Abstract.
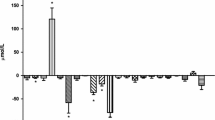
The aim of this study was to investigate the impact of orthotopic liver transplantation (OLT) on plasma levels and splanchnic turnover of key amino acids for muscular (branched-chain amino acids: BCAAs) and hepatic metabolism (aromatic amino acids (AAAs) and methionine) in 48 patients with cirrhosis, 14 patients after OLT, and 46 controls. Also, hepatic amino-acid supply and resting energy expenditure were measured. BCAA levels (no hepatic uptake) decreased in cirrhosis (P<0.001) and were improved, although not normalized, after OLT (P<0.001). AAA and methionine levels were raised in cirrhosis (P<0.001) and normalized after OLT (P<0.001). Hepatic supply of these amino acids increased in patients graded Child B and C and decreased significantly after OLT. Splanchnic uptake of AAAs and methionine increased significantly in Child-B and decreased in Child-C patients. After OLT, splanchnic extraction of AAAs and methionine was as in Child A. Circulating AAAs and methionine correlated with indocyanine-green half-life (r=0.71, P<0.001) and resting energy expenditure (r=0.50, P<0.001), indicating that levels of circulating AAAs and methionine in cirrhosis are determined by hepatic and extra-hepatic metabolic factors. This study demonstrates persistent changes in muscular metabolism of BCAAs after OLT, while the hepatic amino-acid metabolism is normalized due to (1) a significant reduction in the rate of peripheral proteolysis, and (2) improved liver function compared with that in patients with cirrhosis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ansley JD, Isaacs JW, Rikkers LF, Kutner MH, Nordlinger BM, Rudman D (1978) Quantitative tests of nitrogen metabolism in cirrhosis: relation to other manifestations of liver disease. Gastroenterology 75:570–579
Bahr MJ, Böker KHW, Horn W, Günzler V, Manns MP (1997) Serum laminine P1 levels do not reflect critically elevated portal pressure in patients with liver cirrhosis. Hepatogastroenterology 44:1200–1205
Bugianesi E, Bianchi GP, Marchi E, Zoli M, Marchesini G (1990) Methionine plasma clearance in cirrhosis. J Hepatol 10 [Suppl 1]:S4
Clements D, West R, Elias E (1987) Comparison of bolus and infusion methods for estimating hepatic blood flow in patients with liver disease using indocyanine green. J Hepatol 5:282–287
Clowes GHAJ, McDermott WV, Williams LF, Loda M, Menzoian JO, Pearl R (1984) Amino acid clearance and prognosis in surgical patients with cirrhosis. Surgery 96:675–684
Fath JJ, Ascher NL, Konstantinides FN, Bloomer J, Sharp H, Najarian JS, Cerra FB (1984) Metabolism during hepatic transplantation: indicators of allograft function. Surgery 96:664–674
Felig P (1975) Amino acid metabolism in man. Annu Rev Biochem 44:933–955
Felig P, Wahren J (1971) Amino acid metabolism in exercising man. J Clin Invest 50:2703–2714
Francavilla A, Polimeno L, van Thiel DH, Todo S, Kam I, Lynch S, Starzl TE (1987) Pancreatic hormones and amino acid levels following liver transplantation. Hepatology 7:918–924
Gelfand RA, Glickman MG, Jacob R, Sherwin RS, DeFronzo RA (1986) Removal of infused amino acids by splanchnic and leg tissue in humans. Am J Physiol 250:E407–E413
Goto T, Asano T, Morita T, Sakamoto K, Kenmochi T, Nakagohri T, Ochiai T, Isono K (1989) Experimental studies of hepatic clearance rates of amino acids as an initial function test of the liver graft. Transplant Proc 21:2305–2307
Hagenfeldt L, Eriksson LS, Wahren J (1983) Amino acids in liver disease. Proc Nutr Soc 42:497–506
Häussinger D, Gerok W (1986) Metabolism of amino acids and ammonia. In: Thurman RG, Kauffman FC, Jungermann K (eds) Regulation of hepatic metabolism. Plenum Press, New York, pp 27–35
Heberer M, Talke H, Maier KP, Gerok W (1980) Metabolism of phenylalanine in liver disease. Klin Wochenschr 58:1189–1196
Hellerstein MK, Munro HN (1988) Interaction of liver and muscle in the regulation of metabolism in response to nutritional and other factors. In: Arias IM, Jakoby WB, Popper H, Shafritz DA (eds) The liver: biology and pathobiology. Raven Press, New York, pp 965–984
Herrmann R, McIntyre N (1991) Amino-acid metabolism, urea production, and pH regulation. In: McIntyre N, Benhamou JP, Bircher J, Rizetto M, Rodes J (eds) Textbook of clinical hepatology. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 157–174
Hoffmann JC, Bahr MJ, Tietge UJF, Braunstein J, Bayer B, Böker KHW, Manns MP (1996) Detection of a soluble form of the adhesion receptor lymphocyte function-associated antigen (LFA-3) in patients with chronic liver disease. J Hepatol 25:465–473
Iber FL, Rosen H, Levenson SM, Chalmers TC (1957) The plasma amino acids in patients with liver failure. J Lab Clin Med 50:417–425
Jagenburg R, Olsson R, Regårdh C-G, Rodjer S (1977) Kinetics of intravenous administered l-phenylalanine in patients with cirrhosis of the liver. Clin Chim Acta 78:453–463
Jones EA, Gammal SH (1988) Hepatic encephalopathy. In: Arias IM, Jakoby WB, Popper H, Shafritz DA (eds) The liver: biology and pathobiology. Raven Press, New York, pp 985–1006
