Abstract
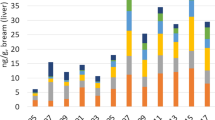
Due to the strict control on bisphenol A (BPA) in many countries, bisphenol analogues (BPs) are being widely used as alternative materials to manufacture epoxy resins and polycarbonate plastics, resulting in their occurrence in sewage treatment plants (STPs). In this study, the occurrence and distribution of 7 BPs in a large-scale STP in Beijing China was investigated. Wastewater samples were collected from the influents and effluents of each processing unit, and extracted by solid-phase extraction. Target compounds were quantified by ultra-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC–MS/MS). The total concentrations of seven BPs (ΣBPs) were 400.42 ± 48.12 ng/L in the raw sewage, 438.60 ± 46.50 ng/L in the primary effluent, 17.21 ± 13.12 ng/L in the secondary effluent, and 11.33 ± 4.84 ng/L in the tertiary effluent, respectively. Bisphenol S (BPS) and BPA were the predominant congener in raw sewage with an overall contribution of 29.32% and 70.22% to the ΣBPs, indicating that there was a large amount of BPS and BPA consumption in the study area. During a one-week sampling period, ΣBPs changed slightly at the same sampling site. It was found that high removal efficiencies were achieved for BPs in anoxic and oxic secondary clarifier treatment units, suggesting that biodegradation and sorption played major roles in BPs elimination in the STP. After tertiary treatment, all BPs except BPA were completely removed, suggesting the necessity to investigate the fate and toxicity of BPA in the aquatic environment.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker ME, Chandsawangbhuwana C (2012) 3D models of MBP, a biologically active metabolite of bisphenol A, in human estrogen receptor α and estrogen receptor β [J]. PLoS ONE 7(10):e46078
Blair BD, Crago JP, Hedman CJ et al (2013) Pharmaceuticals and personal care products found in the Great Lakes above concentrations of environmental concern [J]. Chemosphere 93(9):2116–2123
Caballero-Casero N, Lunar L, Rubio S (2016) Analytical methods for the determination of mixtures of bisphenols and derivatives in human and environmental exposure sources and biological fluids A review [J]. Anal Chim Acta 908:22–53
Cirja M, Ivashechkin P, Schaffer A (2008) Factors affecting the removal of organic micropollutants from wastewater in conventional treatment plants (CTP) and membrane bioreactors (MBR) [J]. Reviews in Environmental Science & Bio/technology 7(1):61–78
Costanza J, Lynch DG, Boethling RS et al (2012) Use of the bioaccumulation factor to screen chemicals for bioaccumulation potential [J]. Environ Toxicol Chem 3(10):2261
Fernandezfontaina E, Omil F, Lema JM et al (2012) Influence of nitrifying conditions on the biodegradation and sorption of emerging micropollutants [J]. Water Res 46(16):5434–5444
Golovko O, Kumar V, Fedorova G et al (2014) Removal and seasonal variability of selected analgesics/anti-inflammatory, anti-hypertensive/cardiovascular pharmaceuticals and UV filters in wastewater treatment plant [J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(12):7578–7585
Gramec SD, Peterlin ML (2016) Bisphenol A and its analogs: do their metabolites have endocrine activity? [J]. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 47:182–199
Guerra P, Kim M, Teslic S et al (2015) Bisphenol-A removal in various wastewater treatment processes: operational conditions, mass balance, and optimization [J]. J Environ Manage 152(2):192–200
Haifeng Z et al (2018) Occurrence and exposure assessment of bisphenol analogues in source water and drinking water in China [J]. Sci Total Environ 655:607–613
He YJ, Chen W, Zheng XY et al (2013) Fate and removal of typical pharmaceuticals and personal care products by three different treatment processes [J]. Sci Total Environ 447(1):248–254
Heinonen J, Honkanen J, Kukkonen JV et al (2002) Bisphenol A accumulation in the freshwater clam Pisidium amnicum at low temperatures. Arch Environ Contaminat Toxicol 43(1):50–55
Koh YK, Chiu TY, Boobis A et al (2008) Treatment and removal strategies for estrogens from wastewater [J]. Environ Technol 29(3):245–267
Lee S, Liu X, Takeda S et al (2013) Genotoxic potentials and related mechanisms of bisphenol A and other bisphenol compounds: A comparison study employing chicken DT40 cells [J]. Chemosphere 93(2):434–440
