Abstract
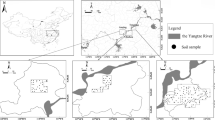
Knowledge from the negative impacts of the counties’ anthropogenic activities on soil pollution was of great significance in China, and valuable information was urgently needed for the control and remediation of soil pollution. The current pollution levels of heavy metals (Cu, Pb, Cd, Zn, Ni, and Cr) in farmland soils were investigated in Yangxin County, Hubei Province, central China. The comprehensive results of quantitative comparison and evaluation in this study showed that Cu (144.9 ± 298.6 mg kg−1), Cd (2.9 ± 1.6 mg kg−1), and Ni (137.0 ± 111.0 mg kg−1) posed higher pollution risks to public and ecosystem health, which were higher than the corresponding soil background values. The combined results of geostatistics, spatial and statistical analysis indicated that studied heavy metals were mainly attributed to agricultural, traffic and industrial induced pollution. Overall, urgent attention should be paid to the risk reduction and management of soil Cu, Cd, and Ni pollution in the study area.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chakraborty P, Sampath S, Mukhopadhyay M et al (2019) Baseline investigation on plasticizers, bisphenol a, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and heavy metals in the surface soil of the informal electronic waste recycling workshops and nearby open dumpsites in Indian metropolitan cities. Environ Pollut 248:1036–1045
Chen T, Chang QR, Liu J et al (2016) Identification of soil heavy metal sources and improvement in spatial mapping based on soil spectral information: a case study in Northwest China. Sci Total Environ 565:155–164
Ciarkowska K (2018) Assessment of heavy metal pollution risks and enzyme activity of meadow soils in urban area under tourism load: a case study from Zakopane (Poland). Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:13709–13718
CNEMC (China National Environmental Monitoring Center) (1990) Background values of soil elements in China. Environmental Science Press, Beijing, China (in Chinese)
Dong RZ, Jia ZM, Li SY (2018) Risk assessment and sources identification of soil heavy metals in a typical county of Chongqing municipality, southwest China. Process Safe Environ 113:275–281
Dong B, Zhang RZ, Gan YD et al (2019) Multiple methods for the identification of heavy metal sources in cropland soils from a resource-based region. Sci Total Environ 651:3127–3138
Doyi I, Essumang D, Gbeddy G et al (2018) Spatial distribution, accumulation and human health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil and groundwater of the Tano Basin, Ghana. Ecotox Environ Safe 165:540–546
Fei XF, Christakos G, Xiao R et al (2019) Improved heavy metal mapping and pollution source apportionment in shanghai city soils using auxiliary information. Sci Total Environ 661:168–177
Gao J, Wang LC (2018) Ecological and human health risk assessments in the context of soil heavy metal pollution in a typical industrial area of Shanghai, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:27090–27105
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. a sedimentological approach. Water Res 14:975–1001
He JY, Yang Y, Christakos G et al (2019) Assessment of soil heavy metal pollution using stochastic site indicators. Geoderma 337:359–367
Huang JH, Guo ST, Zeng GM et al (2018) A new exploration of health risk assessment quantification from sources of soil heavy metals under different land use. Environ Pollut 243:49–58
Iwegbue CMA, Martincigh BS (2018) Ecological and human health risks arising from exposure to metals in urban soils under different land use in Nigeria. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:12373–12390
Jia XL, Hu BF, Marchant B et al (2019) A methodological framework for identifying potential sources of soil heavy metal pollution based on machine learning: a case study in the Yangtze Delta, China. Environ Pollut 250:601–609
Jiang YF, Ye YC, Guo X (2019) Spatiotemporal variation of soil heavy metals in farmland influenced by human activities in the Poyang Lake region, China. CATENA 176:279–288
Kim JY, Kim KW, Lee JU et al (2002) Assessment of As and heavy metal contamination in the vicinity of Duckum Au-Ag mine, Korea. Environ Geochem Health 24:213–225
Kumar V, Sharma A, Kaur P et al (2019) Pollution assessment of heavy metals in soils of India and ecological risk assessment: a state-of-the-art. Chemosphere 216:449–462
Li YF, Zhao ZQ, Yuan Y et al (2019) Application of modified receptor model for soil heavy metal sources apportionment: a case study of an industrial city, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:16345–16354
Lian MH, Wang J, Sun LN et al (2019) Profiles and potential health risks of heavy metals in soil and crops from the watershed of Xi River in Northeast China. Ecotox Environ Safe 169:442–448
Liu HW, Wang HY, Zhang Y et al (2018) Risk assessment, spatial distribution, and source apportionment of heavy metals in Chinese surface soils from a typically tobacco cultivated area. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:16852–16863
Luo P, Xiao X, Han XX et al (2019) Application of different single extraction procedures for assessing the bioavailability of heavy metal(loid)s in soils from overlapped areas of farmland and coal resources. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:14932–14942
MEEC (Ministry of Ecology and Environment of China) (2018) Environmental quality standard for soils (GB 15618–2008). Beijing, China (in Chinese)
