Abstract
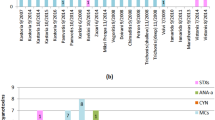
A study which probed the occurrence and quantitative variations hepatotoxic microcystin in a Sub Saharan drinking freshwater reservoir was carried out between November 2014 and March 2015. Results reveal the presence of MCYST-YR, MCYST-LR, MCYST-RR, MCYST-LA and MCYST-LF variants either in cells collected directly from bloom or toxic isolates cultured under laboratory conditions. Two minor microcystin congeners (MCYST-(H4)YR) and (D-Asp3, Dha7) MCYST-RR) were identified, but not quantified. Variants dominance were in the order MCYST-LR > MCYST-RR > MCYST-YR > MCYST-LA > MCYST-LF across sampling sites. Maximum and minimum concentrations of quantified MCYSTs congeners were (489.25, 50.95 µg toxin/g DW), (98.92, 9.11 µg toxin/g DW), (140.25, 12.07 µg toxin/g DW), (56.99, 6.20 µg toxin/g DW) and (50.46, 3.65 µg toxin/g DW) for MCYST-LR, MCYST-YR, MCYST-RR, MCYST-LA and MCYST-LF, respectively. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) revealed there was a high significant difference between mean microcystin concentrations across sampling sites (p < 0.05).


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amrani A, Nasri H, Azzouz A, Kadi Y, Bouaïcha N (2014) Variation in cyanobacterial hepatotoxin (microcystin) content of water samples and two species of fishes collected from a shallow lake in Algeria. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 66:379–389. doi:10.1007/s00244-013-9993-2
Bateman KP, Thibault P, Douglas DJ, White RL (1995) Mass spectral analyses of microcystins from toxic cyanobacteria using online chromatographic and electrophoretic separations. J Chromatogr A 712:253–268. doi:10.1016/0021-9673(95)00438-S
Cazenave J, de los Ángeles BM, Zwirnmann E, Wunderlin DA, Wiegand C (2006) Attenuating effects of natural organic matter on microcystin toxicity in zebra fish (Danio Rerio) embryos; benefits and costs of microcystin detoxication. Environ Toxicol 21:22–32. doi:10.1002/tox.20151
Conradie KR, Barnard S (2012) The dynamics of toxic microcystis strains and microcystin production in two hypertrofic South African reservoirs. Harmful Algae 20:1–10. doi:10.1016/j.hal.2012.03.006
Conti RAL, Guerrero JM, Regueira JM (2005) Levels of microcystins in two Argentinian reservoirs used for water supply and recreation: Differences in the implementation of safe levels. Environ Toxicol 20:263–269. doi:10.1002/tox.20107
Corbel S, Mougin C, Bouaicha N (2014) Cyanobacterial toxins: modes of action, fate in aquatic and soil ecosystems, phytotoxicity and bioaccumulation in agricultural crops—a review. Chemosphere 96:1–15 doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.07.056
Dziallas C, Grossart HP (2012) Microbial interactions with the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa and their dependence on temperature. Mar Biol 4:1927–1934. doi:10.1007/s00227-012-1927-4
Gilroy DJ, Kauffman KW, Hall RA, Huang X, Chu FS (2000) Assessing potential health risks from microcystin toxins in blue–green algae dietary supplements. Environ Health Perspect 108:435–439
Greenwald I (2012) The solubility of Calcium Phosphate I. The Effects of pH and of amount of solid phase. Hydrobiol 72:855–863. doi:10.1007/s11157-014-9334-6
Ha MH, Pflugmacher S (2013) Phytotoxic effects of the cyanobacterial neurotoxin anatoxin-a: morphological, physiological and biochemical responses in aquatic macrophyte, Ceratophyllum demersum. Toxicon 70:1–8 doi:10.1016/j.toxicon.2013.03.021
Jochimsen EM, Carmichael WW, An J, Cardo DM, Cookson ST, Holmes CEM, Antunes MB, de Melo Filho DA, Lyra TM, Barreto VST, Azevedo SMFO, Jarvis WR (1998) Liver failure and death after exposure to microcystins at a hemodialysis center in Brazil. N Engl J Med 338:873–878. doi:10.1056/NEJM199803263381304
Lawrence JF, Niedzwiadek B, Menard C, Lau BP, Lewis D, Kuper-Goodman T, Carbone S, Holmes C (2001) Comparison of liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry, ELISA, and phosphatase assay for the determination of microcystins in blue-green algae products. J AOAC Int 84:1035–1044
Li YW, Zhan XJ, Xiang L, Deng ZS, Huang BH, Wen HF, Sun TF, Cai QY, Li H, Mo CH (2014) Analysis of trace microcystins in vegetables using solid-phase extraction followed by high performance liquid chromatography triple-quadrupole mass spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem 62:11831–11839. doi:10.1021/jf5033075
