Abstract
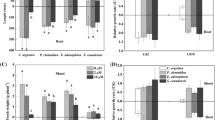
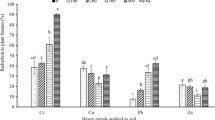
Cyclocarya paliurus seedlings were cultivated in three types of lead (Pb)-contaminated soils with Pb concentration of 305 ± 17 mg/kg (T1), 1964 ± 59 mg/kg (T2) and 3502 ± 107 mg/kg (T3), respectively. The results showed that after 180 days of cultivation, the contents of exchangeable and carbonate-bound Pb fractions significantly decreased in T1 and T2, but increased in T3. The growth indices of C. paliurus seedlings decreased with increasing Pb concentration; however, no difference was found between that in T1 and in Pb-free soil. The Pb concentration in the roots was an order of magnitude higher than that in the stems and in the leaves. The bioconcentration factor (BCF) of the leaves was the lowest among the three tissues investigated, and decreased with the higher concentration of Pb in the soils. These results suggest that C. paliurus can be used as a sustainable and profitable plant for the phytomanagement of Pb-contaminated soil.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelkrim S, Jebara HS, Saadani O, Chiboub M, Abid G, Mannai K, Jebara M (2019) Heavy metal accumulation in Lathyrus sativus growing in contaminated soils and identification of symbiotic resistant bacteria. Arch Microbiol 201:107–121
Al-Askar AA, Saber WIA, Ghoneem KM, Rashad YM (2018) Oxalic acid as the main molecule produced by Trichoderma asperellum MG323528 fermented on corn stover based medium. Biotechnology 17(2):95–103
Antoniadis V, Levizou E, Shaheen SM, Ok YS, Sebastian A, Baum C, Prasad MNV, Wenzel WW, Rinklebe J (2017) Trace elements in the soil-plant interface: phytoavailability, translocation, and phytoremediation. Earth-Sci Rev 171:621–645
Asati A, Pichhode M, Nikhil K (2016) Effect of heavy metals on plants: an overview. Int J Appl Innov Eng Manag 5:56–66
Assche F, Clijsters H (1990) Effects of metals on enzyme activity in plants. Plant Cell Environ 13:195–206
Burges A, AlkortaI I, Epelde L, Garbisu C (2018) From phytoremediation of soil contaminants to phytomanagement of ecosystem services in metal contaminated sites. Int J Phytoremediation 20(4):384–397
Chen J, Shafi M, Wang Y, Wu J, Ye ZQ, Liu C, Zhong B, Guo H, He LZ, Liu D (2016) Organic acid compounds in root exudation of moso bamboo (Phyllostachyspubescens) and its bioactivity as acted by heavy metals. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:20977–20984
Chibuike GU, Obiora SC (2014) Heavy metal polluted soils: effect on plants and bioremediation methods. Appl Environ Soil Sci 1:1–12
Conesa HM, Evangelou MWH, Robinson BH, Schulin R (2012) A critical view of current state of phytotechnologies to remediate soils: still a promising tool? Sci World J 173829:1–10
Cunningham SD, Berti WR, Huang JW (1995) Phytoremediation of contaminated soils. Trend Biotechnol 13(9):393–397
Fang ShZ, Wang JY, Wei ZhY, Zhu ZhX (2006) Methods to break seed dormancy in Cyclocarya paliurus (Batal.) Iljinskaja. Sci Hortic 110:305–309
Feng Y, Lin XL, Qian LW, Hu NJ, Kuang ChF, Li XF, Li Zh, Huang LR, Liu MM (2020) Morphological and physiological variations of Cyclocarya paliurus under different soil water capacities. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 26(8):1663–1674
Fernandez LR, Vandenbussche G, Roosens N, Govaerts C, Goormaghtigh E, Verbruggen N (2012) Metal binding properties and structure of a type III metallothionein from the metal hyperaccumulator plant Noccaea caerulescens. Biochim Biophys Acta 1824(9):1016–1023
Fryzova R, Pohanka M, Martinkova P, Cihlarova H, Brtnicky M, Hladky J, Kynicky J (2018) Oxidative stress and heavy metals in plants. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 245:129–156
García-Alix A, Jiménez-Espejo FJ, Lozano JA, Jiménez-Moreno G, Martinez-ruiz F, Sanjuan LG (2013) Anthropogenic impact and lead pollution throughout the holocene in Southern Iberia. Sci Total Environ 449:451–460
