Abstract
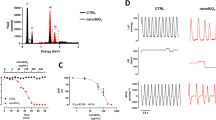
In the present report, we explored the toxicological behaviour of engineered polystyrene–titanium–arsenate (PS–Ti–As) composite using cultured H9c2 cardiomyoblasts in vitro. From in vitro cytotoxicity studies, it appears that the composite can be toxic to the cardiac cells and the value of IC50 investigated to be the highest concentration of 500 μg mL−1, during 16–24 h of incubation period. The cell morphological studies based on dual staining with acridine orange and ethidium bromide indicates that apoptosis is the dominating pathway of cell death. Furthermore, an enhanced DNA fragmentation, increased reactive oxygen species production and caspase release demonstrates the potential risks associated with the exposure of PS–Ti–As composite to the cardiac cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arfin T, Rafiuddin (2009) Electrochemical properties of titanium arsenate membrane. Electrochim Acta 54:6928–6934
Arfin T, Rafiuddin (2010) Thermodynamics of ion conductivity of alkali halides across a polystyrene-based titanium arsenate membrane. Electrochim Acta 55:8628–8631
Baek YW, An YJ (2010) Microbial toxicity of metal oxide nanoparticles (CuO, NiO, ZnO, and Sb2O3) to Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, and Streptococcus aureus. Sci Total Environ 409:1603–1608
Chahina T, Baccarelli A, Litonjua A, Wright RO, Suh H, Gold DR, Sparrow D, Vokonas P, Schwartz J (2007) Particulate air pollution, oxidative stress genes, and heart rate variability in an elderly cohort. Environ Health Perspect 11:1617–1622
Eom HJ, Choi J (2009) Oxidative stress of silica nanoparticles in human bronchial epithelial cell, Beas-2B. Toxicol Vitro 23:1326–1332
Funhoff MA, van Nostrum FC, Lok CM, Kruijtzer AJ, Crommelin JD, Hennink EW (2005) Cationic polymethacrylates with covalently linked membrane destabilizing peptides as gene delivery vectors. J Controlled Release 101:233–246
Godbey TW, Wu KK, Mikos GA (2001) Poly(ethyleneimine)-mediated gene delivery affects endothelial cell function and viability. Biomaterials 22:471–480
Hongtao VL, Zhang S, Wang B, Cui S, Yan J (2006) Toxicity of cationic lipids and cationic polymers in gene delivery. J Controlled Release 114:100–109
Jain CK, Ali I (2000) Arsenic: occurrence, toxicity and speciation techniques. Water Res 34:4304–4312
Mills NL, Donaldson K, Hadoke PW, Boon NA, MacNee W, Cassee FR, Sandström T, Blomberg A, Newby DE (2009) Adverse cardiovascular effects of air pollution. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med 6:36–44
Mohammad F, Balaji G, Weber A, Uppu RM, Kumar CSSR (2010) Influence of gold nanoshell on hyperthermia of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 114:19194–19201
Naranmandura H, Carew MW, Xu S, Lee J, Leslie EM, Weinfeld M, Le XC (2011) Comparative toxicity of arsenic metabolites in human bladder cancer EJ-1 cells. Chem Res Toxicol 24:1586–1596
Sathishkumar K, Haque M, Perumal ET, Francis J, Uppu RM (2005) A major ozonation product of cholesterol, 3b-hydroxy-5-oxo-5,6-secocholestan-6-al, induces apoptosis in H9c2 cardiomyoblasts. FEBS Lett 579:6444–6450
Sathishkumar K, Rangan V, Gao X, Uppu RM (2007) Methyl vinyl ketone induces apoptosis in murine GT1-7 hypothalamic neurons through glutathione depletion and the generation of reactive oxygen species. Free Radical Res 41:469–477
Shimizu T, Numata T, Okada Y (2004) A role of reactive oxygen species in apoptotic activation of volume-sensitive Cl− channel. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 101:6770–6773
Simkhovich BZ, Kleinman MT, Kloner RA (2008) Air pollution and cardiovascular injury. J Am Coll Cardiol 52:719–726
Smith AH, Hopenhayn-Rich C, Bates MN, Goeden HM, Hertzpicciotto I, Duggan H, Wood R, Kosnett MF, Smith MT (1992) Cancer risks from arsenic in drinking water. Environ Health Perspect 97:259–267
Uboldi C, Bonacchi D, Lorenzi G, Hermanns MI, Pohl C, Baldi G, Unger RE, Kirkpatrick CJ (2009) Gold nanoparticles induce cytotoxicity in the alveolar type-II cell lines A549 and NCIH441. Part Fibre Toxicol 6:1–12
Xia T, Kovochick T, Brant J, Hotze M, Sempf J, Oberley T, Sioutas C, Yeh JI, Wiesner MR (2006) Comparison of the abilities of ambient and manufactured nanoparticles to induce cellular toxicity according to an oxidative stress paradigm. Nano Lett 6:1794–1807
Xia T, Kovochich M, Liong M, Zink JI, Nel AE (2008) Cationic polystyrene nanosphere toxicity depends on cell-specific endocytic and mitochondrial injury pathways. ACS Nano 2:85–96
Acknowledgments
FM acknowledges the National Science Foundation (NSF) grant HRD0450375 (from the HBCU-RISE program) for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammad, F., Arfin, T. Cytotoxic Effects of Polystyrene–Titanium–Arsenate Composite in Cultured H9c2 Cardiomyoblasts. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 91, 689–696 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-013-1131-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-013-1131-3