Abstract
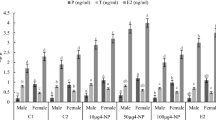
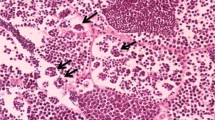
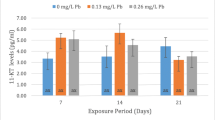
Sera 17β-estradiol (E2), 11-ketotesteron (11-KT) and 17,20-β-dihydroxy-4-pregnen-3-one (17,20βP) levels and hepatosomatic-gonadosomatic indexes (HSI-GSI) were determined after exposing male C. carpio to 0.13 and 0.26 mg L−1 lead after 7, 14 and 21 days. Histological changes in liver and gonad tissues of male C. carpio were also determined. Sera E2, 11-KT and 17,20βP levels of male fish although showed differences from the control fish, these differences were not statistically significant. This was also true for the HSI values, the GSI values however, decreased on day 7 under the effect of 0.26 mg L−1 Pb. Dilatation in bile duct and sinusoids and lymphocyte infiltration were observed under histopathological examination. Low intensities of fibrosis were detected in testis tissues. Exposure to low concentrations of Pb did not cause endocrine disrupting and extensive histopathologic effects in C. carpio at the exposure periods tested.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam M, Maughan O (1992) The effect of malathion, diazinon, and various concentrations of zinc, copper, nickel, lead, iron, and mercury on fish. Biol Trace Elem Res 34(3):225–236
Allen-Gil S, Curtis L, Lasorsa B, Crecelius E, Landers D (1993) Plasma testosterone as a sensitive biomarker to heavy metal exposure in feral arctic fish. Paper presented at the 14 th Annual Meeting (SETAC)-Ecological risk assessment: lessons learned?—Abstract Book
Arellano JM, Storch V, Sarasquete C (1999) Histological changes and copper accumulation in liver and gills of the Senegales sole, Solea senegalensis. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 44(1):62–72
Benze TP, Sakuragui MM, de Paula Zago LH, Fernandes MN (2016) Subchronic exposure to diflubenzuron causes health disorders in neotropical freshwater fish, P. Rochilodus lineatus. Environ Toxicol 31(5):533–542
Bettini S, Ciani F, Franceschini V (2006) Recovery of the olfactory receptor neurons in the African Tilapia mariae following exposure to low copper level. Aquat Toxicol 76(3–4):321–328
Campana O, Sarasquete C, Blasco J (2003) Effect of lead on ALA-D activity, metallothionein levels, and lipid peroxidation in blood, kidney, and liver of the toadfish Halobatrachus didactylus. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 55(1):116–125
Chaube R, Mishra S, Singh RK (2010) In vitro effects of lead nitrate on steroid profiles in the post-vitellogenic ovary of the catfish Heteropneustes fossilis. Toxicol in Vitro 24(7):1899–1904
Choe S-Y, Kim S-J, Kim H-G, Lee JH, Choi Y, Lee H, Kim Y (2003) Evaluation of estrogenicity of major heavy metals. Sci Total Environ 312(1–3):15–21
Choi SM, Yoo SD, Lee BM (2004) Toxicological characteristics of endocrine-disrupting chemicals: developmental toxicity, carcinogenicity, and mutagenicity. J Toxicol Environ Health Part B 7(1):1–23
Costa PM, Diniz MS, Caeiro S, Lobo J, Martins M, Ferreira AM, Caetano M, Vale C, DelValls TÁ, Costa MH (2009) Histological biomarkers in liver and gills of juvenile Solea senegalensis exposed to contaminated estuarine sediments: a weighted indices approach. Aquat Toxicol 92(3):202–212
Darbre P (2006) Metalloestrogens: an emerging class of inorganic xenoestrogens with potential to add to the oestrogenic burden of the human breast. J Appl Toxicol 26(3):191–197
Davey JC, Bodwell JE, Gosse JA, Hamilton JW (2007) Arsenic as an endocrine disruptor: effects of arsenic on estrogen receptor–mediated gene expression in vivo and in cell culture. Toxicol Sci 98(1):75–86
do Carmo Silva JP, da Costa MR, Araújo FG (2019) Energy acquisition and allocation to the gonadal development of Cynoscion leiachus (Perciformes, Sciaenidae) in a tropical Brazilian bay. Mar Biol Res 15(2):170–180