Lautz HU, Selberg O, Körber J, Bürger M, Müller MJ (1992) Protein-calorie malnutrition in liver cirrhosis. Clin Investig 70:478–486
Levine RJ, Conn HO (1967) Tyrosine metabolism in patients with liver disease. J Clin Invest 46:2012–2020
Limberg B, Kommerell B (1984) Correction of altered plasma amino acid pattern in cirrhosis of the liver by somatostatin. Gut 25:1291–1295
Luzi L, Perseghin G, Regalia E, Sereni LP, Battezzati A, Baratti D, Bianchi E, Terruzzi I, Hilden H, Groop LC, Pulvirenti A, Taskinen M-R, Gennari L, Mazzaferro V (1997) Metabolic effects of liver transplantation in cirrhotic patients. J Clin Invest 99:692–700
McCullough AJ, Tavill AS (1991) Disordered energy and protein metabolism in liver disease. Semin Liver Dis 11:265–277
Merli M, Riggio O, Romiti A, Ariosto F, Mango L, Pinto G, Savioli M, Capacaccia L (1990) Basal energy production rate and substrate use in stable cirrhotic patients. Hepatology 12:106–112
Montanari A, Simoni I, Vallisa D, Trifirò A, Colla R, Abbiati R, Borghi L, Novarini A (1988) Free amino acids in plasma and skeletal muscle of patients with liver cirrhosis. Hepatology 8:1034–1039
Morgan MY, Marshall AW, Milsom JP, Sherlock S (1982) Plasma amino acid patterns in liver disease. Gut 23:362–370
Müller MJ, Böker KHW, Selberg O (1994) Metabolism of energy-yielding substrates in patients with liver cirrhosis. Clin Investig 72:568–579
Müller MJ, Böker KHW, Selberg O (1994) Are patients with liver cirrhosis hypermetabolic? Clin Nutr 13:131–144
Müller MJ, Böttcher J, Selberg O, Weselmann S, Böker KHW, Schwarze M, von zur Mühlen A, Manns MP (1999) Hypermetabolism in clinically stable patients with liver cirrhosis. Am J Clin Nutr 69:1194–1201
Munoz SJ, Jarrell BE, Westerberg S, Miller L, Moritz MJ, Maddrey WC (1993) Serum amino acids following human orthotopic liver transplantation. Transplant Proc 25:1779–1782
O'Keefe SJD, Abraham R, El-Zayadi A, Marshall W, Davis M, Williams R (1981) Increased plasma tyrosine concentrations in patients with cirrhosis and fulminant hepatic failure associated with increased plasma tyrosine flux and reduced hepatic oxidation capacity. Gastroenterology 81:1017–1024
Pearl RH, Clowes GHAJ, Bosari S, McDermott WV, Mentoian JO, Love W, Jenkins RL (1987) Amino acid clearance in cirrhosis. Arch Surg 122:468–473
Pugh RNH, Murray-Lyon IM, Dawson JL, Pietroni MC, Williams R (1973) Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg 60:646–649
Record CO, Buxton B, Chase RA, Curzon G, Murray-Lyon IM, Williams R (1976) Plasma and brain amino acids in fulminant hepatic failure and their relationship to hepatic encephalopathy. Eur J Clin Invest 6:386–394
Reilly JJJ, Halow GM, Gerhardt AL, Ritter PS, Gavaler JS, van Thiel D (1985) Plasma amino acids in liver transplantation: correlation with clinical outcome. Surgery 97:263–270
Svensson KL, Persson H, Henriksson BA, Karlberg I, Sonander H, Lundholm K, Stenqvist O, Schersten T (1989) Whole body gas exchange: amino acid and lactate clearance as indicators of initial and early allograft viability in liver transplantation. Surgery 105:472–480
Tietge UJF, Böker KHW, Bahr MJ, Weinberg S, Pichlmayr R, Schmidt HH-J, Manns MP (1998) Lipid parameters predicting liver function in patients with cirrhosis and after liver transplantation. Hepatogastroenterology 45:2255–2260
Tribble DL, Jones DP, Ardehali A, Feeley RM, Rudman D (1989) Hypercysteinemia and delayed sulfur excretion in cirrhotics after oral cystein loads. Am J Clin Nutr 50:1401–1406
Vilstrup H, Bucher D, Krog B, Damgard SE (1982) Elimination of infused amino acids from plasma of control subjects and of patients with cirrhosis of the liver. Eur J Clin Invest 12:197–201
Wu C, Bollmann JL, Butt HR (1955) Changes in free amino acids in the plasma during hepatic coma. J Clin Invest 34:845–849
Zoli M, Bianchi GP, Marzocchi A, Marrozzini C, Capelli M, Mattioli L, Checchia GA, Cassarani S, Dondi C, Marchesini G (1984) Splanchnic, peripheral and renal exchange of amino acids in cirrhotic patients with portal hypertension. In: Kleinberger G, Ferenci P, Riederer P, Thaler H (eds) Advances in hepatic encephalopathy and urea cycle diseases. Karger, Basle, pp 538–544
Acknowledgements.
This study was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SFB 265, project C4). We are indebted to Sigrid Ohlendorf and Brigitte Markfeld for expert technical assistance. We wish to thank Prof. A. Mügge, Prof. I. Amende, and the staff of the diagnostic coronary angiography unit of the Hanover Medical School for the opportunity to investigate the control patients for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Tietge, U.J.F., Bahr, M.J., Manns, M.P. et al. Hepatic amino-acid metabolism in liver cirrhosis and in the long-term course after liver transplantation. Transpl Int 16, 1–8 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00147-002-0484-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00147-002-0484-z