Abstract
Objective
To determine the association between organ dysfunction and hyperglycemia in critically ill children receiving intravenous insulin.
Design
Retrospective chart review (cohort study).
Setting
Pediatric intensive care unit in a university hospital.
Patients
n = 110 patients; inclusion criteria: ICU hospitalization from May 2005 to May 2006; insulin drip to manage hyperglycemia. Exclusion criteria: insulin drip <48 h; diabetic patients.
Measurements
Duration of hyperglycemia: sum of hours of hyperglycemia (≥126 mg/dl). Hypoglycemia (blood glucose <40 mg/dl). Organ dysfunction was determined per International Pediatric Sepsis Consensus Conference criteria. Multiple logistic regression models determined the association between ≥3 compared to <3 organ dysfunctions and hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia, and mortality, after adjustment for confounding variables (age, gender, PRISM score, vasopressors, steroids).
Main results
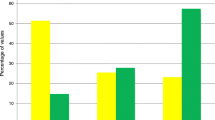
Organ dysfunction ≥3 compared to <3 after adjustment for confounders was associated with intermittent hyperglycemia of ≥24 h (OR 6.1, CI 1.8–21.2; p = 0.004). Hyperglycemia trended towards significance with mortality [3.2 (CI 0.9–11.6, p = 0.079)]. Hypoglycemia, after adjusting for the above, was not associated with mortality.
Conclusions
Organ dysfunction (≥3 versus <3) was significantly associated with hyperglycemia for ≥24 h and hypoglycemia. Hyperglycemia trended toward significance with mortality in critically ill children. There was no association between hypoglycemia and mortality.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Van den Berghe G, Wouters P, Weekers F, Verwaest C, Bruyninckx F, Schetz M, Vlasselaers D, Ferdinande P, Lauwers P, Bouillon R (2001) Intensive insulin therapy in the critically ill patients. N Engl J Med 345:1359–1367
Hansen TK, Thiel S, Wouters PJ, Christiansen JS, Van den Berghe G (2003) Intensive insulin therapy exerts antiinflammatory effects in critically ill patients and counteracts the adverse effect of low mannose-binding lectin levels. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:1082–1088
Krinsley JS (2004) Effect of an intensive glucose management protocol on the mortality of critically ill adult patients. Mayo Clin Proc 79:992–1000
Meynaar IA, Dawson L, Tangkau PL, Salm EF, Rijks L (2007) Introduction and evaluation of a computerised insulin protocol. Intensive Care Med 33:591–596
Srinivasan V, Spinella PC, Drott HR, Roth CL, Helfaer MA, Nadkarni V (2004) Association of timing, duration, and intensity of hyperglycemia with intensive care unit mortality in critically ill children. Pediatr Crit Care Med 5:329–336
Faustino EV, Apkon M (2005) Persistent hyperglycemia in critically ill children. J Pediatr 146:30–34
Chiaretti A, De Benedictis R, Langer A, Di Rocco C, Bizzarri C, Iannelli A, Polidori G (1998) Prognostic implications of hyperglycaemia in paediatric head injury. Child’s Nervous Syst 14:455–459
Hall NJ, Peters M, Eaton S, Pierro A (2004) Hyperglycemia is associated with increased morbidity and mortality rates in neonates with necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr Surg 39:898–901; discussion 898–901
Cochran A, Scaife ER, Hansen KW, Downey EC (2003) Hyperglycemia and outcomes from pediatric traumatic brain injury. J Trauma 55:1035–1038
Rayfield EJ, Ault MJ, Keusch GT, Brothers MJ, Nechemias C, Smith H (1982) Infection and diabetes: the case for glucose control. Am J Med 72:439–450
