Abstract
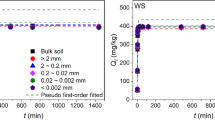
This work studied the vertical migration characteristics of Cd in soil profiles from a zinc smelting site under the influence of simulated reclaimed water containing NaCl and Na2SO4. The isothermal adsorption curves of Cd in the soils of miscellaneous fill and weathered slate well fitted the Freundlich and Langmuir models, with R2 ranging from 0.991 to 0.998. The maximum adsorption capacity of Cd in the soils decreased significantly under the salt ion treatments with NaCl and Na2SO4. After leaching, the Cd concentrations in the leachates and Cd contents in the subsoil layers of 10–60 cm followed the order NaCl treatment > Na2SO4 treatment > CK (p < 0.05), suggesting that the salt ions promoted the vertical migration of exogenous Cd. The proportion of coarse particles (> 0.02 mm) decreased, while that of fine particles (< 0.02 mm) increased under salt ion treatments (p < 0.05). The morphological characterization indicated that salt ions accelerated the erosion and fragmentation of coarse particles to form fine particles. The use of reclaimed water to flush smelting sites may increase the risk of Cd migration with small-sized soil particles from the soil to groundwater.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bradl HB (2004) Adsorption of heavy metal ions on soils and soils constituents. J Colloid Interf Sci 277:1–18
Chen W, Lu S, Peng C et al (2013) Accumulation of Cd in agricultural soil under long-term reclaimed water irrigation. Environ Pollut 178:294–299
Chen Y, Ma J, Li Y et al (2019) Enhanced cadmium immobilization in saturated media by gradual stabilization of goethite in the presence of humic acid with increasing pH. Sci Total Environ 648:358–366
Escudero C, Poch J, Villaescusa I (2013) Modelling of breakthrough curves of single and binary mixtures of Cu(II), cd(II), ni(II) and pb(II) sorption onto grape stalks waste. Chem Eng J 217:129–138
Fan Q, Shao D, Hu J et al (2008) Comparison of Ni2+ sorption to bare and ACT-graft attapulgites: Effect of pH, temperature and foreign ions. Surf Sci 602:778–785
Hashem MS, Qi X (2021) Treated wastewater irrigation-A review. Water-Sui 13:1527–1563
Hu X, Liu Y, Zeng G et al (2014) Effects of background electrolytes and ionic strength on enrichment of cd(II) ions with magnetic graphene oxide-supported sulfanilic acid. J Colloid Interface Sci 435:138–144
Hu T, Wang H, Tan S (2020) Distribution characteristics of soil aggregates and their associated organic carbon under different irrigation modes with reclaimed water. J Agro-Environment Sci 39:143–151
Jiang Z, Guo Z, Peng C et al (2021) Heavy metals in soils around non-ferrous smelteries in China: Status, health risks and control measures. Environ Pollut 282:117038
Jiang Z, Guo Z, Peng C et al (2022) Adsorption of cd on soils with various particle sizes from an abandoned non-ferrous smelting site: characteristics and mechanism. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 109:630–635
Jiang Z, Guo Z, Peng C et al (2023) Model development and probabilistic risks of cadmium transport in slag-soil-groundwater systems with heterogeneous conditions. Sci Total Environ 895:165160
Kilduff JE, Karanfil T, Weber WJ (1996) Competitive interactions among components of humic acids in granular activated carbon adsorption systems: effects of solution chemistry. Environ Sci Technol 30:1344–1351
Liao M, Liu E, Fu L et al (2019) Experimental study on salt ion corrosion of concrete in saline soil environments. Concrete 81–85 + 89
Liu G, Xue W, Wang J et al (2019) Transport behavior of variable charge soil particle size fractions and their influence on cadmium transport in saturated porous media. Geoderma 337:945–955
Lodygin ED, Alekseev II, Vasilevich RS et al (2020) Complexation of lead and cadmium ions with humic acids from arctic peat soils. Environ Res 191:110058
Lu R (2000) Soil and agro-chemistry analytical methods. China Agriculture Science and Technology Press, Beijing
Lu S, Wang J, Pei L (2016) Study on the effects of irrigation with reclaimed water on the content and distribution of heavy metals in soil. Int J Environ Res Public Health 13:298–307
Lu S, Xie F, Zhang X et al (2020) Health evaluation on migration and distribution of heavy metal cd after reclaimed water drip irrigation. Environ Geochem Health 42:841–848
