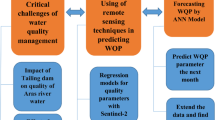
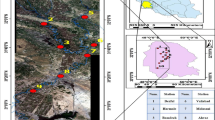
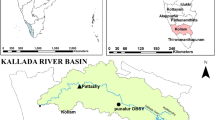
Abstract
In recent days, the quality of water in inland water bodies has been threatened by various natural and anthropogenic activities. Henceforth, the continuous monitoring of water quality is mandatory to control the pollution level in surface water bodies. In this work, remote sensing technology integrated with an Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithm, a new technique called Spatio-Temporal Hybrid Novel Technique (STHNT), was used to predict, and monitor the chemical water quality pollution level through the Water Quality Index (WQI). The Two Bands Regression Empirical (TBRE) water quality model has been used to retrieve water quality parameters from multi-resolution satellite imagery (Sentinel-2 MSI). The Nonlinear Auto-regressive Neural Network (NARNET), which is an Artificial Neural Network (ANN), was set up to predict the water quality index. Based on the model performed on the remote sensing water quality data, it is inferred that NARNET (Coefficient of determination-R2:0.9911, Root Mean Square Error-RMSE:1.693 and Sum of Squares of Error-SSE:14.33) provides significant results in predicting WQI. Therefore, the combined remote sensing technology with artificial intelligence plays a pivotal role in water resource management, which helps in reducing the pollution level in surface water bodies.
Graphical Abstract















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldhyani THH, Alrasheedi M, Alqarni AA, Alzahrani MY, Bamhdi AM (2020) Intelligent hybrid model to enhance time series models for predicting network traffic. IEEE Access 8:130431–130451. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3009169
Carpenter SR, Gurevitch A, Adams MS (1979) Factors causing elevated biological oxygen demand in the littoral zone of lake Wingra. Wis Hydrobiologia 67:3–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00020871
Danijela Voza M Vukovic (2018) The assessment and prediction of temporal variations in surface water quality—a case study. Environ Monit Assess 190:434. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-018-6814-0
David B, Sieger, Adedeji B, Badiru (1993) An artificial neural network case study: prediction versus classification in a manufacturing application. Computers and Industrial Engineering 25(1–4):381–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/0360-8352(93)90301-D
Fernanda MC, Pizani P, Maillard Adrielly FF, Ferreira Camila C, de Amorim, (2020) Estimation of water quality in a reservoir from sentinel-2 MSI and landsat-8 OLI sensors. ISPRS Ann Photogramm Remote Sens Spatial Inf Sci. https://doi.org/10.5194/isprs-annals-V-3-2020-401-2020
Gaya MS, Abba SI, Abdu AM, Tukur AI et al (2020) Estimation of water quality index using artificial intelligence approaches and multi-linear regression. IAES Int J Artif Intell (IJ-AI) 9(1):126–134. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijai.v9.i1.pp126-134
Jayan PR, Nithya S (2012) Aquatic weed classification, environmental effects and the management technologies for its effective control in Kerala. India Int J Agric & Biol Eng 5(1):76–91
Jefferson L, Lerios, Mia V, Villarica (2019) Pattern extraction of water quality prediction using machine learning algorithms of water reservoir. Int J Mech Eng Rob Res 8(6):1–6
Mohandas KA, Brema J (2021) Linear regression based water quality analysis through spatial distribution of parameters for Vembanad Lake. Int J Aquat Sci 12(3):272–289
Murugan P, Sivakumar R, Pandiyan R, Annadurai M (2016) Comparison of in-situ hyperspectral and landsat ETM + data forchlorophyll-a mapping in Case-2 waters (Krishnarajapuram Lake,Bangalore). J Indian Soc Remote Sens 44(6):949–957. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-015-0531-8
Rizal NNM, Hayder G, Yusof KA (2022) Water quality predictive analytics using an artificial neural network with a graphical user interface. Water 14:1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14081221