Zochodne DW, Bolton CF, Wells G, Gilbert JJ, Hahn AF, Brown JD, Sibbald WA (1987) Critical illness polyneuropathy A complication of sepsis and multiple organ failure. Brain 110:819–841
Bolton CF (1996) Sepsis and the systemic inflammatory response syndrome: neuromuscular manifestations. Crit Care Med 24:1408–1416
Fietsam R Jr, Bassett J, Glover JL (1991) Complications of coronary artery surgery in diabetic patients. Am Surg 57:551–557
Allen HF, Rake A, Roy M, Brenner D, McKiernan CA (2008) Prospective detection of hyperglycemia in critically ill children using continuous glucose monitoring. Pediatr Crit Care Med 9:153–158
Yung M, Wilkins B, Norton L, Slater A, AaNZICS PaediatricStudyGroup (2008) Glucose control, organ failure, and mortality in pediatric intensive care. Pediatr Crit Care Med 9:147–152
Rolih CA, Ober KP (1995) The endocrine response to critical illness. Med Clin North Am 79:211–224
Kralisch S, Sommer G, Deckert CM, Linke A, Bluher M, Stumvoll M, Fasshauer M (2007) Adipokines in diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. Minerva Endocrinol 32:161–171
Preissig CM, Hansen I, Roerig PL, Rigby MR (2008) A protocolized approach to identify and manage hyperglycemia in a pediatric critical care unit. Pediatr Crit Care Med 9:581–588
Hoxworth JM, Xu K, Zhou Y, Lust WD, LaManna JC (1999) Cerebral metabolic profile, selective neuron loss, and survival of acute and chronic hyperglycemic rats following cardiac arrest and resuscitation. Brain Res 821:467–479
Siesjo BK, Katsura KI, Kristian T, Li PA, Siesjo P (1996) Molecular mechanisms of acidosis-mediated damage. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien) 66:8–14
Anderson RE, Tan WK, Martin HS, Meyer FB (1999) Effects of glucose and PaO2 modulation on cortical intracellular acidosis, NADH redox state, and infarction in the ischemic penumbra. Stroke 30:160–170
Klein GW, Hojsak JM, Rapaport R (2007) Hyperglycemia in the pediatric intensive care unit. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 10:187–192
Rosenbaum M, Nonas C, Horlick M, Fennoy I, Vargas I, Schachner H, Kringas P, Stanton K, Weil R (2004) Beta-cell function and insulin sensitivity in early adolescence: association with body fatness and family history of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:5469–5476
Cordingley JJ, Vlasselaers D, Dormand NC, Wouters PJ, Squire SD, Chassin LJ, Wilinska ME, Morgan CJ, Hovorka R, Van den Berghe G (2009) Intensive insulin therapy: enhanced model predictive control algorithm versus standard care. Intensive Care Med 35:123–128
Vogelzang M, Loef BG, Regtien JG, van der Horst IC, van Assen H, Zijlstra F, Nijsten MW (2008) Computer-assisted glucose control in critically ill patients. Intensive Care Med 34:1421–1427
Brunkhorst FM, Engel C, Bloos F, Meier-Hellmann A, Ragaller M, Weiler N, Moerer O, Gruendling M, Oppert M, Grond S, Olthoff D, Jaschinski U, John S, Rossaint R, Welte T, Schaefer M, Kern P, Kuhnt E, Kiehntopf M, Hartog C, Natanson C, Loeffler M, Reinhart K (2008) Intensive insulin therapy and pentastarch resuscitation in severe sepsis. N Engl J Med 358:125–139
Oksanen T, Skrifvars MB, Varpula T, Kuitunen A, Pettila V, Nurmi J, Castren M (2007) Strict versus moderate glucose control after resuscitation from ventricular fibrillation. Intensive Care Med 33:2093–2100
