Abstract
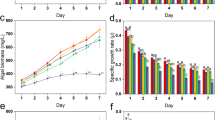
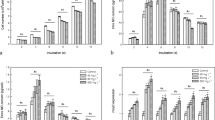
This study investigated the growth, apoptosis and oxidative stress of the cyanobacterium Microcystis viridis exposed to glyphosate. Results showed that growth parameters, namely, cell destiny, chlorophyll a content, and protein content, were affected by glyphosate. The viability of the treated cells was monitored to further investigate the toxicity of glyphosate on M. viridis. After 24 and 48 h of exposure, glyphosate enhanced superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity and decreased malondialdehyde (MDA) concentration. The decrease in the MDA concentration might be caused by the enhanced SOD activity. This study helped elucidate the toxic effects of glyphosate on cyanobacteria and contributed to environmental assessment and protection.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts: polyphenoloxidase in beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24:1–15
Bagchi D, Bagchi M, Stohs SJ (1997) Comparative in vitro oxygen radical scavenging ability of zinc methionine and selected zinc salts and antioxidants. Gen Pharmacol 28:85–91
Baylis AD (2000) Why glyphosate is a global herbicide: strengths, weaknesses and prospects. Pest Manag Sci 56:299–308
Beauchamp C, Fridovich I (1971) Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 44:276–287
Benbrook CM (2016) Trends in glyphosate herbicide use in the United States and globally. Environ Sci Eur 28:3
Bradel BG, Preil W, Jeske H (2000) Remission of the free-branching pattern of Euphorbia pulcherrima by tetracycline treatment. J Phytopathol 148:587–590
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chaufan G, Juárez A, Basack S, Ithuralde E, Sabatini SE, Genovese G, Oneto ML, Kesten E, de Molina Ríos, Mdel C (2006) Toxicity of hexachlorobenzene and its transference from microalgae (Chlorella kessleri) to crabs (Chasmagnatus granulatus). Toxicology 227:262–270
Dokulil MT, Teubner K (2000) Cyanobacterial dominance in lakes. Hydrobiologia 438:1–12
Du YP, Ye J, Wu L, Yang CY, Wang LM, Hu XJ (2017) Physiological effects and toxin release in Microcystis aeruginosa and Microcystis viridis exposed to herbicide fenoxaprop-p-ethyl. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24(8):7752–7763
Gill JPK, Sethi N, Mohan A, Datta S, Girdhar M (2018) Glyphosate toxicity for animals. Environ Chem Lett 16(2):401–426
Hagege D, Nouvelot A, Boucaud J, Gasper T (1990) Malondialdehyde titration with thiobarbiturate in plant extracts: avoidance of pigment interference. Photochem Anal 1:186–189
Hénault-Ethier L, Martin JP, Housset J (2017) A dynamic model for organic waste management in Quebec (D-MOWIQ) as a tool to review environmental, societal and economic perspectives of a waste management policy. Waste Manag 66:196–209
Myers JP, Antoniou MN, Blumberg B, Carroll L, Colborn T, Everett LG, Hansen M, Landrigan PJ, Lanphear BP, Mesnage R, Vandenberg LN, vom Saal FS, Welshons WV, Benbroo CM (2016) Concerns over use of glyphosate-based herbicides and risks associated with exposures: a consensus statement. Environ Health 15:19
OECD (2011) Freshwater alga and cyanobacteria, growth inhibition test (201). OECD guidelines for the testing of chemicals
Popp M, Hann S, Mentler A, Fuerhacker M, Stingeder G, Koellensperger G (2008) Determination of glyphosate and AMPA in surface and waste water using high-performance ion chromatography coupled to inductively coupled plasma dynamic reaction cell mass spectrometry (HPIC–ICP-DRC-MS0). Anal Bioanal Chem 391:695–699
Ross C, Santiago-Vazquez L, Paul V (2006) Toxin release in response to oxidative stress and programmed cell death in the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Aquat Toxicol 78:66–73
Smedbol É, Gomes MP, Paquet S, Labrecque M, Lepage L, Lucotte M, Juneau P (2018) Effects of low concentrations of glyphosate-based herbicide factor 540 agricultural stream freshwater phytoplankton community. Chemosphere 192:133–141
Van Bruggen AHC, He MM, Shin K, Mai V, Jeong KC, Finckh MR, Morris JG (2018) Environmental and health effects of the herbicide glyphosate. Sci Total Environ 616–617:255–268
Wu L, Qiu ZH, Zhou Y, Du YP, Liu CN, Ye J, Hu XJ (2016) Physiological effects of the herbicide glyphosate on the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Aquat Toxicol 178:72–79
Ye J, Wang LM, Zhang ZJ, Liu WP (2013) Enantioselective physiological effects of the herbicide diclofop on cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa. Environ Sci Technol 47:3893–3901
Zhou CF, Li Y, Zhang XY (2013) Research advance in ecotoxicity of glyphosate. Ecol Environ Sci 22:1737–1743
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21307082), and the Project of the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality, China (18ZR1438000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, J., Huang, C., Qiu, Z. et al. The Growth, Apoptosis and Oxidative Stress in Microcystis viridis Exposed to Glyphosate. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 103, 585–589 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-019-02691-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-019-02691-1