Abstract
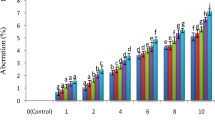
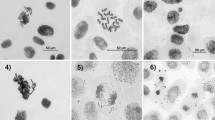
In the present study effects of herbicides glyphosate (GP), alachlor (AL) and maleic hydrazide (MH) is studied on mitotic cells of Trigonella foenum-graecum L. Seeds of T. foenum-graecum L. treated with a series of concentrations ranging from 0.1%, 0.2%, 0.3%, 0.4% and 0.5% for 1, 2 and 6 h and their effect on mitotic index and chromosomal aberrations was studied. The results indicate that these herbicides reduced mitotic index in dose-dependent manner. In addition, increase in the percentage of abnormal mitotic plates was observed in herbicide treated groups which was both concentration and time dependent. Commonly observed abnormalities were c-mitosis, laggards, bridges, stickiness, c-anaphase, precocious separation, un-equal distribution and fragments. The result of the present investigation indicates that commonly used herbicides GP, AL and MH have significant genotoxic effect on T. foenum-graecum plant.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelsalam AZE, Soliman KHA, Hassan HZ (1997) The mutagenic potentialities of two organophosphorus compounds using different biological system. Egypt J Genet Cytol 26:105–120
Barbara LA, William TM, Bugg MW (1991) Effects of herbicide dithiopyr on cell division in wheat root tips. Pest Biochem Physiol 39:110–120
Barriuso J, Marin S, Mellado RP (2010) Effect of the herbicide glyphosate on glyphosate-tolerant maize rhizobacterial communities: a comparison with pre-emergence applied herbicide consisting of a combination of acetochlor and terbuthylazine. Environ Microbiol 12:1021–1030
Bowes J, Crofts AR, Arntzen CJ (1980) Redox reactions on the reducing side of photosystem II in chloroplasts with altered herbicide-binding properties. Arch Biochem Biophys 200:303–308
Burnet MWM, Loveys BR, Holtum JAM, Powles SB (1993) Increased detoxification is a mechanism of simazine resistance in Lolium rigidum. Pesti Biochem Physiol 46:207–218
Claudio De S, Piccolo A, De Marco A (1992) Genotoxic effect induced by herbicides atrazine, glyphosate in plants of Vicia faba grown in different soils. Sci Total Environ (123\124): 233–240
Crosby DG (1982) Pesticides as environmental mutagens. In: Fleck RA, Hollander A (eds) Genetic toxicology: an agricultural perspective. Plenum press, New York, pp 201–218
De Marco A, De Simones C, Roglione M, Testa A, Trinca S (1992) Importance of the type of soil for the induction of micronuclei and the growth of primary roots of Vicia faba treated with the herbicides atrazine, glyphosphate and maleic hydrazide. Mutat Res 279:9–13
Egli MA, Low D, White KR, Howard JA (1985) Effect of herbicides and herbicide analogs on (C14) leucine incorporation by suspension-cultured Solanum nigrum cells. Pest Biochem Physiol 24:112–118
Egorova AB, Uspenskaya YuA, Mikhutkina SV, Stavitskaya EYu (2001) Damage of cytoskeleton and cell membranes in apoptosis. Adv Curr Biol 121:502–510
El-Ghamery AA, El-Nahas AI, Mansour MM (2000) The action of atrazine herbicide as an inhibitor of cell division on chromosomes and nucleic acids content in root meristems of Allium cepa and Vicia faba. Cytologia 65:277–287
Garrett NE, Stack HF, Waters MD (1986) Evaluation of the genetic activity profiles of 65 pesticides. Mutat Res 168:301–325
Gichner T, Menke M, Stavreva DA, Schubert I (2002) Maleic hydrazide induces genotoxic effects but no DNA damages detectable by the comet assay in tobacco and field bean. Mutagenesis 15:385–389
Granby K, Vahl M (2001) Investigation of herbicide glyphosate and plant growth regulators chlormequat and mepiquat in cereals produced in Denmark. Food Addit Contam 18:898–905
Grossmann K, Tresch S, Plath P (2001) Triaziflam and diaminotriazine derivatives affect enantio selectively multiple herbicide target sites. Z Naturforsch C 56:559–569