Nguyen N, Ching K, Fraser R, Chapman M, Holloway R (2007) The relationship between blood glucose control and intolerance to enteral feeding during critical illness. Intensive Care Med 33:2085–2092
Cryer PE (2004) Diverse causes of hypoglycemia-associated autonomic failure in diabetes. N Engl J Med 350:2272–2279
Mitchell I, Finfer S, Bellomo R, Higlett T (2006) Management of blood glucose in the critically ill in Australia and New Zealand: a practice survey and inception cohort study. Intensive Care Med 32:867–874
Ligtenberg JJ, Meijering S, Stienstra Y, van der Horst IC, Vogelzang M, Nijsten MW, Tulleken JE, Zijlstra JG (2006) Mean glucose level is not an independent risk factor for mortality in mixed ICU patients. Intensive Care Med 32:435–438
Honiden S, Schultz A, Im SA, Nierman DM, Gong MN (2008) Early versus late intravenous insulin administration in critically ill patients. Intensive Care Med 34:881–887
Vlasselaers D, Milants I, Desmet L, Wouters PJ, Vanhorebeek I, van den Heuvel I, Mesotten D, Casaer MP, Meyfroidt G, Ingels C, Muller J, Van Cromphaut S, Schetz M, Van den Berghe G (2009) Intensive insulin therapy for patients in paediatric intensive care: a prospective, randomised controlled study. Lancet 373:547–556
Finfer S, Chittock DR, Su SY, Blair D, Foster D, Dhingra V, Bellomo R, Cook D, Dodek P, Henderson WR, Hebert PC, Heritier S, Heyland DK, McArthur C, McDonald E, Mitchell I, Myburgh JA, Norton R, Potter J, Robinson BG, Ronco JJ (2009) Intensive versus conventional glucose control in critically ill patients. N Engl J Med 360:1283–1297
Schultz MJ, de Graaff MJ, Kuiper MA, Spronk PE (2008) The new Surviving Sepsis Campaign recommendations on glucose control should be reconsidered. Intensive Care Med 34:779–780; author reply 781–772
Wintergerst KA, Buckingham B, Gandrud L, Wong BJ, Kache S, Wilson DM (2006) Association of hypoglycemia, hyperglycemia, and glucose variability with morbidity and death in the pediatric intensive care unit. Pediatrics 118:173–179
Yates AR, Dyke PC 2nd, Taeed R, Hoffman TM, Hayes J, Feltes TF, Cua CL (2006) Hyperglycemia is a marker for poor outcome in the postoperative pediatric cardiac patient. Pediatr Crit Care Med 7:351–355
Weber-Carstens S, Deja M, Bercker S, Dimroth A, Ahlers O, Kaisers U, Keh D (2007) Impact of bolus application of low-dose hydrocortisone on glycemic control in septic shock patients. Intensive Care Med 33:730–733
Schoefield WN (1985) Predicting basal metabolic rate, new standards and review of previous work. Human Nutrition. Hum Nutr Clin Nutr 39c (suppl 5–41)
Morris AH, Orme J Jr, Truwit JD, Steingrub J, Grissom C, Lee KH, Li GL, Thompson BT, Brower R, Tidswell M, Bernard GR, Sorenson D, Sward K, Zheng H, Schoenfeld D, Warner H (2008) A replicable method for blood glucose control in critically Ill patients. Crit Care Med 36:1787–1795
Morris AH, Orme JF, Rocha BH, Holman J, Clemmer T, Nelson N, Allen J, Jephson A, Sorenson DK, Sward K, Warner H (2008) An electronic protocol for translation of research results to clinical practice: a preliminary report. J Diabetes Sci Technol 2:802–808
Thompson BT, Orme JF, Zheng H, Luckett P, Truwit JD, Wilsson DF, Hite RD, Brower RG, Bernard GR, Curley MAQ, Steingrub JS, Sorenson DK, Sward K, Hirshberg E, Morris AH RCCCRI (2008) Multicenter validation of a computer-based clinical decision support tool for glucose control in adult and pediatric intensive care units. J Diabetes Sci Technol 2:357–368