Magalhaes VD, Marinho M, Domingos P, Oliveira A, Costa S, Azevedo LOD et al (2003) Microcystins (cyanobacteria hepatotoxins) bioaccumulation in fish and crustaceans from Sepetiba Bay (Brasil, RJ). Toxicon 42:289–295 doi:10.1016/S0041-0101(03)00144-2
Mekebri A, Blondina GJ, Crane DB (2009) Method validation of microcystins in water and tissue by enhanced liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1216:3147–3155 doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2009.01.095
Messineo V, Bogialli S, Melchiorre S, Sechi N, Lugliè A, Casiddu P., et al (2009) Cyanobacterial toxins in Italian freshwaters. Limnologica 39:95–106. doi:10.1016/j.limno.2008.09.001
Moreno IM, Herrador MÁ, Atencio L, Puerto M, González AG, Cameán AM (2009) Differentiation between microcystin contaminated and uncontaminated fish by determination of unconjugated MCs using an ELISA anti-Adda test based on receiver-operating characteristic curves threshold values: application to Tinca tinca from natural ponds. Environ Toxicol 26:45–56. doi:10.1002/tox.20528
Msango MG (2007) A Comparative analysis of the cytotoxicity of cyanotoxins using In-Vitro (Cell culture) and In-Vivo (Mouse) assays. MS Thesis, University of Pretoria, Pretoria, South Africa
Oberholster PJ, Botha AM (2010) Use of remote sensing and molecular markers to detect toxic cyanobacterial hyperscum crust: A case study on Lake Hartbeespoort, South Africa. Afr J Biotech 9:8791–8799. doi:10.5897/ajb10.1201
Osswald J, Carvalho A, Claro J, Vasconcelos V (2009) Effects of cyanobacterial extracts containing anatoxin-a and of pure anatoxin-a on early developmental stages of carp. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:473–478. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2008.05.011
Papadimitriou T, Kagalou L, Stallikas C, Pilidis G, Leonardos ID (2012) Assessment of microcystin distribution and biomagnifications in tissues of aquatic food web compartments from a shallow lake and evaluation of potential risk to public health. Ecotoxicol 2:1155–1166. doi:10.1007/s10646-012-0870-y
Poon K, Lam MH, Lam PK, Wong BS (2001) Determination of microcystins in cyanobacterial blooms by solid-phase microextraction-high-performance liquid chromatography. Environ Toxicol Chem 20:1648–1655. doi:10.1002/etc.5620200805
Rastogi RP, Sinha RP, Incharoensakdi A (2014) The cyanotoxin-microcystins: current overview. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 13:215–249. doi:10.1007/s11157-014-9334-6
Shimizu K, Sano T, Kubota R, Kobayashi N, Tahara M, Obama T, Sugimoto N, Ikarashi Y (2014) Effects of the amino acid constituents of microcystin variants on cytotoxicity to primary cultured rat hepatocytes. Toxins 6:168–179. doi:10.3390/toxins6010168
Yuan M, Namikoshi M, Otsuki A, Rinehart KL, Sivonen K, Watanabe MF (1999) Low-energy collisionally activated decomposition and structural characterization of cyclic heptapeptide microcystins by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J Mass Spectrum 34:33–43. doi:10.1002/(sici)1096-9888(199901)34:1<33::aid-jms754>3.0.co;2-l
Zurawell RW, Chen HR, Burke J M, Prepas EE (2005) Hepatotoxic cyanobacteria: a review of the biological importance of microcystins in freshwater environments. J Toxicol Environ Health B 8:1–37. doi:10.1080/10937400590889412
Acknowledgments
The authors express their thanks to the NRF/DST Innovation Postdoctoral Fellowship (Grant UID 95470) awarded to Dr. Kennedy Eguzozie. We are grateful to the University of Johannesburg for financial support from the Biopharmaceutics & Bioprocess Research Group in the department of Biotechnology & Food Technology. We also would like to thank the two anonymous reviewers and editor whose generous views and comments on the original draft manuscript helped us shape this final documents.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eguzozie, K.U., Mavumengwana, V., Nkosi, D. et al. Screening of Cyanobacterial Peptide Toxin, Microcystins in Hyperscum Water Samples from an Inland Sub Saharan Drinking Freshwater Reservoir. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 97, 728–736 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-1916-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-1916-2