Abstract
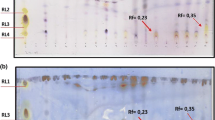
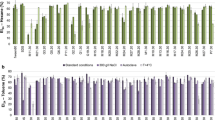
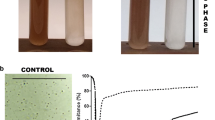
Our purpose was to detect, isolate and characterize tensioactive agents with or without emulsifying activity from marine bacterial strains present in seawater and sediment samples from the Venezuelan Atlantic Front. Biosurfactants found in cell-free supernatants from all cultures presented high surface activity as they were able to reduce the water surface tension from 72 dynes cm−1 to values between 41.7 and 33.9 dynes cm−1. However, high indirect CMC values were registered for the most of these compounds (51.4 %–56.1 % v/v). Culture supernatants from S3 and S29 strains showed highest emulsifying activity in the dispersion assay with diesel oil (absorbance 1.06 and 1.18, respectively), while supernatant from the S10 strain induced the most stable oil-in-water emulsions with 16° and 25°API crude oils. Only culture supernatant from S3 strain was able to produce stable oil-in water emulsions with diesel oil and both type of crude oils.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Mawgoud AM, Lépine F, Déziel E (2010) Rhamnolipids: diversity of structures, microbial origins and roles. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86:1323–1336
Agarrad J, Boodoosing M, Gobin J (1988) Petroleum residues in superficial sediments from the Gulf of Paria, Trinidad. Mar Poll Bull 219:231–233
Bodour AA, Drees KP, Maier RM (2003) Distribution of biosurfactant-producing bacteria in undisturbed and contaminated arid southwestern soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:3280–3287
Cameotra SS, Bollang JM (2003) Biosurfactant-enhanced bioremediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 30:111–126
Churchill SA, Harper JP, Churchill PF (1999) Isolation and characterization of a Mycobacterium species capable of degrading three and four-ring aromatic and aliphatic hydrocarbons. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:549–552
Conde JE (2001) The Orinoco River Delta, Venezuela. In: Seeliger U, Kjerfve B (eds) Ecological studies coastal marine ecosystems of Latin America, vol 144. Springer, Berlin, pp 61–69
Cooper DG, Zajic JE (1980) Surface-active compounds from microorganisms. Adv Appl Microbiol 26:229–253
Haba E, Espuny MJ, Busquets M, Manresa A (2000) Screening and production of rhamnolipids by Pseudomonas aeruginosa 47T2 NCIB 40044 from waste frying oils. J Appl Microbiol 88:379–387
Lizarraga-Partida ML, Izquierdo-Vicuna FB, Wong-Chang I (1991) Marine bacteria on the Campeche Bank oil field. Mar Poll Bull 22:401–405
Malavé R, Barbosa M, Suárez P (2005) Detección de bacterias tolerantes a metales en el agua y los sedimentos del frente Atlántico Venezolano. In: Capaldo M, Yanes C, Martín A, Gómez MG (eds) Frente Atlántico Venezolano. Investigaciones geoambientales: ciencias ambientales. Tomo I, Petróleos de Venezuela, SA (PDVSA)-Fondo Editorial Fundambiente, Caracas, pp 22–30
Margaritis A, Zajic JE, Gerson DF (1979) Production and surface-active properties of microbial surfactants. Biotechnol Bioeng 21:1151–1162
Rocha CA, Infante C (1997) Enhanced oily sludge biodegradation by a tensio-active agent isolated from Pseudomonas aeruginosa USB-CS1. Appl Biotechnol Bioeng 47:615–619
Rocha CA, González D, Iturralde L, Lacoa U, Morales F (2000) Production of oily emulsions mediated by a microbial tensio-active agent (Process). U.S. Pat. 6.060 287.r
Rocha CA, Pedregosa AM, Laborda F (2011) Biosurfactant-mediated biodegradation of straight and methyl-branched alkanes by Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 55925. AMB Express 1:9–18
Satpute SK, Banpurkar AG, Dhakephalkar PK, Banat IM, Chopade BA (2010a) Methods for investigating biosurfactants and bioemulsifiers: a review. Crit Rev Biotechnol 30:127–144
Satpute SK, Banat IM, Dhakephalkar PK, Banpurkar AG, Chopade BA (2010b) Biosurfactants, bioemulsifiers and exopolysaccharides from marine microorganisms. Biotechnol Adv 28:436–450
Thavasi R, Subramanyam VRM, Jayalakshmi S, Balasubramanian T, Banat IM (2011) Biosurfactant production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa from renewable resources. Indian J Microbiol 51:30–36
Torres JM, Sánchez JA (2001) Producción de un biosurfactante microbiano por Torulopsis magnoliae en cultivos sumergidos por carga. Ciencia 9:305–312
Yateem A, Balba MT, Al-Shayji Y, Al-Awadhi N (2002) Isolation and characterization of biosurfactant-producing bacteria from oil-contaminated soil. Soil Sediment Contam 11:41–55
Zeinali M, Vossoughi M, Ardestani SK (2007) Characterization of a moderate thermophilic Nocardia species able to grow on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Lett Appl Microbiol 45:622–628
Zhang Y, Miller RM (1992) Enhanced octadecane dispersion and biodegradation by a Pseudomonas rhamnolipid surfactant (biosurfactant). Appl Environ Microbiol 58:3276–3282
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support from Projects of INTEVEP-PDVSA and the Decanato de Investigación y Desarrollo of the Universidad Simón Bolívar.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bozo-Hurtado, L., Rocha, C.A., Malavé, R. et al. Biosurfactant Production by Marine Bacterial Isolates from the Venezuelan Atlantic Front. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 89, 1068–1072 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-012-0820-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-012-0820-7