Ghosh M, Singh SP (2005) Comparative uptake and phytoextraction study of soil induced chromium by accumulator and high biomass weed species. Appl Ecol and Environ Res 3(2):67–79
Guo ZhP, Gao YN, Cao XL, Jiang WB, Liu X, Liu Q, Chen Zh, Zhou WN, Cui J, Wang QZh (2019) Phytoremediation of Cd and Pb interactive polluted soils by switch grass (Panicum virgatum L.). Int J Phytoremediat 21(14):1486–1496
Gupta D, Fatima A, Singh SK, Singh P, Prasad AM (2019) Repercussion of soil pollution on plants. Int J Fauna Biol Stud 6(2):89–98
Han Y, Zhang L, Yang Y, Yuan H, Zhao J, Gu J, Huang S (2016) Pb uptake and toxicity to Iris halophila tested on Pb mine tailing materials. Environ Pollut 214:510–516
Hossain Z, Komatsu S (2013) Contribution of proteomic studies towards understanding plant heavy metal stress response. Front Plant Sci 3(310):1–12
Lee CS, Li XD, Shi WZ, Cheung SC, Thornton I (2006) Metal contamination in urban, suburban, and country park soils of Hong Kong: a study based on GIS and multivariate statistics. Sci of Total Environt 356(1–3):45–61
Madejón P, Murillo JM, MarañónT CF, Soriano MA (2003) Trace element and nutrient accumulation in sunflower plants two years after the Aznalcóllar mine spill. Sci Total Environ 307(1–3):239–257
Malar S, Favas PJC, Sahi SV, Venkatachalam P (2014) Effect of lead on phytotoxicity, growth, biochemical alterations and its role on genomic template stability in Sesbania grandiflora: a potential plant for phytoremediation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 108:249–257
Maslennikov VP, Chupakhina NG, Skrypnik NL, Feduraev VP, Melnik SA (2018) The contribution of polyphenols to plant resistance to Pb soil pollution. Int J Environ Stud. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207233.2018.1440816
Mattina MI, Lannucci-Berger W, Musante C, White JC (2003) Concurrent plant uptake of heavy metals and persistent organic pollutants from soil. Environ Pollut 124(3):375–378
McCauley A, Jones C, Jacobsen J (2009) Soil pH and organic matter. Montana State University Extension Service, Bozeman Montana
Nahar K, Hasanuzzaman M, Alam MM, Fujita M (2015) Exogenous glutathione confers high temperature stress tolerance in mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) by modulating antioxidant defense and methylglyoxal detoxification system. Environ Exp Bot 112:44–54
Oseni OM, Adelusi AA, Data EO, Rufai AB (2016) Effects of heavy metal (Pb) concentration on some growth parameters of plants grown in leaf polluted soil under organic fertilizer amendment. Sci Cold Arid Reg 8(1):0036–0045
Reddy AM, Kumar SG, Jyotsnakumari G, Thimmanayak S, Sudhakar C (2005) Lead induced changes in antioxidant metabolism of horsegram (Macrotyloma uniflorum (Lam.) Verdc.) and bengal-gram (Cicer arietinum L.). Chemosphere 60:97–104
Rodríguez-Vila A, Asensio V, Forján R, Covelo EF (2016) Carbon fractionation in a mine soil amended with compost and biochar and vegetated with Brassica juncea L. J Geochem Explor 169:137–143
Roongtanakiat N, Sanoh S (2015) Comparative growth and distribution of Zn, Cd and Pb in rice, vetiver and sunflower grown in contaminated soils. Kasetsart J 49(5):663–675
Shen ZJ, Xua DC, Chena YS, Zhang Z (2017) Heavy metals translocation and accumulation from the rhizosphere soils to the edible parts of the medicinal plant Fengdan (Paeonia ostii) grown on a metal mining area, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 143:19–27
Shrirangasami SR, Murugaragavan SSRR, Ramesh PT, Varadharaj S, Elangovan R, Saravanakumar S (2020) Phytoremediation of contaminated soils—a review. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 9(11):3269–3283
Soudek P, Petrová Š, Vaňková R, Song J (2014) Accumulation of heavy metals using Sorghum sp. Chemosphere 104:15–24
Stein WI, Edwards JL, Tinus RW (1975) Outlook for container-grown seedling use in reforestation. J For 73:337–341
