Abstract
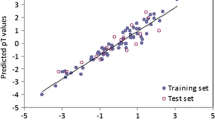
The widespread production of esters combined with their ability to migrate in different compartments, makes their environmental toxicity important. In this background, the multivariate image analysis-quantitative structure–toxicity relationship (MIA-QSTR) method coupled to principal component analysis-adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference systems (PCA-ANFIS) was applied to assess the toxicity of esters to Daphnia magna. In MIA-QSTR, pixels of chemical structures (2D images) stand for descriptors, and structural changes account for the variance in toxicities. The ANFIS procedure was capable of correlating the inputs (PCA scores) with the toxicities accurately. The PCA-ANFIS also was statistically validated for its predictive power using cross-validation, applicability domain and Y-scrambling evaluation procedures. The satisfactory results (R 2p = 0.926, Q 2LOO = 0.887, R 2L25 %O = 0.843, RMSELOO = 0.320 and RMSEL25 %O = 0.379) suggests that the QSTR model could be proposed as an alternative method for aquatic toxicity assessment of esters allowing possible application in the European Union regulation REACH.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alamdari RF, Mani-Varnosfaderani A, Asadollahi-Baboli M, Khalafi-Nezhad A (2012) Monte Carlo sampling and multivariate adaptive regression splines as tools for QSAR modeling of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitors. SAR QSAR Environ Res 23:665–682
Asadollahi-Baboli M (2012) In silico prediction of the aniline derivatives toxicities to Tetrahymena pyriformis using chemometrics tools. Toxicol Environ Chem 94:2019–2034
Freitas MP (2009) MIA-QSTR study of different organic compounds to Pimephales promelas. Med Chem Res 18:648–655
Freitas MP, Goodarzi M (2009) On the use of PLS and N-PLS in MIA-QSAR: azole antifungals. Chemom Intel Lab Sys 96:59–62
Freitas MP, Goodarzi M (2010) MIA-QSAR coupled to principal component analysis-adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference systems (PCA-ANFIS) for the modeling of the anti-HIV reverse transcriptase activities of TIBO derivatives. Eur J Med Chem 45:1352–1358
Freitas MP, Antunes JE, Rittner R (2008) Bioactivities of a series of phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE-5) inhibitors as modeled by MIA-QSAR. Eur J Med Chem 43:1632–1638
Gramatica P (2007) Principles of QSAR models validation: internal and external. QSAR Comb Sci 26:694–701
Gramatica P, Papa E, Battaini F (2005) Ranking of aquatic toxicity of esters modeled by QSAR. Chemosphere 58:559–570
Hodges G, Roberts DW, Marshall SJ, Dearden JC (2006) The aquatic toxicity of anionic surfactants to Daphnia magna-A comparative QSAR study of linear alkylbenzene sulphonates and ester sulphonates. Chemosphere 63:1443–1450
Jalali-Heravi M, Asadollahi-Baboli M, Mani-Varnosfaderani A (2009) Shuffling multivariate adaptive regression splines and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system as tools for QSAR study of SARS inhibitors. J Pharm Biomed Anal 50:853–860
Jiang L, Lin ZF, Hu XL, Yin DQ (2010) Toxicity prediction of antibiotics on luminescent bacteria, Photobacterium phosphoreum, based on their quantitative structure-activity relationship models. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 85:550–555
Karelson M (2000) Molecular descriptors in QSAR/QSPR. Wiley, New York
Meylan WM, Howard PH (2003) A review of quantitative structure-activity relationship methods for the prediction of atmospheric oxidation of organic chemicals. Environ Toxicol Chem 22:1724–1732
Papa E, Gramatica P (2010) QSPR as a support for the EU REACH regulation and rational design of environmentally safer chemicals: PBT identification from molecular structure. Green Chem 12:836–843
Roy K, Das RN (2010) QSTR with extended topochemical atom (ETA) indices. 14. QSAR modeling of toxicity of aromatic aldehydes to Tetrahymena pyriformis. J Hazard Mater 183:913–922
Shahbazikhah P, Asadollahi-Baboli M, Khaksar R, Alamdari RF, Zare-Shahabadi V (2011) Predicting partition coefficients of migrants in food simulant/polymer systems using adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system. J Braz Chem Soc 22:1446–1451
Tropsha A (2010) Best practices for QSAR model development, validation and exploitation. Mol Inf 29:476–488
Tropsha A, Gramatica P, Gombar VK (2003) The importance of being earnest: validation is the absolute essential for successful application and interpretation of QSPR models. QSAR Comb Sci 22:69–77
Wang R, Jiang JC, Pan Y, Cao HY, Cui Y (2009) Prediction of impact sensitivity of nitro energetic compounds by neural network based on electrotopologicalstate indices. J Hazard Mater 166:155–186
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asadollahi-Baboli, M. Aquatic Toxicity Assessment of Esters Towards the Daphnia magna Through PCA-ANFIS. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 91, 450–454 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-013-1066-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-013-1066-8