Abstract
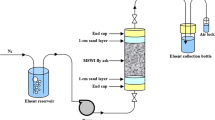
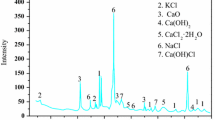
Through batch adsorption and column leaching experiments, this study aimed to investigate the adsorption and transport behavior of aniline in loess and related mechanism under different hydrochemical conditions. Batch experiments results indicated that aniline adsorption reached equilibrium after about 120 min, and the adsorption fitted the pseudo-second-order kinetic and Freundlich models well. The adsorption was spontaneous and exothermic process, indicating the aniline adsorbed by inherent colloidal particles (ICPs) tended to transport. Low pH value, ionic strength and temperature benefitted the adsorption. Column experiments results under different ionic strengths (100, 10 and 1 mM) confirmed the potential transport of aniline. The FT-IR spectra have further suggested that aniline was adsorbed by the ICPs through hydrogen-bond, hydrophobic effect and cation exchange interactions. Low ionic strength was advantageous for the adsorption of aniline in loess and the stabilities of ICPs in solution, but enhanced the co-transport probability of ICPs with aniline in loess.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadi S, Igwegbe CA (2018) Adsorptive removal of phenol and aniline by modified bentonite: adsorption isotherm and kinetics study. Appl Water Sci 8:170
Azar MT, Leili M, Taherkhani F et al (2016) A comparative study for the removal of aniline from aqueous solutions using modified bentonite and activated carbon. Desalin Water Treat 60:1–14
Bradford SA, Kim H (2010) Implications of cation exchange on clay release and colloid-facilitated transport in porous media. J Environ Qual 39:2040–2046
Chen L, Zhu Y, Luo H, Yang J (2020a) Characteristic of adsorption, desorption, and co-transport of vanadium on humic acid colloid. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 190:110087
Chen L, Long C, Wang D et al (2020b) Phytoremediation of cadmium (Cd) and uranium (U) contaminated soils by Brassica juncea L. enhanced with exogenous application of plant growth regulators. Chemosphere 242:125112
Chen S, Nyman M (2009) Influence of pH on sediment-associated sorption reactions of benzidine. Environ Toxicol Chem 28:1834–1841
Donaldson FP, Nyman MC (2006) Short-term interactions of aniline and benzidine with three soils in both natural and artificial matrices. Chemosphere 65:854–862
Guido B, Kai-Uwe G (2016) Sorption of organic chemicals to soil organic matter: influence of soil variability and pH dependence. Environ Sci Technol 45:1307–1312
Hu S, Wu Y, Zhang Y et al (2018) Nitrate removal from groundwater by heterotrophic/autotrophic denitrification using easily degradable organics and nano-zero valent iron as co-electron donors. Water Air Soil Pollut 229:56
Kakavandi B, Jonidi A, Rezaei R et al (2013) Synthesis and properties of Fe3O4-activated carbon magnetic nanoparticles for removal of aniline from aqueous solution: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Iran J Environ Health 10:19
Kanti ST, Khilar KC (2006) Review on subsurface colloids and colloid-associated contaminant transport in saturated porous media. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 119:71–96
Kaur P, Kaur P (2018) Time and temperature dependent adsorption-desorption behaviour of pretilachlor in soil. Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 161:145–155
Kaur P, Makkar A, Kaur P et al (2018) Temperature dependent adsorption-desorption behaviour of pendimethalin in punjab soils. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 100:167–175
Kaur P, Kaur P, Kaur K (2020) Adsorptive removal of imazethapyr and imazamox from aqueous solution using modified rice husk. J Clean Prod 244:118699
Khan S, Zhang D, Yang M et al (2018) Isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamic studies of adsorption of Ni and Cu by modification of Al2O3 nanoparticles with natural organic matter. Fuller Nanotubes Carbon Nanostruct 26:158–167
Koyuncu H, Kul AR (2019) Removal of aniline from aqueous solution by activated kaolinite: kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. Colloid Surface A 569:59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.02.057
Lee LS, Nyman AK, Hui L et al (2010) Initial sorption of aromatic amines to surface soils. Environ Toxicol Chem 16:1575–1582
