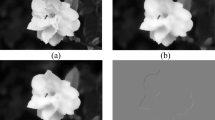
Abstract
Local motion deblurring is a highly challenging problem as both the blurred region and the blur kernel are unknown. Most existing methods for local deblurring require a specialized hardware, an alpha matte, or user annotation of the blurred region. In this paper, an automatic method is proposed for local motion deblurring in which a segmentation step is performed to extract the blurred region. Then, for blind deblurring, i.e., simultaneously estimating both the blur kernel and the latent image, an optimization problem in the form of maximum-a-posteriori (MAP) is introduced. An effective image prior is used in the MAP based on both the first- and second-order gradients of the image. This prior assists to well reconstruct salient edges, providing reliable edge information for kernel estimation, in the intermediate latent image. We examined the proposed method for both global and local deblurring. The efficiency of the proposed method for global deblurring is demonstrated by performing several quantitative and qualitative comparisons with the state-of-the-art methods, on both a benchmark image dataset and real-world motion blurred images. In addition, in order to demonstrate the efficiency in local motion deblurring, the proposed method is examined to deblur some real-world locally linear motion blurred images. The qualitative results show the efficiency of the proposed method for local deblurring at various blur levels.













Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
A pixon is a region that is made up of a set of connected pixels with associated properties such as color, intensity or texture.
References
Cho, S., Lee, S.: Fast motion deblurring. In: ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG), vol. 28. ACM, New York (2009)
Fergus, R., Singh, B., Hertzmann, A., Roweis, S.T., Freeman, W.T.: Removing camera shake from a single photograph. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 25(3), 787–794 (2006)
Krishnan, D., Tay, T., Fergus, R.: Blind deconvolution using a normalized sparsity measure. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2011 IEEE Conference on IEEE, 2011, pp. 233–240
Shan, Q., Jia, J., Agarwala, A.: High-quality motion deblurring from a single image. In: ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG), vol. 27, ACM, New York (2008)
Sun, L., Cho, S., Wang, J., Hays, J.: Edge-based blur kernel estimation using patch priors. In: 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computational Photography (ICCP), pp. 1–8 (2013)
Xu, L., Jia, J.: Two-Phase Kernel Estimation for Robust Motion Deblurring. Springer, New York (2010)
Xu, L., Zheng, S., Jia, J.: Unnatural l0 sparse representation for natural image deblurring. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1107–1114 (2013)
Joshi, N., Szeliski, R., Kriegman, D.J.: PSF estimation using sharp edge prediction. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2008. IEEE Conference on CVPR 2008, pp. 1–8 (2008)
Cho, T.S., Paris, S., Horn, B.K., Freeman, W.T.: Blur kernel estimation using the radon transform. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2011 IEEE Conference on IEEE, pp. 241–248 (2011)
Pan, J., Liu, R., Su, Z., Liu, G.: Motion blur kernel estimation via salient edges and low rank prior. In: 2014 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), IEEE, pp. 1–6 (2014)
Pan, J., Liu, R., Su, Z., Gu, X.: Kernel estimation from salient structure for robust motion deblurring. Sign. Process. Image Commun. 28(9), 1156–1170 (2013)
Pan, J., Su, Z.: Fast-regularized kernel estimation for robust motion deblurring. IEEE Sign. Process. Lett. 20(9), 841–844 (2013)
Cai, J.-F., Ji, H., Liu, C., Shen, Z.: Blind motion deblurring from a single image using sparse approximation. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2009. IEEE Conference on CVPR 2009, IEEE, pp. 104–111
Chen, J., Yuan, L., Tang, C.-K., Quan, L.: Robust dual motion deblurring. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2008. IEEE Conference on CVPR 2008, IEEE, pp. 1–8
H. Hong, I. K. Park, Single image motion deblurring using anisotropic regularization. In: 2010 17th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), IEEE, pp. 1149–1152
Li, W., Zhang, J., Dai, Q.-H.: Robust blind motion deblurring using near-infrared flash image. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 24(8), 1394–1413 (2013)
Dai, S., Wu, Y.: Removing partial blur in a single image. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2009. IEEE Conference on CVPR 2009, IEEE, pp. 2544–2551
Martinello, M., Favaro, P.: Fragmented aperture imaging for motion and defocus deblurring. In: 2011 18th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), IEEE, pp. 3413–3416
Levin, A.: Blind motion deblurring using image statistics. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2006, pp. 841–848
