Abstract
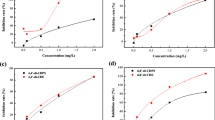
DCOIT (4,5-dichloro-2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one) is the main ingredient in SeaNine-211, a new antifouling agent that replaces organotin compounds to prevent the growth of fouling organisms on board. Biocides from antifoulants can cause problems for marine ecosystems by destroying non-target algal species. This study evaluated the potential adverse effects DCOIT using the Marine Chlorella sp. The concentration of DCOIT were set according to the semi-inhibitory concentrations for acute exposure experiments, and relevant oxidative stress indicators were measured to assess the acute toxic effects. The results showed that the inhibition concentrations (IC50) of DCOIT against Marine Chlorella sp was 2.522 mg/L. The genes related to photosynthesis and antioxidant capacity showed the effect of promoting low concentration and inhibiting high concentration. In addition, based on the ultrastructural observation and the expression analysis of photosynthesis related genes, it was found that DCOIT had a significant effect on plant photosynthesis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arning J, Matzke M, Stolte S, Nehen F, Bottin-Weber U, Boschen A, Abdulkarim S, Jastorff B, Ranke J (2009) Analyzing Cytotoxic Effects of Selected Isothiazol-3-one Biocides Using the Toxic Ratio Concept and Structure-Activity Relationship Considerations. Chem Res Toxicol 22:1954–1961
Bellas J (2006) Comparative toxicity and of alternative antifouling biocides on embryos larvae of marine invertebrates. Sci Total Environ 367:573–585
Calabrese EJ (2005) Paradigm lost, paradigm found: The re-emergence of hormesis as a fundamental dose response model in the toxicological sciences. Environ Pollut 138:378–411
Chen LG, Ye R, Xu Y, Gao ZM, Au DWT, Qian PY (2014) Comparative safety of the antifouling compound butenolide and 4,5-dichloro-2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one (DCOIT) to the marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma). Aquat Toxicol 149:116–125
Chen LR, Duan YY, Cui M, Huang RL, Su RX, Qi W, He ZM (2021) Biomimetic surface coatings for marine antifouling: Natural antifoulants, synthetic polymers and surface microtopography.Sci Total Environ766
Cordero BF, Couso I, Leon R, Rodriguez H, Vargas MA (2011) Enhancement of carotenoids biosynthesis in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by nuclear transformation using a phytoene synthase gene isolated from Chlorella zofingiensis. Appl Microbiol Biot 91:341–351
Guardiola FA, Cuesta A, Meseguer J, Esteban MA (2012) Risks of Using Antifouling Biocides in Aquaculture. Int J Mol Sci 13:1541–1560
Guernier V, Brennan B, Yakob L, Milinovich G, Clements ACA, Magalhaes RJS (2017) Gut microbiota disturbance during helminth infection: can it affect cognition and behaviour of children?Bmc Infect Dis17
Guo X, Cai Y, Ma C, Han L, Yang Z (2021) Combined toxicity of micro/nano scale polystyrene plastics and ciprofloxacin to Corbicula fluminea in freshwater sediments. Sci Total Environ 789:147887
Hu P, Xie QY, Ma CF, Zhang GZ (2020) Silicone-Based Fouling-Release Coatings for Marine Antifouling. Langmuir 36:2170–2183
Jacobson AH, Willingham GL (2000) Sea-nine antifoulant: an environmentally acceptable alternative to organotin antifoulants. Sci Total Environ 258:103–110
Jayaraman V, Hwangbo K, Lim JM, Min SR, Ahn JW, Choi DW, Jeong WJ (2017) Reduced gene expression at the branch point of chlorophyll and heme biosynthesis in Arctic Chlorella ArM0029B. Plant Biotechnol Rep 11:9–15
Khrebtukova I, Spreitzer RJ (1996) Elimination of the Chlamydomonas gene family that encodes the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase. P Natl Acad Sci USA 93:13689–13693
Kumar M, Jaiswal S, Sodhi KK, Shree P, Singh DK, Agrawal PK, Shukla P (2019) Antibiotics bioremediation: Perspectives on its ecotoxicity and resistance. Environ Int 124:448–461
Li P, Li ZH, Zhong L (2019) Effects of low concentrations of triphenyltin on neurobehavior and the thyroid endocrine system in zebrafish. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 186:109776
Li P, Li ZH (2020) Environmental co-exposure to TBT and Cd caused neurotoxicity and thyroid endocrine disruption in zebrafish, a three-generation study in a simulated environment. Environ Pollut 259:113868
Li P, Li ZH, Zhong L (2020) Parental exposure to triphenyltin inhibits growth and disrupts thyroid function in zebrafish larvae. Chemosphere 240:124936
Masuda T, Tanaka A, Melis A (2003) Chlorophyll antenna size adjustments by irradiance in Dunaliella salina involve coordinate regulation of chlorophyll a oxygenase (CAO) and Lhcb gene expression. Plant Mol Biol 51:757–771
Onduka T, Ojima D, Ito M, Ito K, Mochida K, Fujii K (2013) Toxicity of the antifouling biocide Sea-Nine 211 to marine algae, crustacea, and a polychaete. Fisheries Sci 79:999–1006
Qian HF, Chen W, Sheng GD, Xu XY, Liu WP, Fu ZW (2008) Effects of glufosinate on antioxidant enzymes, subcellular structure, and gene expression in the unicellular green alga Chlorella vulgaris. Aquat Toxicol 88:301–307
Steen RJCA, Ariese F, van Hattum B, Jacobsen J, Jacobson A (2004) Monitoring and evaluation of the environmental dissipation of the marine antifoulant 4,5-dichloro-2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one (DCOIT) in a Danish Harbor. Chemosphere 57:513–521
Su Y, Li H, Xu C, Wang X, Xie J, Qin JG, Chen L, Li E (2018) Endoplasmic reticulum stress mediates 4,5-dichloro-2-n-octyl-4-isothiazolin-3-one (DCOIT)-induced toxicity and liver lipid metabolism changes in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Environ Pollut 242:1981–1987
Thomas KV, McHugh M, Waldock M (2002) Antifouling paint booster biocides in UK coastal waters: inputs, occurrence and environmental fate. Sci Total Environ 293:117–127
Thomas KV, Brooks S (2010) The environmental fate and effects of antifouling paint biocides. Biofouling 26:73–88
Zhao FF, Xiang QQ, Zhou Y, Xu X, Qiu XY, Yu Y, Ahmad F (2017) Evaluation of the toxicity of herbicide topramezone to Chlorella vulgaris: Oxidative stress, cell morphology and photosynthetic activity. Ecotox Environ Safe 143:129–135
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFD0900905, 2018YFD0900902).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ru, JC., Zhao, XL., Cao, ZH. et al. Acute Toxicity of a Novel anti-fouling Material Additive DCOIT to Marine Chlorella sp. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 109, 1018–1022 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-022-03623-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-022-03623-2