Tang L, Hamid Y, Zehra A, Sahito ZA, He Z, Hussain B, Yang X (2019) Characterization of fava bean (Vicia faba L.) genotypes for phytoremediation of cadmium and lead cocontaminated soils coupled with agro-production. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 171:190–198
Tessier AP, Campbell PGC, Bisson MX (1979) Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal Chem 51(7):844–851
Udovic M, McBride M (2012) Influence of compost addition on lead and arsenic bioavailability in reclaimed orchard soil assessed using Porcellio scaber bioaccumulation test. J Hazard Mater 205:144–149
Velásquez L, Dussan J (2009) Biosorption and bioaccumulation of heavy metals on dead and living biomass of Bacillus sphaericus. J Hazard Mater 167(3):713–716
Venkatachalam P, Jayaraj M, Manikandan R, Geetha N, Rene ER, Sharma NC (2016) Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnONPs) alleviate heavy metal induced toxicity in Leucaena leucocephala seedlings: a physiochemical analysis. Plant Physiol Biochem 110:59–69
Wani PA, Khan MS, Zaidi A (2008) Effects of heavy metal toxicity on growth, symbiosis, seed yield and metal uptake in pea grown in metal amended soil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 81:152–158
Wuana R, Okieimen FE (2010) Phytoremediation potential of maize (Zea mays L.). Afr J Gen Agric 6(4):275–287
Xie JH, Xie MY, Nie SP, Shen MY, Wang YX, Li C (2010) Isolation, chemical composition and antioxidant activities of a water-soluble polysaccharide from Cyclocarya paliurus (Batal.) Iljinskaja. Food Chem 119(4):1626–1632
Xie JH, Shen MY, Xie MY, Nie SP, Chen Y, Li C, Gong DM, Xie MY (2012) Ultrasonicassistedextraction, antimicrobial and antioxidant activity of Cyclocarya paliurus (Batal.) Iljinskaja polysaccharides. Carbohydr Polym 89:177–184
Xie JH, Liu X, Shen MY, Nie SP, Zhang H, Li C, Gong DM, Xie MY (2013) Purification physicochemical characterization and anticancer activity of a polysaccharides from Cyclocarya paliurus leaves. Food Chem 136(3–4):1453–1460
Xiong L, Ouyang KH, Jiang Y, Yang ZhW, Hu WB, Chen H, Wang N, Liu X, Wang WJ (2018) Chemical composition of Cyclocarya paliurus polysaccharide and inflammatory effects in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophage. Int J Biol Macromol 107:1898–1907
Xu L, Lu A, Wang J, Ma Z, Pan L, Feng X, Luan Y (2015) Accumulation status, sources and phytoavailability of metals in greenhouse vegetable production systems in Beijing, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 122:214–220
Yan A, Wang Y, Tan SN, MohdYusof ML, Ghosh S, Chen Z (2020) Phytoremediation: a promising approach for revegetation of heavy metal-polluted land. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00359
Zehra A, Sahito AZ, Tong WB, Tang L, Hamid Y, Khan BM, Ali Z, Naqvi B, Yang X (2020) Assessment of sunflower gerplasm for phytoremediation of lead-polluted soil and production of seed oil and seed meal for human and animal consumption. J Environ Sci 87:24–38
Zeng F, Ali S, Zhang H, Ouyang Y, Qiu B, Wu F, Zhang G (2011) The influence of pH and organic matter content in paddy soil on heavy metal availability and their uptake byrice plants. Environ Pollut 159(1):84–91
Zhao K, Liu X, Xu J, Selim HM (2010) Heavy metal contaminations in a soil–rice system: identification of spatial dependence in relation to soil properties of paddy fields. J Hazard Mater 181(1–3):778–787
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the Agricultural Guidance Project of Fujian Provincial Science and Technology Department (Grant Nos. 2018N0028 and 2019N0015) and the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in Fujian Province University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, Y., Xu, J., Wu, Z. et al. Cyclocarya paliurus for Phytomanagement of Lead-Contaminated Soils. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 106, 1003–1008 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03194-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-021-03194-8