Pachler C, Plank J, Weinhandl H, Chassin LJ, Wilinska ME, Kulnik R, Kaufmann P, Smolle KH, Pilger E, Pieber TR, Ellmerer M, Hovorka R (2008) Tight glycaemic control by an automated algorithm with time-variant sampling in medical ICU patients. Intensive Care Med 34:1224–1230
Khatib OMN (2006) Guidelines for the prevention, management and care of diabetes mellitus. In: Khatib OMN (ed) EMRO Technical Publications Series. World Health Organization, Geneva, pp 1–82
Goldstein B, Giroir B, Randolph A, International Consensus Conference on Pediatric Sepsis (2005) International pediatric sepsis consensus conference: definitions for sepsis and organ dysfunction in pediatrics. Pediatr Crit Care Med 6:2–8
De León AL, Romero-Gutiérrez G, Valenzuela CA, González-Bravo FE (2005) Simplified PRISM III score and outcome in the pediatric intensive care unit. Pediatr Int 47:80–83
Pollack MM, Patel KM, Ruttimann UE (1996) PRISM III: an updated pediatric risk of mortality score. Crit Care Med 24:743–752
Leteurtre S, Duhamel A, Grandbastien B, Lacroix J, Leclerc F (2006) Paediatric logistic organ dysfunction (PELOD) score. Lancet 367:897; author reply 900–892
Leteurtre S, Martinot A, Duhamel A, Proulx F, Grandbastien B, Cotting J, Gottesman R, Joffe A, Pfenninger J, Lacroix J, Leclerc F (2006) Validation of the paediatric logistic organ dysfunction (PELOD) score: prospective, observational, multicentre study. Lancet 362:192–197
Branco RG, Garcia PC, Piva JP, Casartelli CH, Seibel V, Tasker RC (2005) Glucose level and risk of mortality in pediatric septic shock. Pediatr Crit Care Med 6:470–472
Yendamuri S, Fulda GJ, Tinkoff GH (2003) Admission hyperglycemia as a prognostic indicator in trauma. J Trauma 55:33–38
Rovlias A, Kotsou S (2000) The influence of hyperglycemia on neurological outcome in patients with severe head injury. Neurosurgery 46:335–342; discussion 342–343
Breitkreutz R, Pittack N, Nebe CT, Schuster D, Brust J, Beichert M, Hack V, Daniel V, Edler L, Droge W (2000) Improvement of immune functions in HIV infection by sulfur supplementation: two randomized trials. J Mol Med 78:55–62
Paret G, Barzilai A, Lahat E, Feldman Z, Ohad G, Vardi A, Ben-Abraham R, Barzilay Z (1998) Gunshot wounds in brains of children: prognostic variables in mortality, course, and outcome. J Neurotrauma 15:967–972
Wilson M, Weinreb J, Hoo GW (2007) Intensive insulin therapy in critical care: a review of 12 protocols. Diabetes Care 30:1005–1011
Lacherade JC, Jabre P, Bastuji-Garin S, Grimaldi D, Fangio P, Theron V, Outin H, De Jonghe B (2007) Failure to achieve glycemic control despite intensive insulin therapy in a medical ICU: incidence and influence on ICU mortality. Intensive Care Med 33:814–821
McCowen KC, Malhotra A, Bistrian BR (2001) Stress-induced hyperglycemia. Crit Care Clin 17:107–124
Marik PE, Raghavan M (2004) Stress-hyperglycemia, insulin and immunomodulation in sepsis. Intensive Care Med 30:748–756
Van Waardenburg DA, Jansen TC, Vos GD, Buurman WA (2006) Hyperglycemia in children with meningococcal sepsis and septic shock: the relation between plasma levels of insulin and inflammatory mediators. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:3916–3921
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kyle, U.G., Coss Bu, J.A., Kennedy, C.E. et al. Organ dysfunction is associated with hyperglycemia in critically ill children. Intensive Care Med 36, 312–320 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-009-1703-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-009-1703-1