Abstract
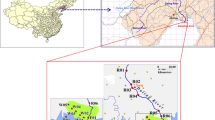
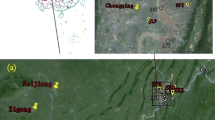
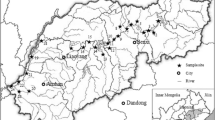
In this study, nine heavy metals (Cd, Cr, As, Hg, Pb, Cu, Ni, Be, and Sb) in the sediments of 17 typical rivers on the western bank of Taihu Lake were determined. Several statistical methods were applied to analyze the distribution, sources, pollution status, and potential ecological risk of these metals. The mean concentrations of heavy metals in sediments other than Be exceeded their local background values. Geoaccumulation index and potential ecological risk index analyses demonstrated that most sediment samples were contaminated and may pose ecological risks, especially those from the Taihu Lake estuary. In particular, Cd concentrations indicated moderate contamination and potentially serious to severe ecological risk. Principal component, cluster, and correlation analyses demonstrated that Ni, Sb, Cr, and Cu were derived from industrial sources, whereas the other metals had complex origins.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bengrane K, Marhaba TF (2003) Using principal component analysis to monitor spatial and temporal changes in water quality. J Hazard Mater 100:179–195
Chen Y, Fan C, Teubner K et al (2003) Changes of nutrients and phytoplankton chlorophyll-a in a large shallow lake, Taihu, China: an 8-year investigation. Hydrobiologia 506:273–279
Chen C, Zheng B, Jiang X et al (2013) Spatial distribution and pollution assessment of mercury in sediments of Lake Taihu, China. J Environ Sci 25(2):316–325
China Environmental Monitoring Station (CEMS) (1990) Natural background values of soil elements in China. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Dong B, Renzhi Z, Yandong G et al (2019) Multiple methods for the identification of heavy metal sources in cropland soils from a resource-based region. Sci Total Environ 651:3127–3138
Hai X, Paerl HW, Qin B et al (2010) Nitrogen and phosphorus inputs control phytoplankton growth in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Limnol Oceanogr 55:420–432
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001
Hong Y, Jian L, Xin Y et al (2014) Concentrations, bioavailability, and spatial distribution of soil heavy metals in a long-term wastewater irrigation area in North China. Clean Soil Air Water 42:331–338
Jang CS, Liu CW, Lin KH et al (2006) Spatial analysis of potential carcinogenic risks associated with ingesting arsenic in aquacultural Tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) in blackfoot disease hyperendemic areas. Environ Sci Technol 40:1707–1713
Krishna AK, Satyanarayanan M, Govil PK (2009) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in water using multivariate statistical techniques in an industrial area: a case study from Patancheru, Medak District, Andhra Pradesh, India. J Hazard Mater 167:366–373
Li J, Ming H, Han W et al (2009) Analysis and assessment on heavy metal sources in the coastal soils developed from alluvial deposits using multivariate statistical methods. J Hazard Mater 164:976–981
Li Y, Mei L, Zhou S et al (2018) Analysis of historical sources of heavy metals in Lake Taihu based on the positive matrix factorization model. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15:1540
Liu H, Liqing LI, Yin C et al (2008) Fraction distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Moshui Lake. J Environ Sci 20:390–397
Liu J, Li Y, Bao Z, Cao J et al (2009) Ecological risk of heavy metals in sediments of the Luan River source water. Ecotoxicology 18:748–758
Muller G (1969) Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. GeoJournal 2:109–118
Mwanamoki PM, Devarajan N, Thevenon F et al (2015) Trace metals and persistent organic pollutants in sediments from river-reservoir systems in Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC): spatial distribution and potential ecotoxicological effects. Chemosphere 119:466
Niu Y, Jiang X, Wang K et al (2019) Meta analysis of heavy metal pollution and sources in surface sediments of Lake Taihu, China. Sci Total Environ 700:134509
Qin B, Xu P, Wu Q et al (2007) Environmental issues of Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 581:3–14
Qu W, Dickman M, Wang S (2001) Multivariate analysis of heavy metal and nutrient concentrations in sediments of Taihu Lake, China. Hydrobiologia 450:83–89
Suthar S, Nema AK, Chabukdhara M et al (2009) Assessment of metals in water and sediments of Hindon River, India: impact of industrial and urban discharges. J Hazard Mater 171:1088–1095
Tokalioglu S, Yilmaz V, Kartal S et al (2015) An assessment on metal sources by multivariate analysis and speciation of metals in soil samples using the BCR sequential extraction procedure. Clean Soil Air Water 38:713–718
Tume P, Roca N, Rubio R et al (2018) An assessment of the potentially hazardous element contamination in urban soils of Arica, Chile. J Geochem Expl 184:345–357
Xie Q (2011) Pollution and the potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the sediment of Dadong River. Ind Saf Environ Prot 10:24–26 (in Chinese)
Yao S, Xue B (2010) Nutrients and heavy metals in multi-cores from Zhushan Bay at Taihu Lake, the largest shallow lake in the Yangtze Delta, China. Quat Int 226:23–28
Ying C, Zhang W, Zhou M et al (2016) Comprehensive assessment of heavy metal contamination in surface sediments from the inflow rivers of Taihu Basin. Clean Soil Air Water 43:1582–1591
Zhang YP, Qu WC (2001) Determination of heavy metals in sediments of Taihu Lake and its environmental significance. Rock Miner Anal 20(1):34–36 (in Chinese)
Zhang JC, Lin CH, Lin SX et al (2014) Characteristics of migration and accumulation of heavy metals in soil-plant system in different functional areas of Caohai Watershed in Guizhou. J Soil Water Conserv 2:169–174 (in Chinese)
Zhuang P (2009) Health risk from heavy metals via consumption of food crops in the vicinity of Dabaoshan mine, South China. Sci Total Environ 407:1551–1561
Zhuang W, Wang Q, Tang L et al (2018) A new ecological risk assessment index for metal elements in sediments based on receptor model, speciation, and toxicity coefficient by taking the Nansihu Lake as an example. Ecol Ind 89:725–737
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Open Research Fund of Jiangsu Province Key Laboratory of Environmental Engineering (ZX2018001), and the Taihu Water Pollution Control Fund (TH2018404).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Ren, X., Qiu, Y. et al. Characterization and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in River Sediments on the Western Bank of Taihu Lake, China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 109, 609–615 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03430-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03430-1