Abstract
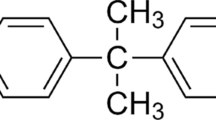
2,2',3,5',6-Pentachlorobiphenyl (PCB-95) is an environmentally relevant, chiral PCB congener that has been shown to act as a developmental neurotoxicant (DNT), targeting the developing brain. However, understanding enantioselective toxic effects for PCB-95 is in its infancy. To investigate these toxic effects, zebrafish embryos were exposed to racemates and enantiomers of PCB-95. Brain areas and pathology were studied. Results indicated dose dependent reduction of brain sizes with increased brain cell death in racemic and Ra (-)-PCB-95 treated groups. To provide a mechanistic basis for the observed neurotoxicity, gene expressions of antioxidant proteins such as Cu/Zn-SOD, Mn-SOD, and GPx were analysed. Antioxidant genes were up regulated with the PCB-95 exposure and racemic PCB-95 showed higher toxicity. These results suggest that the exposure to PCB-95 contributed to developmental neurotoxicity in early developing zebrafish larvae and may confer risks associated with enantioselective enrichment of PCB-95 in the environment.
Graphical Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bambino K, Chu J (2017) Zebrafish in toxicology and environmental health. Curr Top Biol Dev 124:331–367
Bandara SB, Eubig PA, Sadowski RN, Schantz SL (2016) Developmental PCB exposure increases audiogenic seizures and decreases glutamic acid decarboxylase in the inferior colliculus. Toxicol Sci 149(2):335–345
Cedergreen N (2014) Quantifying synergy A systematic review of mixture toxicity studies within environmental toxicology. PLoS ONE 9(5):e96580
Chen SJ, Tian M, Zheng J, Zhu ZC, Luo Y, Luo XJ, Mai BX (2014) Elevated levels of polychlorinated biphenyls in plants, air, and soils at an e-waste site in Southern China and enantioselective biotransformation of chiral PCBs in plants. Environ Sci Technol 48(7):3847–3855
Chu S, Covaci A, Schepens P (2003) Levels and chiral signatures of persistent organochlorine pollutants in human tissues from Belgium. Environ Res 93:167–176
Dang VD, Walters DM, Lee CM (2010) Transformation of chiral Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) in a stream food web. Environ Sci Technol 44:2836–2841
D’Amora M, Sancataldo G, Cella Zanacchi F, Diaspro A (2016) Influence of nanoparticle exposure on nervous system development in zebrafish studied by means of light sheet fluorescence microscopy. Biophys J 110:148A
DeLeon S, Webster MS, DeVoogd TJ, Dhondt AA (2020) Developmental polychlorinated biphenyl exposure influences adult zebra finch reproductive behaviour. PLoS ONE 15(3):0230283
Feng W, Zheng J, Robin G, Dong Y, Ichikawa M, Inoue Y, Mori T, Nakano T, Pessah I (2017) Enantioselectivity of 2,2′,3,5′,6-Pentachlorobiphenyl (PCB 95) atropisomers toward ryanodine receptors (RyRs) and their influences on hippocampal neuronal networks. Environ Sci Technol 51(24):14406–14416
Gonzalez ST, Remick D, Creton R, Colwill RM (2016) Effects of embryonic exposure to polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) on anxiety-related behaviors in larval zebrafish. Neurotoxicology 53:93–101
Howe K, Clark MD, Torroja CF, Torrance J, Berthelot C, Muffato M (2013) The zebrafish reference genome sequence and its relationship to the human genome. Nature 496:498–503
Jacobson SW, Fein GG, Jacobson JL, Schwartz PM, Dowler JK (1985) The effect of intrauterine PCB exposure on visual recognition memory. Child Dev 56:856–860
Kalueff AV, Echevarria D, Stewart AM (2014) Gaining translational momentum: more zebrafish models for neuroscience research. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 55:1–6
Kania-Korwel I, Barnhart C, Stamou M, Truong K, Lein E-K (2012) 2,2′,3,5′,6-Pentachlorobiphenyl (PCB 95) and its hydroxylated metabolites are enantiomerically enriched in female mice. Environ Sci Technol 46(20):11393–11401
Kania-Korwel I, Garrison AW, Avants JK, Hornbuckle KC, Robertson LW, Sulkowski WW, Lehmler H-J (2006) Distribution of chiral PCBs in selected tissues in the laboratory rat. Environ Sci Technol 40:3704–3710
Keil KP, Miller GW, Chen H, Sethi S, Schmuck MR, Dhakal K, Kim JW, Lein PJ (2018) PCB 95 promotes dendritic growth in primary rat hippocampal neurons via mTOR-dependent mechanisms. Arch Toxicol 92(10):3163–3173
Kim J, Oh H, Ryu B, Kim U, Lee JM, Jung C-R (2018) Triclosan affects axon formation in the neural development stages of zebrafish embryos (Danio rerio). Environ Pollut 236:304–312
Klocke C, Lein PJ (2020) Evidence implicating non-dioxin-like congeners as the key mediators of polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) developmental neurotoxicity. Int J Mol Sci 21(3):1013
Lee DW, Notter SA, Thiruchelvam M, Dever DP, Fitzpatrick R, Kostyniak PJ, Cory-Slechta DA, Opanashuk LA (2012) Subchronic polychlorinated biphenyl (Aroclor 1254) exposure produces oxidative damage and neuronal death of ventral midbrain dopaminergic systems. Toxicol Sci 125(2):496–508
Lehmler H-J, Price DJ, Garrison AW, Birge WJ, Robertson LW (2003) Distribution of PCB 84 enantiomers in C57Bl/6 mice. Fresenius’ Environ Bull 12:254–260
Lesiak A, Zhu M, Chen H, Appleyard S, Impey S, Lein P, Wayman G (2014) The environmental neurotoxicant PCB 95 promotes synaptogenesis via ryanodine receptor-dependent miR132 upregulation. J Neurosci 34(3):717–725
