Abstract
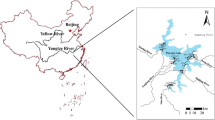
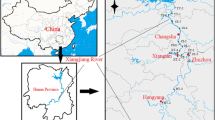
Human activities can introduce heavy metals to water bodies, where they are then deposited in sediments. The risks, spatial distributions, and toxicities of heavy metals in sediment were investigated along the North Canal in the densely Beijing–Tianjin area. The average geoaccumulation index ranged from 0.2 to 2.91 and the highest value was obtained for Cd. All the pollution load indexes were greater than one, indicating that the heavy metals originated from anthropogenic sources. The risk indexes at three sampling points were greater than 300, indicating high potential ecological risk. Two probable effect concentration quotient values greater than 0.5, suggesting potential toxicity to certain sediment-dwelling organisms. Identification and evalution heavy metals could assist in improvement of the water quality, and support management strategies to restore the environment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhuiyan MAH, Parvez L, Islam MA, Dampare SB, Suzuki S (2010) Heavy metal pollution of coal mine-affected agricultural soils in the northern part of Bangladesh. J Hazard Mater 173:384–392
Chen L, Li LF, Zhi XS (2019) Pollution Characteristics and health risk assessment of microorganism pollutions in the Beiyun River. Environ Sci 040(002):633–639
Dai G, Wang B, Huang J, Dong R, Deng S, Yu G (2015) Occurrence and source apportionment of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the Beiyun River of Beijing. China Chemosphere 119:1033–1039
Deng GP, Yang WQ, Zhou GY, Li Y, Liu SL (2014) Heavy metals and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments from the Shenzhen River, South China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:10594–10600
Guo WH, Liu XB, Liu ZG, Li GF (2010) Pollution and potential ecological risk evaluation of heavy metals in the sediments around Dongjiang Harbor, Tianjin. Procedia Environ Sci 2:729–736
Håkanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: A sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001
Hanif N, Eqani S, Cincinelli A, Ali N, Katsoyiannis IA, Tanveer ZI, Bokhari H (2016) Geo-accumulation and enrichment of trace metals in sediments and their associated risks in the Chenab River. Pakistan J Geochem Explor 165:62–70
Hong SW, Kim HS, Chung TH (2010) Alteration of sediment organic matter in sediment microbial fuel cells. Environ Pollu 158:185–191
Huang J, Ge XP, Wang DS (2012) Distribution of heavy metals in the water column, suspended particulate matters and the sediment under hydrodynamic conditions using an annular flume. J Environ Sci 24:2051–2059
Islam MS, Ahmed MK, Raknuzzaman M, Habibullah-Al-Mamun M, Islame MK (2015) Heavy metal pollution in surface water and sediment: a preliminary assessment of an urban river in a developing country. Ecolog Indic 48:282–291
Ji ZH, Zhang H, Zhang Y, Chen T, Long ZW, Li M, Pei YS (2019) Distribution, ecological risk and source identification of heavy metals in sediments from the Baiyangdian Lake, Northern China. Chemosphere 237
Liu J, Li YL, Zhang B, Cao JL, Cao ZG, Domagalski J (2009) Ecological risk of heavy metals in sediments of the Luan River source water. Ecotoxicology 18:748–758
Ma Z, Chen K, Yuan Z, Bi J, Huang L (2013) Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of six major Chinese freshwater lakes. J Environ Quality 42:341–350
Martínez-Santos M, Probst A, García-García J, Ruiz-Romera E (2015) Influence of anthropogenic inputs and a high-magnitude flood event on metal contamination pattern in surface bottom sediments from the Deba River urban catchment. Sci Total Environ 514:10–25
Müller G (1969) Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal 2:108–118
Niu HY, Deng WJ, Wu QH, Chen XG (2009) Potential toxic risk of heavy metals from sediment of the Pearl River in South China. J Environ Sci-China 21:1053–1058
Noronha-D’Mello CA, Nayak GN (2016) Assessment of metal enrichment and their bioavailability in sediment and bioaccumulation by mangrove plant pneumatophores in a tropical (Zuari) estuary, west coast of India. Mar Pollut Bull 110:221–230