Lee S, Liao C, Song GJ et al (2015) Emission of bisphenol analogues including bisphenol A and bisphenol F from wastewater treatment plants in Korea [J]. Chemosphere 119(119C):1000–1006
Li D, Zhou Z, Qing D et al (2010) Occupational exposure to bisphenol-A (BPA) and the risk of self-reported male sexual dysfunction [J]. Hum Reprod 25(2):519–527
Liao C, Liu F, Guo Y et al (2012a) Occurrence of eight bisphenol analogues in indoor dust from the united states and several asian countries: implications for human exposure [J]. Environ Sci Technol 46(16):9138–9145
Liao C, Liu F, Moon HB et al (2012b) Bisphenol analogues in sediments from industrialized areas in the United States, Japan, and Korea: spatial and temporal distributions [J]. Environ Sci Technol 46(21):11558–11565
Liu YH, Zhang SH, Ji GX et al (2016) Occurrence, distribution and risk assessment of suspected endocrine-disrupting chemicals in surface water and suspended particulate matter of Yangtze River (Nanjing section) [J]. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 135:90–97
Lu J, Wu J, Stoffella PJ et al (2015) Uptake and distribution of bisphenol A and nonylphenol in vegetable crops irrigated with reclaimed water. J Hazardous Mater 283:865–870
Nie M, Yan C, Dong W et al (2015) Occurrence, distribution and risk assessment of estrogens in surface water, suspended particulate matter, and sediments of the Yangtze Estuary [J]. Chemosphere 127:109–116
Perez P, Olea N (1998) The estrogenicity of bisphenol a-related diphenylalkanes with various substituents at the central carbon and the hydroxy groups [J]. Environ Health Perspect 106(3):167–174
Qian Y, Jia X, Ding T et al (2021) Occurrence and removal of bisphenol analogues in wastewater treatment plants and activated sludge bioreactor [J]. Sci Total Environ 758:143606
Rodayan A, Segura PA, Yargeau V (2014) Ozonation of wastewater: removal and transformation products of drugs of abuse [J]. Sci Total Environ 487(14):763–770
Song S, Song M, Zeng L et al (2014) Occurrence and profiles of bisphenol analogues in municipal sewage sludge in China [J]. Environ Pollut 186(1):14–19
Sun Q, Wang Y, Li Y et al (2017) Fate and mass balance of bisphenol analogues in wastewater treatment plants in Xiamen City, China [J]. Environ Pollut 225:542–549
Usman A, Ahmad M (2016) From BPA to its analogues: Is it a safe journey? [J]. Chemosphere 158:131–142
Wu Q, Lam JCW, Kwok KY et al (2017) Occurrence and fate of endogenous steroid hormones, alkylphenol ethoxylates, bisphenol A and phthalates in municipal sewage treatment systems [J]. J Environ Sci 61(11):49–58
Xue J, Kannan K (2018) Mass flows and removal of eight bisphenol analogs, bisphenol A diglycidyl ether and its derivatives in two wastewater treatment plants in New York State, USA [J]. Sci Total Environ 648:442–449
Xue W, Wu C, Xiao K et al (2010) Elimination and fate of selected micro-organic pollutants in a full-scale anaerobic/anoxic/aerobic process combined with membrane bioreactor for municipal wastewater reclamation [J]. Water Res 44(20):5999–6010
Yamazaki E, Yamashita N, Taniyasu S et al (2015) Bisphenol A and other bisphenol analogues including BPS and BPF in surface water samples from Japan, China, Korea and India [J]. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 122:565–572
Yang Y, Lu L, Zhang J et al (2014) Simultaneous determination of seven bisphenols in environmental water and solid samples by liquid chromatography–electrospray tandem mass spectrometry [J]. J Chromatogr A 1328(3):26–34
Yeo M, Patisaul H, Liedtke W (2013) Decoding the language of epigenetics during neural development is key for understanding development as well as developmental neurotoxicity [J]. Epigenetics Off J Dna Methylat Soc 8(11):1128–1132
Zhao J, Li Y, Zhang C et al (2008) Sorption and degradation of bisphenol A by aerobic activated sludge [J]. J Hazard Mater 155(1–2):305–311
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41673120) and the Research on Environmental Safety Monitoring, Assessment and Early Warning Technology of Centralized Drinking Water Source (2018002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, D., Song, Z., Kang, H. et al. Occurrence, Profiles and Ecological Risk of Bisphenol Analogues in a Municipal Sewage Treatment Plant. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 106, 1044–1049 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03214-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03214-7