Couzinie-Devy, F., Sun, J., Alahari, K., Ponce, J.: Learning to estimate and remove non-uniform image blur. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1075–1082
Raskar, R., Agrawal, A., Tumblin, J.: Coded exposure photography: motion deblurring using fluttered shutter. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 25(3), 795–804 (2006)
Levin, A., Fergus, R., Durand, F., Freeman, W.T. : Image and depth from a conventional camera with a coded aperture. In: ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG), Vol. 26, p. 70, ACM (2007)
Tai, Y.-W., Kong, N., Lin, S., Shin, S.Y.: Coded exposure imaging for projective motion deblurring. In: 2010 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), IEEE, pp. 2408–2415
Tai, Y.-W., Du, H., Brown, M.S., Lin, S.: Correction of spatially varying image and video motion blur using a hybrid camera. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 32(6), 1012–1028 (2010)
Shan, Q., Xiong, W., Jia, J.:Rotational motion deblurring of a rigid object from a single image. In: ICCV 2007. IEEE 11th International Conference on Computer Vision, 2007, IEEE, pp. 1–8
Kim, T.H., Lee, K.M.: Segmentation-free dynamic scene deblurring. In: 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), IEEE, pp. 2766–2773
Kim, T., Ahn, B., Lee, K.: Dynamic scene deblurring. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3160–3167 (2013)
Hyun Kim, T., Mu Lee, K.: Generalized video deblurring for dynamic scenes. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5426–5434 (2015)
Javaran, T.A., Hassanpour, H., Abolghasemi, V.: A noise-immune no-reference metric for estimating blurriness value of an image. Signal Process Image Commun (2016). doi:10.1016/j.image.2016.06.009
Levin, A., Lischinski, D., Weiss, Y.: A closed-form solution to natural image matting. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 30(2), 228–242 (2008)
Pan, J., Hu, Z., Su, Z., Lee, H.-Y., Yang, M.-H.: Soft-segmentation guided object motion deblurring. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2016. IEEE Conference on CVPR 2016
Javaran, T. A., Hassanpour, H., Abolghasemi, V.: Automatic estimation and segmentation of partial blur in natural images. Vis. Comput. 33, 151 (2017). doi:10.1007/s00371-015-1166-z
Levin, A., Weiss, Y., Durand, F., Freeman, W.T.: Understanding blind deconvolution algorithms. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 33(12), 2354–2367 (2011)
Joshi, N., Zitnick, C. L., Szeliski, R., Kriegman, D. J. Image deblurring and denoising using color priors. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2009. IEEE Conference on CVPR 2009, IEEE, pp. 1550–1557 (2009)
Osher, S., Rudin, L.I.: Feature-oriented image enhancement using shock filters. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 27(4), 919–940 (1990)
S. Roth, M. J. Black, Fields of experts: A framework for learning image priors. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2005. IEEE Computer Society Conference on CVPR 2005, vol. 2, IEEE, pp. 860–867 (2005)
Y. Weiss, W. T. Freeman, What makes a good model of natural images?. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2007. IEEE Conference on CVPR’07, IEEE, pp. 1–8 (2007)
Levin, A., Fergus, R., Durand, F., Freeman, W.T.: Deconvolution Using Natural Image Priors. Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (2007)
A. Levin, Y. Weiss, F. Durand, W. T. Freeman, Understanding and evaluating blind deconvolution algorithms. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2009. IEEE Conference on CVPR 2009, IEEE, pp. 1964–1971 (2009)
Geman, D., Reynolds, G.: Constrained restoration and the recovery of discontinuities. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 3, 367–383 (1992)
Geman, D., Yang, C.: Nonlinear image recovery with half-quadratic regularization. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 4(7), 932–946 (1995)
Wang, Y., Yang, J., Yin, W., Zhang, Y.: A new alternating minimization algorithm for total variation image reconstruction. SIAM J. Imag. Sci. 1(3), 248–272 (2008)
D. Krishnan, R. Fergus, Fast image deconvolution using hyper-laplacian priors. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 1033–1041 (2009)
Javaran, T.A., Hassanpour, H., Abolghasemi, V.: Non-blind deconvolution for image deblurring using a regularization based on re-blurring process. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 154, 16–34 (2017)
Shao, W.-Z., Li, H.-B., Elad, M.: Bi-l 0-l 2-norm regularization for blind motion deblurring. J. Vis. Commun. Image Rep. 33, 42–59 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Askari Javaran, T., Hassanpour, H. & Abolghasemi, V. Local motion deblurring using an effective image prior based on both the first- and second-order gradients. Machine Vision and Applications 28, 431–444 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-017-0824-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-017-0824-8