Sojka M, Siepak M, Jaskuła J, Wicher-Dysarz J (2018) Heavy metal transport in a river-reservoir system: a case study from central poland. Pol J Environ Stud 27:1725–1734
Suresh G, Sutharsan P, Ramasamy V, Venkatachalapathy R (2012) Assessment of spatial distribution and potential ecological risk of the heavy metals in relation to granulometric contents of Veeranam lake sediments, India. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 84:117–124
Strom D, Simpson SL, Batley GE, Jolley DF (2011) The influence of sediment particle size and organic carbon on toxicity of copper to benthic invertebrates in oxic/suboxic surface sediments. Environ Toxic Chem 30:1599–1610
Tagliaferro M, Gonçalves A, Bergman M, Sobral O, Graça M (2018) Assessment of metal exposure (uranium and copper) by the response of a set of integrated biomarkers in a stream shredder. Ecol Ind 95:991–1000
Tang W, Zhao Y, Wang C, Shan BQ, Cui JG (2013) Heavy metal contamination of overlying waters and bed sediments of Haihe Basin in China. Ecotoxic Environ Safety 98:317–323
Tang WZ, Pei YS, Zheng H, Zhao Y, Shu LM, Zhang H (2022) Twenty years of China’s water pollution control: Experiences and challenges. Chemosphere 295:133875. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.133875
Wang LF, Yang LY, Kong LH, Li S, Zhu JR, Wang YQ (2014) Spatial distribution, source identification and pollution assessment of metal content in the surface sediments of Nansi Lake, China. J Geochem Explor 140:87–95
Wang X, Zhang L, Zhao Z, Cai Y (2018) Heavy metal pollution in reservoirs in the hilly area of southern China: Distribution, source apportionment and health risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 634:158–169
Wang YB, Liu CW, Wang SW (2015) Characterization of heavy-metal-contaminated sediment by using unsupervised multivariate techniques and health risk assessment. Ecotox Environ Safe 113:469–476
Wei GH, Fan LM, Zhu WF, Fu YY, Yu JF, Tang M Isolation and characterization of the heavy metal resistant bacteria CCNWRS33-2 isolated from root nodule of Lespedeza cuneata I n gold mine tailings in China.(2009). J Hazard Mater, 162(1):50–56
Wu HH, Xu CB, Wang JH, Xiang Y, Ren M, Qie HT, Zhang YJ, Yao RH, Li L, Lin AJ (2021) Health risk assessment based on source identification of heavy metals: A case study of Beiyun River, China. Ecotox Environ Safe 213:112046
Yang Y, Sun W, Liu JB, Xie LP, Wei YS, Zhu LY, Zhang JY, Wu JF, Zhao HQ, Xu CG (2021) Distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Shahe Reservoir in Northern Canal Basin. Acta Sci Circum 41(1):217–227
Yu GB, Liu Y, Yu S, Wu SC, Leung AOW, Luo XS, Xu B, Li HB, Wong MH (2011) Inconsistency and comprehensiveness of risk assessments for heavy metals in urban surface sediments. Chemosphere 85:1080–1087
Zahra A, Hashmi MZ, Malik RN, Ahmed Z (2014) Enrichment and geo-accumulation of heavy metals and risk assessment of sediments of the Kurang Nallah-Feeding tributary of the Rawal Lake Reservoir, Pakistan. Sci Total Environ 470:925–933
Zhang C, Yu ZG, Zeng GM, Jiang M, Yang ZZ, Cui F, Zhu MY, Shen LQ, Hu L (2014) Effects of sediment geochemical properties on heavy metal bioavailability. Environ Intern 73:270–281
Zhang C, Shan BQ, Tang WZ, Dong LX, Zhang WQ, Pei YS (2017) Heavy metal concentrations and speciation in riverine sediments and the risks posed in three urban belts in the Haihe Basin. Ecotox Environ Safe 139:263–271
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Key-Area Research and Development Program of Guangdong Province (grant number 2019B110205002); the Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS from the Chinese Academy of Sciences (grant number 2018058); and the National Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment (grant number 2017ZX07107-004). We thank Gabrielle David, PhD, from Liwen Bianji (Edanz) (www.liwenbianji.cn/), for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, S., Zhang, W., Li, W. et al. Accumulation and potential ecological risks of Heavy Metals in sediments from Rivers in the Beijing–Tianjin Area. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 109, 691–697 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-022-03561-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-022-03561-z