Abstract
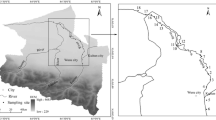
The particle size distribution characteristics of sediments and the concentrations of heavy metals in Jiaozhou Bay were investigated in this study. The average concentrations of Cu, Pb, Zn, Cr, Cd, Hg and As were 36.88, 29.60, 82.08, 77.48, 0.083, 0.048 and 11.00 mg/kg, respectively. The heavy metal concentrations were highest in the eastern sediments, followed by those at the top of the bay, and the lowest concentrations were observed in the central region. Overall, a decreasing trend from the center of the bay to the periphery was observed. Additionally, the distribution of heavy metals in sediments was not completely controlled by sediment particle size. The degree of heavy metal contamination was evaluated using the geoaccumulation index and Hakanson’s method. The results revealed that the level of heavy metal pollution in the sediments was relatively low and that the main pollution elements were Cu and Hg. In addition, the sediments are associated with various levels of potential ecological risk due to the high pollution levels of Hg and Cd.

(data from Dong et al. 2006)

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chi QH, Yan MC (2007) Handbook of elemental abundance for applied geochemistry. Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese)
Dong HP, Li SQ, Li GX, Li C (2006) On the off shore tidal depositional system in Qingdao. Preiod Ocean Univ China 36:31–36 (in Chinese)
Gao S, Collins MB, Lanckneus J, Moor GD, Lancker VV (1994) Grain size trends associated with net sediment transport patterns: an example from the Belgian continental shelf. Mar Geol 121:171–185
Hakanson L (1980) An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control: a sediment logical approach. Water Res 14:975–1001
Harikrishnan N, Ravisankar R, Chandrasekaran A, Gandhi MS (2017) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in marine sediments of east coast of Tamil Nadu affected by different pollution Sources. Mar Pollut Bull 121:418–424
Hartmann PC, Quinn JG, Cairns RW, King JW (2005) Depositional history of organic contaminants in Narragansett Bay, Rhode Island, USA. Mar Pollut Bull 50:388–395
Li P, Li CZ, Li NS (1999) Geological circumstances for harbor construction in Jiaozhou Bay. Mar Sci 23:27–30 (in Chinese)
Li TT, Luo W, Lv YL, Song S (2016) On distribution and pollution of heavy metals in water environment of Jiaozhou Bay in Yellow Sea. J Southwest China Norm Univ 41:60–66 (in Chinese)
Ma SH, He HX (1998) Application and related monitoring of “comprehensive sewage discharge standards”. Adm Tech Environ Monit 10:24–27 (in Chinese)
Mcmanus J (1988) Grain size determination and interpretation. Tech Sedimentol 3:33–48
Muller G (1969) Index of geo-accumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geojournal 2:108–118
Muller G (1981) Die Schwermetallbelastung der sedimenten des necker und seiner nebefluse. Chem Ztg 6:164–175
Shen MG, Cui JL, Shi Q, Li L, Gen Y (2014) Analysis sediment dishcharge characteristics of rivers in Jiaozhou Bay, Qingdao city. J China Hydrol 34:92–96 (in Chinese)
Wu YS, Wang ZY (2002) Numerical simulation of 1998 red tide of the Bohai sea. Int J Sedim Res 17:175–185
Xiao CL, Chen LF, Li YB (2017) Distribution characteristics and potential risk assessment of heavy metals in the sediment of Jiaozhou Bay. China Sciencepap 9:1079–1086
Zhang K, Wang CH, Feng J, Fang J, Shu YH, Mou DH, Wu QH (2011) Distribution and pollution assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Jiaozhou Bay. J Instrum Anal 30:1406–1411 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgements
Funding for this research was provided by the National Key Research and Development Project (2016YFC0402801) and the National Basic Project (2014FY210600) of the Ministry of Science and Technology, People's Republic of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhuang, H., Xu, S., Gao, M. et al. Heavy Metal Pollution Characteristics in the Modern Sedimentary Environment of Northern Jiaozhou Bay, China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 101, 473–478 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-018-2439-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-018-2439-9