Abstract
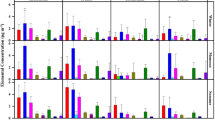
This study aims to determine the composition and sources of particulate matter with an aerodynamic diameter of 10 μm or less (PM10) in a semi-urban area. PM10 samples were collected using a high volume sampler. Heavy metals (Fe, Zn, Pb, Mn, Cu, Cd and Ni) and cations (Na+, K+, Ca2+ and Mg2+) were detected using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, while anions (SO4 2−, NO3 −, Cl− and F−) were analysed using Ion Chromatography. Principle component analysis and multiple linear regressions were used to identify the source apportionment of PM10. Results showed the average concentration of PM10 was 29.5 ± 5.1 μg/m3. The heavy metals found were dominated by Fe, followed by Zn, Pb, Cu, Mn, Cd and Ni. Na+ was the dominant cation, followed by Ca2+, K+ and Mg2+, whereas SO4 2− was the dominant anion, followed by NO3 −, Cl− and F−. The main sources of PM10 were the Earth’s crust/road dust, followed by vehicle emissions, industrial emissions/road activity, and construction/biomass burning.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harrison MR, Deacon RA, Jones RM, Appleby RS (1997) Sources and processes affecting concentrations of PM10 and PM2.5 particulate matter in Birmingham (UK). Atmos Environ 31:4103–4117
Ismail I, Laiman R, Ahmad H (2011) Study of particulate matter (PM10) concentration and elemental composition at Damansara–Puchong highway. 2011 International Conference on Biology, Environment and Chemistry. Singapore
Juneng L, Latif MT, Tangang F (2011) Factors influencing the variations of PM10 aerosol dust in Klang Valley, Malaysia during the summer. Atmos Environ 45(26):4370–4378
Latif MT, Baharudin NH, Velayutham P, Awang N, Hamdan H, Mohamad R, Mokhtar MB (2011) Composition of heavy metals and airborne fibers in the indoor environment of a building during renovation. Environ Monit Assess 181(1–4):479–489
Mansha M, Ghauri B, Rahman S, Amman A (2012) Characterization and source apportionment of ambient air particulate matter (PM2.5). Sci Total Environ 425:176–183
Mazzei F, D’Alessandro A, Lucarelli F, Nava S, Prati P, Valli G, Vecchi R (2008) Characterization of particulate matter sources in an urban environment. Sci Total Environ 401(1–3):81–89
Miller KA, Siscovick DS, Sheppard L, Shepherd K, Sullivan JH, Anderson GL, Kaufman JD (2007) Long-term exposure to air pollution and incidence of cardiovascular events in women. N Eng J Med 356(5):447–458
Mohd Tahir N, Poh SC, Hamzah S, Wood KH, Rahman SA, Wee BS, Elias S, Salim NAA (2008) Analysis of PM10 in Kuala Terengganu by instrumental neutron activation analysis. Malays J Anal Sci 12(1):187–194
Mohd Tahir N, Poh SC, Suratman S, Ariffin MM, Shazali NAM, Yunus K (2009) Determination of trace metals in airborne particulate matter of Kuala Terengganu, Malaysia. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 83:199–203
Mohd Tahir N, Suratman S, Fong FT, Hamzah MS, Latif MT (2013) Temporal distribution and chemical characterization of atmospheric particulate matter in the eastern coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Aerosol Air Qual Res 13(2):584–595
Mukae H, Vincent R, Quinlan K, English D, Hards J, Hogg JC, Van Eeden SF (2001) The effect of repeated exposure to particulate air pollution (PM10) on the bone marrow. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 163(1):201–209
Orlic I, Wen X, Ng TH, Tang SM (1999) Two years of aerosol pollution monitoring in Singapore: a review. Nucl Inst B 150(1–4):457–464
Shi G-L, Zeng F, Li X, Feng Y-C, Wang Y-Q, Liu G-X, Zhu T (2011) Estimated contributions and uncertainties of PCA/MLReCMB results: source apportionment for synthetic and ambient datasets. Atmos Environ 45(17):2811–2819
Shukla SP, Sharma M (2008) Source apportionment of atmospheric PM10 in Kanpur, India. Environ Eng Sci 25(6):849–862
Sternbeck J, Sjodin A, Andreasson K (2002) Metal emissions from road traffic and the influence of resuspension: results from two tunnel studies. Atmos Environ 36(30):4735–4744
Sulaiman N, Abdullah M, Chieu PLP (2005) Concentration and composition of PM10 in outdoor and indoor air in industrial area of Balakong Selangor, Malaysia. Sains Malays 34(2):43–47
Sunder-Raman R, Hopke P, Holsen T (2008) Characterization of fine aerosol and its inorganic components at two rural locations in New York State. Environ Monit Assess 144(1–3):351–366
Terzi E, Argyropoulos G, Bougatioti A, Mihalopoulos N, Nikolaou K, Samara C- (2010) Chemical composition and mass closure of ambient PM10 at urban sites. Atmos Environ 44(18):2231–2239
Tsitouridou R, Voutsa D, Kouimtzis T (2003) Ionic composition of PM10 in the area of Thessaloniki, Greece. Chemosphere 52(5):883–891
Viana M, Kuhlbusch TAJ, Querola X, Alastueya A, Harrison RM, Hopke PK, Winiwarter W, Vallius M, Szidat S, Prévôt ASH, Hueglin C, Bloemen H, Wåhlin P, Vecchi R, Miranda AI, Kasper-Giebl A, Maenhaut W, Hitzenberger R (2008) Source apportionment of particulate matter in Europe: a review of methods and results. J Aerosol Sci 39(10):827–849
Wahid NBA, Latif MT, Suratman S (2013) Composition and source apportionment of surfactants in atmospheric aerosols of urban and semi-urban areas in Malaysia. Chemosphere 91(11):1508–1516
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by research Grant (FRGS/1/2013/STWN01/UKM/02/2) and industrial Grant (INDUSTRI-2011-013). Special thanks to K. Alexander and Dr. Rose Norman for assistance with the proofreading of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wahid, N.B.A., Latif, M.T., Suan, L.S. et al. Source Identification of Particulate Matter in a Semi-urban Area of Malaysia Using Multivariate Techniques. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 92, 317–322 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-014-1201-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-014-1201-1