Sahaya Vasanthi S, Adish Kumar S (2018) Application of Artificial neural network techniques for Predicting the Water Quality Index in the Parakai Lake, Tamil Nadu, India. Appl Ecol Environ Res 17(2):1947–1958. https://doi.org/10.15666/aeer/1702_19471958
Sivakumar R, Prasanth BRSV, Ramaraj M (2022) An empirical approach for deriving specific inland water quality parameters from high spatio-spectral resolution image. Wetlands Ecol Manage 30:405–422. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11273-022-09874-4
Srivastava G, Kumar P (2013) Water quality index with missing parameters. Int J Res Eng Technol 2(4):609–614. https://doi.org/10.15623/ijret.2013.0204035
Sruthy S, Ramasamy EV (2017) Microplastic pollution in Vembanad Lake, Kerala, India: the first report of microplastics in lake and estuarine sediments in India. Environ Pollut 222:315–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.12.038
Theyazn HH, Aldhyani M, Al-Yaari H, Alkahtani M (2020) Maashi water quality prediction using artificial intelligence algorithms. Appl Bionics Biomechanics. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/6659314
Tyagi S, Sharma B, Singh P, Dobhal R (2013) Water quality assessment in terms of water quality index. Am J Water Resour 1(3):34–38. https://doi.org/10.12691/ajwr-1-3-3
Venkataramana Veeramsetty N, Shadamaki R, Pinninti N, Guduri G (2022) Ashish water quality index estimation using linear regression model. AIP Conf Proc 2418(1):040033. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0081794
Vishnu Prasanth BR, Sivakumar R, Ramaraj M (2022) Study on algae bloom pigment in the eutrophic lake using bio–optical modelling: hyperspectral remote sensing approach. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-022-03511-9
WWF (2012) Water scarcity affects 2.7 billion, finds new detailed report, https://wwf.panda.org/wwf_news/?203746/Water-scarcity-affects-27-billion-finds-new-detailed-report, Accessed: 29, February, 2012
Xiaoliang Ji Xu, Shang, Randy A, Dahlgren, Minghua Zhang (2017) Prediction of dissolved oxygen concentration in hypoxic river systems using support vector machine: a case study of Wen-Rui Tang River, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:16062–16076. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9243-7
Xuehua SuX, He G, Zhang Y, Chen Li K (2022) Research on SVR Water Quality Prediction Model Based on Improved Sparrow Search Algorithm. Comput Intell Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/7327072
Yang H, Kong J, Hu H, Du Y, Gao M, Chen F (2022) A review of remote sensing for water quality retrieval: progress and challenges. Remote Sens 14:1770. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14081770
Yeon S, Kim JH, Jun KW (2008) Application of artificial intelligence models. Water Qual Forecast Environ Technol 25(6):625–631. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330801984456
Zhang L, Zou Z, Shan W (2017) Development of a method for comprehensive water quality forecasting and its application in Miyun reservoir of Beijing, China. J Environ Sci 56:240–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2016.07.017
Zhai W, Zhou X, Man J, Xu Q, Jiang Q, Yang Z, Jiang L, Gao Z, Yuan Y, Gao W (2019) Prediction of water quality based on artificial neural network with grey theory. IOP Conf Series: Earth and Environmental Science 295:042009. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/295/4/042009
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by Big Data Analytics/ Hyperspectral Remote Sensing, ICPS Division, Department of Science and Technology, Government of India (Reference Number: BDID/01/23/2014-HSRS/14). We thank the SRM Institute of Science and Technology for providing all facilities to carry out the research and constant Encouragement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ramaraj, M., Sivakumar, R. Remote Sensing and Nonlinear Auto-regressive Neural Network (NARNET) Based Surface Water Chemical Quality Study: A Spatio-Temporal Hybrid Novel Technique (STHNT). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 110, 28 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-022-03646-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-022-03646-9