Li BZ, Lei ZP, Huang ZG (2010) Surface-treated activated carbon for removal of aromatic compounds from water. Chem Eng Technol 32:763–770
Li ZZ, Tang XW, Chen YM et al (2009) Sorption behavior and mechanism of Pb(II) on Chinese loess. J Environ Eng 135:58–67
Malakootian M, Gharaghani MA, Dehdarirad A et al (2019) ZnO nanoparticles immobilized on the surface of stones to study the removal efficiency of 4-nitroaniline by the hybrid advanced oxidation process (UV/ZnO/O3). J Mol Struct 1176:766–776
Mohanty SK, Saiers JE, Ryan JN (2015) Colloid mobilization in a fractured soil during dry-wet cycles: role of drying duration and flow path permeability. Environ Sci Technol 49:9100–9106
O'Brien J, O'Dwyer TF, Curtin T (2008) A novel process for the removal of aniline from wastewaters. J Hazard Mater 159:476–482
Pardo B, Ferrer N, Sempere J et al (2016) A key parameter on the adsorption of diluted aniline solutions with activated carbons: the surface oxygen content. Chemosphere 162:181–188
Sharma P, Mayes MA, Tang G (2013) Role of soil organic carbon and colloids in sorption and transport of TNT, RDX and HMX in training range soils. Chemosphere 92:993–1000
Sun C, Zhu Y, Li H et al (2015) Natural degradation and chemical oxidation remediation of aniline in soil. J Shanxi Univ (Natural Science Edition) 38(01):165–172 (In Chinese)
Suresh S, Srivastava VC, Mishra IM (2012) Adsorptive removal of aniline by granular activated carbon from aqueous solutions with catechol and resorcinol. Environ Technol 33:773–781
Tarlani Azar M, Leili M, Taherkhani F et al (2016) A comparative study for the removal of aniline from aqueous solutions using modified bentonite and activated carbon. Desalin Water Treat 57:24430–24443
Tran HN, You SJ, Hosseini-Bandegharaei A et al (2017) Mistakes and inconsistencies regarding adsorption of contaminants from aqueous solutions: a critical review. Water Res 120:88–116
Wang H, Xu J, Liu X et al (2019) Effects of long-term application of organic fertilizer on improving organic matter content and retarding acidity in red soil from China. Soil Till Res 195:104382
Wang Y, Tang X, Chen Y et al (2009) Adsorption behavior and mechanism of Cd(II) on loess soil from China. J Hazard Mater 172:30–37
Wu Y, Fan L, Hu S et al (2019) Role of dissolved iron ions in nanoparticulate zero-valent iron/H2O2 Fenton-like system. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:4551–4562
Zakari S, Liu H, Zhou H (2019) Transport velocities of aniline and nitrobenzene in sandy sediment. J Soil Sediment 19:2570–2579
Zhang J, Xu Y, Wu Y et al (2019) Dynamic characteristics of heavy metal accumulation in the farmland soil over Xiaoqinling gold-mining region, Shaanxi. China Environ Earth Sci 78:25
Zheng H, Liu D, Zheng Y et al (2009) Sorption isotherm and kinetic modeling of aniline on Cr-bentonite. J Hazard Mater 167:141–147
Zhou B, Wu Y, Chan J et al (2019a) Batch adsorption and column transport studies of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene in Chinese loess. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 103:75–81
Zhou B, Wu Y, Chan J et al (2019b) Wetting–drying cycles enhance the release and transport of autochthonous colloidal particles in Chinese loess. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 25:335–353
Zhou B, Wu Y, Zhang Z et al (2019c) Laboratory tests on effects of wetting–drying cycles and loess layer thickness on release and transport of loess colloidal particles in artificial loess columns. Environ Earth Sci 78:473
Acknowledgements
We thank editors and reviewers for their efforts to improve this article and further research sincerely. The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 41502240 and 41601338), the Natural Science Basic Research Plan in Shaanxi Province of China (Nos. 2017JM4005 and 2018JQ4019). In addition, Bo Zhou especially wishes to thank JiaHuan Wang, whose love has given him powerful spiritual support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, B., Zhang, Z., Wang, S. et al. Batch Adsorption and Column Leaching Studies of Aniline in Chinese Loess Under Different Hydrochemical Conditions. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 104, 511–519 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-020-02830-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-020-02830-z