Dyer C (2007) Heavy metals as endocrine-disrupting chemicals. In: Gore AC (ed) Endocrine-disrupting chemicals: from basic research to clinical practice. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 111–133
Ebrahimi M, Taherianfard M (2011) The effects of heavy metals exposure on reproductive systems of cyprinid fish from Kor River. Iran J Fish Sci 10(1):13–26
Fatima M, Usmani N (2013) Histopathology and bioaccumulation of heavy metals (Cr, Ni and Pb) in fish (Channa striatus and Heteropneustes fossilis) tissue: a study for toxicity and ecological impacts. Pak J Biol Sci 16(9):412–420
Figueiredo-Fernandes A, Ferreira-Cardoso JV, Garcia-Santos S, Monteiro SM, Carrola J, Matos P, Fontaínhas-Fernandes A (2007) Histopathological changes in liver and gill epithelium of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, exposed to waterborne copper. Pesq Vet Bras 27(3):103–109
Friedmann A, Watzin M, Leiter J, Brinck-Johnsen T (1996) Effects of environmental mercury on gonadal function in Lake Champlain northern pike (Esox lucius). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 56(3):486–492
Georgescu B, Georgescu C, Dărăban S, Bouaru A, Paşcalău S (2011) Heavy metals acting as endocrine disrupters. Sci Papers Anim Sci Biotechnol 44(2):89–93
Ghasemi A, Zahediasl S (2012) Normality tests for statistical analysis: a guide for non-statisticians. Int J Endocrinol Metab 10(2):486
Hammerschmidt CR, Sandheinrich MB, Wiener JG, Rada RG (2002) Effects of dietary methylmercury on reproduction of fathead minnows. Environ Sci Technol 36(5):877–883
Iavicoli I, Fontana L, Bergamaschi A (2009) The effects of metals as endocrine disruptors. J Toxicol Environ Health Part B 12(3):206–223
Kaoud H, El-Dahshan A (2010) Bioaccumulation and histopathological alterations of the heavy metals in Oreochromis niloticus fish. Nat Sci 8(4):147–156
Kim J-H, Kang J-C (2015) The lead accumulation and hematological findings in juvenile rock fish Sebastes schlegelii exposed to the dietary lead (II) concentrations. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 115:33–39
Kime DE (2012) Endocrine disruption in fish. Springer, New York
Kirubagaran R, Joy K (1992) Toxic effects of mercury on testicular activity in the freshwater teleost, Clarias batrachus (L.). J Fish Biol 41(2):305–315
Korkmaz C, Ay Ö, Dönmez AE, Demirbağ B, Erdem C (2020) Influence of lead on reproductive physiology and gonad and liver histology of female Cyprinus carpio. Thalassas 36:1–10
Kumar S, Pant S (1984) Comparative effects of the sublethal poisoning of zinc, copper and lead on the gonads of the teleost Puntius conchonius Ham. Toxicol Lett 23(2):189–194
Kumari M, Dutt NG (1991) Cadmium-induced histomorphological changes in the testis and pituitary gonadotrophic hormone secreting cells of the cyprinid Puntius sarana. Ital J Zool 58(1):71–76
Kunz PY, Fent K (2006) Estrogenic activity of UV filter mixtures. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 217(1):86–99
Levesque H, Moon T, Campbell P, Hontela A (2002) Seasonal variation in carbohydrate and lipid metabolism of yellow perch (Perca flavescens) chronically exposed to metals in the field. Aquat Toxicol 60(3–4):257–267
Maanan M (2008) Heavy metal concentrations in marine molluscs from the Moroccan coastal region. Environ Pollut 153(1):176–183
Mansour DF, Saleh DO, Ahmed-Farid OA, Rady M, Bakeer RM, Hashad IM (2021) Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) mitigates methotrexate-induced testicular insult in rats: targeting oxidative stress, energy deficit and spermatogenesis. Biomed Pharmacother 143:112201
Mantovani A, Stazi A, Macri C, Maranghi F, Ricciardi C (1999) Problems in testing and risk assessment of endocrine disrupting chemicals with regard to developmental toxicology. Chemosphere 39(8):1293–1300