MEEC and MNRC. (2014) Report on the national general survey of soil pollution condition. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of China (MEEC) and Ministry of Natural Resources of China (MNRC), Beijing, China (in Chinese)
Ni MF, Mao R, Jia ZM et al (2018) Heavy metals in soils of Hechuan County in the upper Yangtze (SW China): comparative pollution assessment using multiple indices with high-spatial-resolution sampling. Ecotox Environ Safe 148:644–651
Notten MJM, Oosthoek AJP, Rozema J et al (2005) Heavy metal concentrations in a soil–plant–snail food chain along a terrestrial soil pollution gradient. Environ Pollut 138:178–190
Pan LB, Ma J, Wang XL et al (2016a) Heavy metals in soils from a typical county in Shanxi Province, China: levels, sources and spatial distribution. Chemosphere 148:248–254
Pan LB, Ma J, Hu Y et al (2016b) Assessments of levels, potential ecological risk, and human health risk of heavy metals in the soils from a typical county in Shanxi Province, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:19330–19340
Qiao PW, Yang SC, Lei M et al (2018) Quantitative analysis of the factors influencing spatial distribution of soil heavy metals based on geographical detector. Sci Total Environ 664:392–413
Ren J, Chen J, Han L et al (2018) Spatial distribution of heavy metals, salinity and alkalinity in soils around bauxite residue disposal area. Sci Total Environ 628–629:1200–1208
Wang L, Yang D, Li ZT et al (2019a) A comprehensive mitigation strategy for heavy metal contamination of farmland around mining areas-screening of low accumulated cultivars, soil remediation and risk assessment. Environ Pollut 245:820–828
Wang MS, Han Q, Gui CL et al (2019b) Differences in the risk assessment of soil heavy metals between newly built and original parks in Jiaozuo, Henan Province, China. Sci Total Environ 676:1–10
Wang S, Cai LM, Wen HH et al (2019c) Spatial distribution and source apportionment of heavy metals in soil from a typical county-level city of Guangdong Province, China. Sci Total Environ 655:92–101
Weissmannová HD, Pavlovský J (2017) Indices of soil contamination by heavy metals-methodology of calculation for pollution assessment (minireview). Environ Monit Assess 189:616
Wu W, Wu P, Yang F et al (2018) Assessment of heavy metal pollution and human health risks in urban soils around an electronics manufacturing facility. Sci Total Environ 630:53–61
Xiao R, Guo D, Ali A et al (2019) Accumulation, ecological-health risks assessment, and source apportionment of heavy metals in paddy soils: a case study in Hanzhong, Shaanxi, China. Environ Pollut 248:349–357
Xu DM, Yan B, Chen T et al (2017) Contaminant characteristics and environmental risk assessment of heavy metals in the paddy soils from lead (Pb)-zinc (Zn) mining areas in Guangdong Province, south China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:24387–24399
Xu DM, Zhang JQ, Yan B et al (2018) Contamination characteristics and potential environmental implications of heavy metals in road dusts in typical industrial and agricultural cities, southeastern Hubei Province, central China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:36223–36238
Yadav IC, Devi NL, Singh VK et al (2019) Spatial distribution, source analysis, and health risk assessment of heavy metals contamination in house dust and surface soil from four major cities of Nepal. Chemosphere 218:1100–1113
Yang QQ, Li ZY, Lu XN et al (2018) A review of soil heavy metal pollution from industrial and agricultural regions in China: pollution and risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 642:690–700
Zhang XY, Lin FF, Wong MTF et al (2009) Identification of soil heavy metal sources from anthropogenic activities and pollution assessment of Fuyang County, China. Environ Monit Assess 154:439–449
Zhang Y, Yin CB, Cao SZ et al (2018) Heavy metal accumulation and health risk assessment in soil-wheat system under different nitrogen levels. Sci Total Environ 622–623:1499–1508
Zhao KL, Zhang WW, Zhou L et al (2009) Modeling transfer of heavy metals in soil–rice system and their risk assessment in paddy fields. Environ Earth Sci 59:519–527
Zhao XQ, Huang J, Lu J et al (2019) Study on the influence of soil microbial community on the long-term heavy metal pollution of different land use types and depth layers in mine. Ecotox Environ Safe 170:218–226
Zhong LY, Liu LM, Yang JW (2012) Characterization of heavy metal pollution in the paddy soils of Xiangyin County, Dongting Lake drainage basin, central South China. Environ Earth Sci 67:2261–2268
Zhuo HM, Fu SZ, Liu H et al (2019) Soil heavy metal contamination and health risk assessment associated with development zones in Shandong, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:30016–30028
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Foundation of State Key Laboratory of Loess and Quaternary Geology (No. SKLLQG1935), the Key Program of Hubei Polytechnic University (No. 19XJK01Z), the Young Talents Project of Science and Technology Research Program of Hubei Education Department (No. Q20204503), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41603117). The authors are very grateful to the anonymous reviewers for their revising suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, D., Zhou, Z., Zhan, C. et al. Pollution Characteristics and Associated Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Farmland Soils From a Typical County of Hubei Province, Central China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 107, 327–335 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03303-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03303-7