Abstract
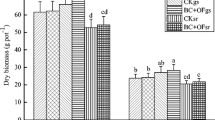
This field study explored safe rice production in Cd-contaminated red paddy soil by application of the combined Si-/Se- containing foliar inhibitors (Si or Se) and the mixture amendments of quicklime (Q), polyacrylamide (A), or/and sepiolite (S) at low (1) and high (2) application rates. The results showed that all treatments increased soil pH and decreased total P and soil organic matter (excluding QSe2). With the increasing application rates, QAS significantly decreased the available Cd because of the enhanced stabilization, while QSi and QSe significantly increased the available Cd because of the inhibited plant uptake. After remediation, QA1, QSi2, and QSe2 most effectively decreased the uptake Cd by rice to meet the threshold of National Food Safety Standard of China. The treatments excluding Q1, QA1, QSi1, and QSi2 did not dramatically change the bacterial community structure in soil. Collectively, QSe2 was recommended for remediating Cd-contaminated red paddy soil.
Highlights
Combined foliar inhibitor and conditioner was used to remediate Cd-polluted paddy soil.
Increase in soil pH and decrease in TP and SOM facilitated stabilization of metals.
Most treatments had little influence on bacterial genus composition in soil studied.
The QSe2 remediation strategy was recommended for Cd-polluted red paddy soil.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen G, Shah KJ, Shi L, Chiang PC, You Z (2019) Red soil amelioration and heavy metal immobilization by a multi-element mineral amendment: performance and mechanisms. Environ Pollut 254:112964
Hou D, O’Connor D, Igalavithana AD, Alessi DS, Luo J, Tsang DCW, Ok YS (2020) Metal contamination and bioremediation of agricultural soils for food safety and sustainability. Nat Reviews Earth Environ 1:366–381
Huang Y, Deng MH, Wu SF, Japenga J, Li TQ, Yang XE, He ZL (2018) A modified receptor model for source apportionment of heavy metals pollution in soil. J Hazard Mater 345:161–169
Hussain B, Lin Q, Hamid Y, Sanaullah M, Di L, Hashmi ML, Khan MB, He Z, Yang X (2020) Foliage application of selenium and silicon nanoparticles alleviates cd and pb toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L). Sci Total Environ 712:136497
Jiang YX, Hu T, Peng O, Chen AW, Tie BQ, Shao JH (2021) Responses of microbial community and soil enzyme to heavy metal passivators in cadmium contaminated paddy soils: an in situ field experiment. Int bioderioration biodegradation 164:105292
Jing F, Chen C, Chen XM, Liu W, Wen X, Hu SM, Yang ZJ, Guo BL, Xu YL, Yu QX (2019) Effects of wheat straw derived biochar on cadmium availability in a paddy soil and its accumulation in rice. Environ Pollut 257:113592
Khan MA, Khan S, Khana A, Alam M (2017) Soil contamination with cadmium, consequences and remediation using organic amendments. Sci Total Environ 601–602:1591–1605
Lei SC, Shi Y, Xue C, Wang JL, Che L, Qiu YP (2020) Hybrid ash/biochar biocomposites as soil amendments for the alleviation of cadmium accumulation by Oryza sativa L. in a contaminated paddy field. Chemosphere 239:124805
Li HH, Liu YT, Tang SY, Yu ZC, Cai XZ, Xu SP, Chen YH, Wang MK, Wang G (2021) Mechanisms for potential pb immobilization by hydroxyapatite in a soil-rice system. Sci Total Environ 783:147037
Li N, Feng AX, Liu N, Jiang ZM, Wei SQ (2020) Silicon application improved the yield and nutritional quality while reduced cadmium concentration in rice. Environ Sci Pollution Res 27:20370–20379
Liang JW, Yu XQ, Cao YF, Zhang JG, Yan N, Xue L, Cai XJ, Shen GM (2021) Effect of quicklime on microbial community in strong acidic soil. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 21:1771–1781