Mishra AK, Mohanty B (2012) Effect of sublethal hexavalent chromium exposure on the pituitary-ovarian axis of a teleost, Channa punctatus (Bloch). Environ Toxicol 27(7):415–422
Muramoto S (1983) Elimination of copper from Cu-contaminated fish by long-term exposure to EDTA and fresh water. J Environ Sci Health Part A 18(3):455–461
Oishi S (2002) Effects of propyl paraben on the male reproductive system. Food Chem Toxicol 40(12):1807–1813
Pine M, Lee B, Dearth R, Hiney JK, Dees WL (2005) Manganese acts centrally to stimulate luteinizing hormone secretion: a potential influence on female pubertal development. Toxicol Sci 85(2):880–885
Raldúa D, Díez S, Bayona JM, Barceló D (2007) Mercury levels and liver pathology in feral fish living in the vicinity of a mercury cell chlor-alkali factory. Chemosphere 66(7):1217–1225
Roy D, Palangat M, Chen C-W, Thomas RD, Colerangle J, Atkinson A, Yan Z-J (1997) Biochemical and molecular changes at the cellular level in response to exposure to environmental estrogen-like chemicals. J Toxicol Environ Health A 50(1):1–30
Ruby SM, Jaroslawski P, Hull R (1993) Lead and cyanide toxicity in sexually maturing rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss during spermatogenesis. Aquat Toxicol 26(3–4):225–238
Sellin MK, Kolok AS (2006) Cadmium exposures during early development: do they lead to reproductive impairment in Fathead minnows? Environ Toxicol Chem 25(11):2957–2963
Short S and Meyers TR (2001) Histology for finfish. NWFHS laboratory procedures manual. Version, 1(0).
Shukla JP, Pandey K (1984) Impaired spermatogenesis in arsenic treated freshwater fish, Colisa fasciatus (Bl. and Sch.). Toxicol Lett 21(2):191–195
Singh H (1989) Interaction of xenobiotics with reproductive endocrine functions in a protogynous teleost, Monopterus albus. Mar Environ Res 28(1–4):285–289
Srivastava A (1987) Changes induced by lead in fish testis. J Environ Biol 8(4):329–332
Tseng C-H, Chong C-K, Tseng C-P, Hsueh Y-M, Chiou H-Y, Tseng C-C, Chen C-J (2003) Long-term arsenic exposure and ischemic heart disease in arseniasis-hyperendemic villages in Taiwan. Toxicol Lett 137(1–2):15–21
Van Dyk JC, Pieterse G, Van Vuren J (2007) Histological changes in the liver of Oreochromis mossambicus (Cichlidae) after exposure to cadmium and zinc. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 66(3):432–440
Velma V, Tchounwou PB (2010) Chromium-induced biochemical, genotoxic and histopathologic effects in liver and kidney of goldfish, Carassius auratus. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen 698(1):43–51
Weber D (1993) Exposure to sublethal levels of waterborne lead alters reproductive behavior patterns in fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas). Neurotoxicology 14(2–3):347–358
Wong P, Silverberg B, Chau Y, Hodson P (1978) Lead and the aquatic biota. The biogeochemistry of lead in the environment. Part B. Biological effects. Elsevier/North Holland Biomedical Press, Amsterdam, pp 279–342
Yamaguchi S, Miura C, Ito A, Agusa T, Iwata H, Tanabe S, Tuyen BC, Miura T (2007) Effects of lead, molybdenum, rubidium, arsenic and organochlorines on spermatogenesis in fish: monitoring at Mekong Delta area and in vitro experiment. Aquat Toxicol 83(1):43–51
Funding
This study was funded by Research Project Coordination Unit of Mersin University (2016-2-TP3-1835).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors Cengiz Korkmaz, Özcan Ay, Ahmet Erdem Dönmez, Burcu Demirbağ and Cahit Erdem declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Korkmaz, C., Ay, Ö., Dönmez, A.E. et al. Effects of Lead on Reproduction Physiology and Liver and Gonad Histology of Male Cyprinus carpio. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 108, 685–693 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03426-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03426-x