 is preferable in children after renal transplantation on mycophenolate mofetil and tacrolimus therapy. Transpl Int 17, 120–125 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00147-003-0678-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00147-003-0678-z