Liu PY, Wang P, Lu Y, Ding Y, Lu GN, Dang Z, Shi ZQ (2019) Modeling kinetics of heavy metal release from field-contaminated soils: roles of soil adsorbents and binding sites. Chem Geol 506:187–196
Luo LY, Xie LL, Jin DC, Mi BB, Wang DH, Li XF, Dai XZ, Zou XX, Zhang Z, Ma YQ, Liu F (2019) Bacterial community response to cadmium contamination of agricultural paddy soil. Appl Soil Ecol 139:100–106
Nwuche CO, Ujam OT, Ihedioha JN, Chime CC (2017) An “ex situ” microbial process for the removal of heavy metals from polluted soil: a case study of Ada rice field, Adani, Enugu State, Nigeria. Bioremediat J 21(3–4):128–137
Rađenović D, Kerkez Đ, Pilipović DT, Dubovina M, Grba N, Krčmar D, Dalmacija B (2019) Long-term application of stabilization/solidification technique on highly contaminated sediments with environment risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 684:186–195
Song B, Zeng G, Gong J, Liang J, Ren X (2017) Evaluation methods for assessing effectiveness of in situ remediation of soil and sediment contaminated with organic pollutants and heavy metals. Environ Int 105:43–55
Vrinceanu N, Motelica D, Dumitru M, Calciu I, Tanase V, Preda M (2019) Assessment of using bentonite, dolomite, natural zeolite, and manure for the immobilization of heavy metals in a contaminated soil: the Copșa Mică case study (Romania). CATENA 176:336–342
Wan YA, Huang QQ, Wang Q, Yu Y, Su DC, Qiao YH, Li HF (2020) Accumulation and bioavailability of heavy metals in an acid soil and their uptake by paddy rice under continuous application of chicken and swine manure. J Hazard Mater 384:121293
Wang F, Zhang W, Miao L, Ji T, Wang Y, Zhang, Ding Y, Zhu WQ (2021a) The effects of vermicompost and shell powder addition on cd bioavailability, enzyme activity and bacterial community in Cd-contaminated soil: a field study. Ecotoxicol Environmetal Saf 215:112163
Wang F, Zhang W, Miao L, Ji T, Wang Y, Zhang H, Ding Y, Zhu WQ (2021b) The effects of vermicompost and shell powder addition on cd bioavailability, enzyme activity and bacterial community in Cd-contaminated soil: a field study. Ecotoxicol Environmetal Saf 215:112163
Xue T, Liao XY, Wang LQ, Gong XG, Zhao FH, Ai JH, Zhang YZ (2019) Effects of adding selenium on different remediation measures of paddy fields with slight–moderate cadmium contamination. Environ Geochem Health 42:377–388
Yang JL, Cang L, Wang X, Xu HT, Zhou DM (2020) Field survey study on the difference in cd accumulation capacity of rice and wheat in rice-wheat rotation area. J Soils Sediments 20:2082–2092
Zhang GX, Guo XF, Zhao ZH, He QS, Wang SF, Zhu YE, Yan YL, Liu XT, Sun K, Zhao Y, Qian TW (2016) Effects of biochars on the availability of heavy metals to ryegrass in an alkaline contaminated soil. Environ Pollut 218:513–522
Zhang WJ, Jiang JG, Li KM, Li TR, Li DA, Wang JM (2017) Amendment of vanadium-contaminated soil with soil conditioners: a study based on pot experiments with canola plants (Brassica campestris L). Int J Phytoremediation 20:454–461
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2018YFC1802803), the Second Tibetan Plateau Scientific Expedition and Research Program (No. 2019QZKK1003), Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. XDA23010400), Foundation of President of the Zhongke-Ji’an Institute for Eco-Environmental Sciences (No. 2020ZKJA03), and the Natural Science Foundation of Shanxi Province (No. 20210302123204).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, G., He, L., Zhang, F. et al. Safe Rice Production in Cd-Contaminated Paddy Soil: Strategy and Environmental Implications. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 110, 83 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-023-03712-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-023-03712-w