Abstract
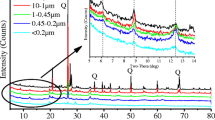
Soil particle size could intensively impact the Cd adsorption in soils. The adsorption characteristics of Cd on miscellaneous fill (MF) and weathered slate (WS), collected from a zinc smelting site, were studied by batch experiments under conditions of different initial Cd concentrations and soil particle sizes. The results showed that the adsorption kinetics of Cd for soil particles from MF and WS were well fitted with the pseudo-first-order model, and the Cd adsorption isotherms well conformed to the Freundlich model. Soil particle size had an inconspicuous influence on adsorption rate, while the adsorption capacity decreased with particle size increase. The Cd adsorption on soil particles could be due to the exchange with Fe/Al, and -OH/C=O sites were the predominant adsorption sites. The MF may cause secondary pollution risk due to its low adsorption ability for Cd in smelting sites.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bradl HB (2004) Adsorption of heavy metal ions on soils and soils constituents. J Colloid Interface Sci 277:1–18
de Oliveira SA, de Lucena Tavares SR, Barbosa MC (2018) Pb adsorption on soil typical to an ammunition destruction site. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 101:365–371
Escudero C, Poch J, Villaescusa I (2013) Modelling of breakthrough curves of single and binary mixtures of Cu(II), Cd(II), Ni(II) and Pb(II) sorption onto grape stalks waste. Chem Eng J 217:129–138
Ettler V (2016) Soil contamination near non-ferrous metal smelters: a review. Appl Geochem 64:56–74
Farshadirad A, Hosseinpur A, Motaghian H (2018) Distribution and availability of copper in aggregate size fractions of some calcareous soils. J Soil Sediment 19:1866–1874
Freundlich H (1906) Über die adsorption in lösungen. J Phys Chem 57U:385–470
Huang B, Yuan Z, Li D et al (2020) Effects of soil particle size on the adsorption, distribution, and migration behaviors of heavy metal(loid)s in soil: a review. Environ Sci Proc Imp 22:1596–1615
Jamal A, Delavar MA, Naderi A et al (2019) Distribution and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil surrounding a lead and zinc smelting plant in Zanjan, Iran. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 25:1018–1033
Jiang Z, Guo Z, Peng C et al (2021) Heavy metals in soils around non-ferrous smelteries in China: status, health risks and control measures. Environ Pollut 282:117038
Lagergreen S (1907) Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption gelöster stoffe. Z Chem Ind Kolloide 2:15–15
Li Y, Padoan E, Ajmone-Marsan F (2021) Soil particle size fraction and potentially toxic elements bioaccessibility: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 209:111806
Liu G, Wang J, Xue W et al (2017) Effect of the size of variable charge soil particles on cadmium accumulation and adsorption. J Soil Sediment 17:2810–2821
Lu RK (2000) Soil and agro-chemistry analytical methods. China Agriculture Science and Technology, Beijing
Mouta ER, Soares MR, Casagrande JC (2008) Copper adsorption as a function of solution parameters of variable charge soils. J Brazil Chem Soc 19:996–1009
Park H-J, Park H-J, Yang HI et al (2019) Sorption of Pb in chemical and particle-size fractions of soils with different physico-chemical properties. J Soil Sediment 19:310–321
Peng L, Liu P, Feng X et al (2018) Kinetics of heavy metal adsorption and desorption in soil: developing a unified model based on chemical speciation. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 224:282–300
Rauret G, Lo´pez-Sa´nchez JF, Sahuquillo A et al (1999) Improvement of the BCR three step sequential extraction procedure prior to the certification of new sediment and soil reference materials. J Environ Monitor 1:57–61
Ren Z-l, Sivry Y, Dai J et al (2016) Exploring Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn dynamic speciation in mining and smelting-contaminated soils with stable isotopic exchange kinetics. Appl Geochem 64:157–163
Shi Z, Yang Y, Liu F et al (2020) Effect of soil particle size on the kinetics of Cu release from field-contaminated soils: Experiments and a quantitative model. Chem Geol 552:119780
Silvetti M, Demurtas D, Garau G et al (2017) Sorption of Pb, Cu, Cd, and Zn by municipal solid waste composts: Metal retention and desorption mechanisms. Clean Soil Air Water 45:1–10
Sugita R, Marumo Y (2001) Screening of soil evidence by a combination of simple techniques: validity of particle size distribution. Forensic Sci Int 122:155–158
Verla EN, Verla AW, Osisi AF et al (2019) Finding a relationship between mobility factors of selected heavy metals and soil particle size in soils from children’s playgrounds. Environ Monit Assess 191:742
Wang G, Pan X, Zhang S et al (2020) Remediation of heavy metal contaminated soil by biodegradable chelator–induced washing: efficiencies and mechanisms. Environ Res 186:109554
Wu W, Sheng H, Gu C et al (2018) Extraneous dissolved organic matter enhanced adsorption of dibutyl phthalate in soils: Insights from kinetics and isotherms. Sci Total Environ 631–632:1495–1503
Xu Z, Guo Z, Xiao X et al (2019) Effect of inorganic potassium compounds on the hydrothermal carbonization of Cd-contaminated rice straw for experimental-scale hydrochar. Biomass Bioenergy 130:105357
Yang J, Wang S, Guo Z et al (2020) Spatial distribution of toxic metal(loid)s and microbial community analysis in soil vertical profile at an abandoned nonferrous metal smelting site. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17:7101
Zhang Q, Li Z, Huang B et al (2017) Effect of land use pattern change from paddy soil to vegetable soil on the adsorption-desorption of cadmium by soil aggregates. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24:2734–2743
Zhang F, Liu Z, Chen Y et al (2020) Numerical simulation of mutually embedded settlement in miscellaneous fill. Adv Civil Eng 2020:6695661
Zhang L, Xiao J, Ji J et al (2021) Arsenate adsorption on different fractions of iron oxides in the paddy soil from the karst region of China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 106:126–133
Zhu HW, Xiao XY, Guo ZH et al (2018) Adsorption of vanadium (V) on natural kaolinite and montmorillonite: characteristics and mechanism. Appl Clay Sci 161:310–316
Zong Y, Xiao Q, Lu S (2016) Distribution, bioavailability, and leachability of heavy metals in soil particle size fractions of urban soils (northeastern China). Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:14600–14607
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2018YFC1800400) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of Central South University (Grant No. 2020zzts094).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Z., Guo, Z., Peng, C. et al. Adsorption of Cd on Soils with Various Particle Sizes from an Abandoned Non-ferrous Smelting Site: Characteristics and Mechanism. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 109, 630–635 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-022-03465-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-022-03465-y