Lyu S, Chen W (2016) Soil quality assessment of urban green space under long-term reclaimed water irrigation. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23:4639–4649
Lyu S, Wu L, Wen X et al (2022) Effects of reclaimed wastewater irrigation on soil-crop systems in China: a review. Sci Total Environ 813:152531
Ma J, Zhong B, Khan MA et al (2021) Transport of mobile particles in heavy metal contaminated soil with simulated acid rain leaching. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 106:965–969
Mahjoub O, Mauffret A, Michel C et al (2022) Use of groundwater and reclaimed water for agricultural irrigation: Farmers’ practices and attitudes and related environmental and health risks. Chemosphere 295:133945
Mouta ER, Soares MR, Casagrande JC (2008) Copper adsorption as a function of solution parameters of variable charge soils. J Brazil Chem Soc 19:996–1009
Ren B, Wu Y, Deng D et al (2020) Effect of multiple factors on the adsorption of cd in an alluvial soil from Xiba, China. J Contam Hydrol 232:103605
Shi T, Zhang Y, Gong Y et al (2019) Status of cadmium accumulation in agricultural soils across China (1975–2016): from temporal and spatial variations to risk assessment. Chemosphere 230:136–143
Shi Z, Yang Y, Liu F et al (2020) Effect of soil particle size on the kinetics of Cu release from field-contaminated soils: experiments and a quantitative model. Chem Geol 552:119780
Sugita R, Marumo Y (2001) Screening of soil evidence by a combination of simple techniques: validity of particle size distribution. Forensic Sci Int 122:155–158
Waleeittikul A, Chotpantarat S, Ong SK (2019) Impacts of salinity level and flood irrigation on cd mobility through a Cd-contaminated soil, Thailand: experimental and modeling techniques. J Soil Sediment 19:2357–2373
Wang J, Yuan T, Guo G (2011) Study on influence of Cu adsorption/desorption of the paddy soils under different accompanying anions. Environ Sci Manage 36:40–42
Wang Y, Cheng H, Tan W (2020) Different responses of soil microbial community structure to irrigation with treated wastewater from domestic and industrial sources. Environ Sci 41:4253–4261
Wikiniyadhanee R, Chotpantarat S, Ong SK (2015) Effects of kaolinite colloids on Cd2+ transport through saturated sand under varying ionic strength conditions: column experiments and modeling approaches. J Contam Hydrol 182:146–156
Wu W, Sheng H, Gu C et al (2018) Extraneous dissolved organic matter enhanced adsorption of dibutyl phthalate in soils: insights from kinetics and isotherms. Sci Total Environ 631–632:1495–1503
Xiao X, Jiang Z, Guo Z et al (2017) Effect of simulated acid rain on leaching and transformation of vanadium in paddy soils from stone coal smelting area. Process Saf Environ 109:697–703
Xu D, Zhao S, Cai X et al (2022) Migration characteristics of heavy metals in soil during water loss process. Bull Soil Water Conserv 42:83–92
Yang J, Guo Z, Jiang L et al (2022) Cadmium, lead and arsenic contamination in an abandoned nonferrous metal smelting site in southern China: Chemical speciation and mobility. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 239:113617
Zeng J, Luo X, Cheng Y et al (2021) Spatial distribution of toxic metal(loid)s at an abandoned zinc smelting site, Southern China. J Hazard Mater 425:127970
Zeng J, Li C, Wang J et al (2022) Pollution simulation and remediation strategy of a zinc smelting site based on multi-source information. J Hazard Mater 433:128774
Zhang F, Liu Z, Chen Y et al (2020) Numerical simulation of mutually embedded settlement in miscellaneous fill. Adv Civ Eng 2020:6695661
Zhang Y, Li T, Guo Z et al (2023) Spatial heterogeneity and source apportionment of soil metal(loid)s in an abandoned lead/zinc smelter. J Environ Sci-China 127:519–529
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2019YFC1803600) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of Central South University (Grant No. 2020zzts094).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Z., Guo, Z., Peng, C. et al. Effects of Simulated Reclaimed Water on Soil Particle Sizes and Cd Adsorption and Migration in Soils at Smelting Sites. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 111, 36 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-023-03800-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-023-03800-x