Lovato AK, Creton R, Colwill RM (2016) Effects of embryonic exposure to polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) on larval zebrafish behavior. Neurotoxicol Teratol 53:1
Mitchell MM, Woods R, Chi LH, Schmidt RJ, Pessah IN, Kostyniak PJ, LaSalle JM (2012) Levels of select PCB and PBDE congeners in human postmortem brain reveal possible environmental involvement in 15q11-q13 duplication autism spectrum disorder. Environ Mol Mutagen 53:589–598
Pakdeesusuk U, Lee CM, Coates JT, Freedman DL (2005) Assessment of natural attenuation via in situ reductive dechlorination of polychlorinated biphenyls in sediments of the Twelve Mile Creek arm of Lake Hartwell. SC Environ Sci Technol 39(4):945–952
Patandin S, Koopman-Esseboom C, De Ridder MA, Weisglas-Kuperus N, Sauer PJ (1998) Effects of environmental exposure to polychlorinated biphenyls and dioxins on birth size and growth in Dutch children. Pediatr Res 44(4):538–545
Pessah I, Cherednichenko G, Lein P (2010) Minding the calcium store: Ryanodine receptor activation as a convergent mechanism of PCB toxicity. Pharmacol Ther 125(2):260–285
Pessah IN, Lein PJ, Seegal RF, Sagiv SK (2019) Neurotoxicity of polychlorinated biphenyls and related organohalogens. Acta Neuropathol 11:1–25
Peterson S, Freeman J (2009) RNA isolation from embryonic zebrafish and cDNA synthesis for gene expression analysis. J Visualized Exp 2:30
Ranasinghe P, Olivares C, Champion W, Lee CM (2019) Atropisomeric separation of PCB-95 by HPLC. Sci J Chem 7(2):39–48
Ranasinghe P, Thorn R, Seto R, Creton R, Bridges W, Lee CS (2020) Embryonic exposure to 2,2′,3,5′,6-pentachlorobiphenyl (PCB-95) causes developmental malformations in zebrafish. Environ Toxicol Chem 39(1):162–170
Ross MS, Pulster EL, Ejsmont MB, Chow EA, Hessel CM, Maruya KA, Wong CS (2011) Enantioselectivity of polychlorinated biphenyl atropisomers in sediment and biota from the Turtle/Brunswick River estuary, Georgia, USA. Mar Pollut Bull 63(5–12):548–555
Schlezinger JJ, White RD, Stegeman JJ (1999) Oxidative inactivation of cytochrome P-450 1A (CYP1A) stimulated by 3, 3′, 4, 4′-tetrachlorobiphenyl: production of reactive oxygen by vertebrate CYP1As. Mol Pharmacol 56(3):588–597
Szafran-Urbaniak B (2008) Application of validated method for determination of selected polychlorinated biphenyls in human adipose tissue samples. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 25(2):131–135
Szymkowicz DB, Sims KC, Castro NM, Bridges WC, Bain LJ (2017) Embryonic-only arsenic exposure in killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus) reduces growth and alters muscle IGF levels one year later. Aquat Toxicol 186:1
Uwimana E, Li X, Lehmler HJ (2016) 2, 2′, 3, 5′, 6-Pentachlorobiphenyl (PCB 95) is atropselectively metabolized to para-hydroxylated metabolites by human liver microsomes. Chem Res Toxicol 29(12):2108–2110
Warner NA, Norstrom RJ, Wong CS, Fisk AT (2005) Enantiomeric fractions of chiral polychlorinated biphenyls provide insights on biotransformation capacity of arctic biota. Environ Toxicol Chem 24(11):2763–2767
Wirbisky SE, Weber GJ, Lee JW, Cannon JR, Freeman JL (2014) Novel dose-dependent alterations in excitatory GABA during embryonic development associated with lead (Pb) neurotoxicity. Toxicol Lett 229(1):1–8
Wong F, Robson M, Diamond ML, Harrad S, Truong J (2009) Concentrations and chiral signatures of POPs in soils and sediments: a comparative urban versus rural study in Canada and UK. Chemosphere 74(3):404–411
Xu N, Mu P, Yin Z, Jia Q, Yang S, Qian Y, Qiu J (2016) Analysis of the enantioselective effects of PCB95 in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos through targeted metabolomics by UPLC-MS/MS. PLoS ONE 11(8):e0160584
Yang D, Kim KH, Phimister A, Bachstetter AD, Ward TR, Stackman RW, Mervis RF, Wisniewski AB, Klein SL, Kodavanti PRS, Anderson KA, Wayman G, Pessah IN, Lein PJ (2009) Developmental exposure to polychlorinated biphenyls interferes with experience-dependent dendritic plasticity and ryanodine receptor expression in weanling rats. Environ Health Perspect 117:426–435
Zheng J, Yu L, Chen S, Hu G, Chen K, Yan X, Luo X, Zhang S, Yu Y, Yang Z, Mai B (2016) Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in human hair and serum from e-waste recycling workers in southern China: Concentrations, chiral signatures, correlations, and source identification. Environ Sci Technol 50:1579–1586
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. William C. Bridges for his contribution in statistical analysis; Dr. Susan C. Chapman for her help with the zebrafish husbandry and providing zebrafish for experiments; and Dr. Lisa J. Bain for her contribution in transcriptomic analysis; all from Clemson University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ranasinghe, P., Thorn, R.J., Creton, R. et al. Enantioselective Toxicity Effects of 2,2’,3,5’,6-Pentachloro Biphenyl (PCB-95) on Developing Brains in Zebrafish Larvae. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 107, 351–360 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03294-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03294-5