Abstract
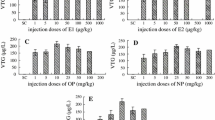
The in vivo estrogenic response and estrogenic contents of the influent and effluent collected from a sewage treatment plant located in Jiaozuo were assessed. The bioassay showed significant serum vitellogenin (VTG) induction in all the treated male goldfish (Carassius auratus) and significant gonad atrophies were only observed in the fish induced the most VTG expressions. Six target estrogens (estrone, 17β-estradiol, 17α-ethynylestradiol, 4-n-octylphenol, 4-n-nonylphenol and bisphenol A) were detected in different polar fractions, with the exception of the 25 % and 50 % methanol fractions extracted from the influent and the 25 %, 50 %, 95 % and 100 % methanol fractions extracted from the effluent. For both the influent and effluent, natural and synthetic steroidal estrogens were detected in those extracted fractions induced the most abundant VTG expressions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auriol M, Filali-Meknassi Y, Tyagi RD, Adams CD, Surampalli RY (2006) Endocrine disrupting compounds removal from wastewater, a new challenge. Process Biochem 41:525–539
Céspedes R, Lacorte S, Ginebreda A, Barceló D (2008) Occurrence and fate of alkylphenols and alkylphenol ethoxylates in sewage treatment plants and impact on receiving waters along the Ter River (Catalonia, NE Spain). Environ Pollut 153:384–392
Clara M, Kreuzinger N, Strenn B, Gans O, Kroiss H (2005) The solids retention time—a suitable design parameter to evaluate the capacity of wastewater treatment plants to remove micropollutants. Water Res 39:97–106
Desbrow C, Routledge EJ, Brighty GC, Sumpter JP, Waldock M (1998) Identification of estrogenic chemicals in STW effluent. 1. Chemical fractionation and in vitro biological screening. Environ Sci Technol 32:1549–1558
Diniz MS, Peres I, Magalhães-Antoine I, Falla J, Pihan JC (2005) Estrogenic effects in crucian carp (Carassius carassius) exposed to treated sewage effluent. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 62:427–435
Gabet-Giraud V, Miège C, Choubert JM, Martin Ruel S, Coquery M (2010) Occurrence and removal of estrogens and beta blockers by various processes in wastewater treatment plants. Sci Total Environ 408:4257–4269
Hashimoto T, Murakami T (2009) Removal and degradation characteristics of natural and synthetic estrogens by activated sludge in batch experiments. Water Res 43:573–582
Hashimoto T, Onda K, Nakamura Y, Tada K, Miya A, Murakami T (2007) Comparison of natural estrogen removal efficiency in the conventional activated sludge process and the oxidation ditch process. Water Res 41:2117–2126
Jin SW, Xu Y, Yang H, Liao T (2005) Quantitative determination of 8 kinds of estrogenic compound in wastewater. China Water Wastewater 21:94–97
Kawahara S, Hrai N, Arai M, Tatarazako N (2009) The effect of in vivo co-exposure to estrone and AhR-ligands on estrogenic effect to vitellogenin production and EROD activity. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 27:139–143
Kumar V, Nakada N, Yasojima M, Yamashita N, Johnson AC, Tanaka H (2009) Rapid determination of free and conjugated estrogen in different water matrices by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 77:1440–1446
Liu ZH, Kanjo Y, Mizutani S (2009) Removal mechanisms for endocrine disrupting compounds (EDCs) in wastewater treatment-physical means, biodegradation, and chemical advanced oxidation: a review. Sci Total Environ 407:731–748
Lu GH, Song WT, Wang C, Yan ZH (2010) Assessment of in vivo estrogenic response and the identification of environmental estrogens in the Yangtze River (Nanjing Section). Chemosphere 80:982–990
Milnes MR, Bermudez DS, Bryan TA, Edwards TM, Gunderson MP, Larkin ILV, Moore BC, Guillette LJ Jr (2006) Contaminant-induced feminization and demasculinization of nonmammalian vertebrate males in aquatic environments. Environ Res 100:3–17
Pawlowski S, van Aerle R, Tyler CR, Braunbecka T (2004) Effects of 17α-ethinylestradiol in a fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas) gonadal recrudescence assay. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 57:330–345
Rey Vázquez G, Meijide FJ, Da Cuña RH, Lo Nostro FL, Piazza YG, Babay PA, Trudeau VL, Maggese MC, Guerrero GA (2009) Exposure to waterborne 4-tert-octylphenol induces vitellogenin synthesis and disrupts testis morphology in the South American freshwater fish Cichlasoma dimerus (Teleostei, Perciformes). Comp Biochem Physiol C 150:298–306
Sim WJ, Lee JW, Shin SK, Song KB, Oh JE (2011) Assessment of fates of estrogens in wastewater and sludge from various types of wastewater treatment plants. Chemosphere 82:1448–1453
Zhong XP, Xu Y, Liang Y, Liao T, Wang JW (2004) Vitellogenin in rare minnow (Gobiocypris Rarus): identification and induction by waterborne diethylstilbestrol. Comp Biochem Physiol C 137:291–298
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by Scientific Research Fund of Henan Provincial Education Department (No. 13A610314, No. 13A440322) and the Doctor Fund of Henan Polytechnic University (No. B2011-056, No. B2010-69).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, W., Wang, Z. & Lian, C. Assessment of In Vivo Estrogenic Response and Identification of Environmental Estrogens in Influent and Effluent from a Sewage Treatment Plant. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 91, 324–329 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-013-1061-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-013-1061-0