Hackett AG, Gustafson DI, Moran SJ, Hendley P, Van Wesenbeeck I, Simmons ND, Klein AJ, Kronenberg JM, Fuhrman JD, Honegger JL, Hanzas J, Healy D, Stone CT (2005) The acetochlor registration partnership surface water monitoring program four corn herbicides. J Environ Qual 34:877–889
Ismail C, Atilla Y, Yusuf T, Levent O (2009) Glyphosate reduced seed and leaf concentrations of calcium, manganese, magnesium and iron in non-glyphosate resistant soybean. Eur J Agro 31:114–119
Kaymak F (2005) Cytogenetic effects of maleic hydrazide on Helianthus annus L. Pak J Biol Sci 8:104–108
Kevin CV, Stephan OD (1986) Ultrastructural effects of glyphosate on Glycine max seedlings. Pest Biochem Physiol 26:56–65
Kiely T, Donaldson D, Grube A (2004) Pesticides industry sales and usage. 2000 and 2001 Market estimates. US Environmental Protection Agency. Washington. May 2004
Lyu BN (2001) An oxygen-peroxide concept of apoptosis and possible versions of its mechanism. Adv Cur Biol 121:488–501
Marc J, Mulner-Lorillon O, Boulben S, Hureau D, Durand G, Belle R (2002) Pesticide roundup provokes cell division dysfunction at the level of CDK1/Cyclin B activation. Chem Res Toxicol 15:326–331
Marc J, Mulner-Lorillon O, Belle R (2004a) Glyphosate-based pesticides affect cell cycle regulation. Biol Cell 96:245–249
Marc J, Belle R, Julia M, Patrick C, Lorillon OM (2004b) Formulated glyphosate activates the DNA-response check point of the cell cycle leading to the prevention of G2/M transition. Toxicol Sci 82:436–442
Mike EF, Emerson DN, Fred WS, Loyd MW (1983) Effect of glyphosate on protein and nucleic acid synthesis and ATP levels in common cocklebur (Xanthium pensylvanicum) root tissue. Weed Sci 31:76–80
Miteva LPE, Ivanov SV, Alexieva VS (2010) Alterations in glutathione pool and some related enzymes in leaves and roots of pea plants treated with herbicide glyphosate. Russ J Plant Physiol 57:131–136
Powles SB, Holtum JAM (eds) (1994) Herbicide resistance in plants: biology and biochemistry. Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton
Qian XW (1998) Improvement on experiment method of micronucleus in root tip cell of Vicia faba. J Wenzhou Norm Coll 19:64–65
Rank J, Jensen AG, Skov B, Pedersen LH, Jensen K (1993) Genotoxicity testing of the herbicide Roundup and its active ingredient glyphosate isopropylamine using the mouse bone marrow micronucleus test, Salmonella mutagenicity test and Allium anaphase–telophase test. Mutat Res/Gene Toxic 300:29–36
Sathasivan K, Haughn GW, Murai N (1991) Molecular basis of imidazolinone herbicide resistance in Arabidopsis thaliana var. Columbia. Plant Physiol 97:1044–1050
Savaskan C, Toker MC (1991) The effects of various doses of gamma irradiation on the seed germination and root tips chromosomes of rye (Secales cereals L.). Turk J Bot 15:349–359
Siddiqui S, Meghvansi MK, Hasan Z (2007) Cytogenetics changes induced by sodium azide on Trigonella foenum-greacum L. seeds. S Afr J Bot 73:632–635
Siddiqui S, Khan SS, Meghvansi MK, Nazoora SA (2008) Mutagenic effect of herbicide maleic hydrazide on seed germination and radicle length on Trigonella foenum-graecum. Indian J Appl Pure Biol 23:103–106
Siddiqui S, Meghvansi MK, Wani MA, Jabee F (2009) Evaluating cadmium toxicity to the root meristem of Pisum sativum L. Acta Physiol Plant 31:531–536
Sinha SP (1989) Genotoxicity of pesticides. Perspect Cytol Genet 6:749–753
Swietlinska Z, Zuk J (1978) Cytotoxic effects of maleic hydrazide. Mutat Res 55:15–30
Tartar G, Fisun K, Fulya DGM (2006) Genotoxic effect of avenoxan on Allium cepa L. and Allium sativum L. Caryologia 59:241–247
Van der Werf HMG (1996) Assessing the impact of pesticides on the environment. Agric Ecosyst Environ 60:81–96
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Mr Z. Shah and Prof S. Nasir Ali, Saifia Education Society, Bhopal, India, for providing the necessary laboratory facilities. Thanks are also due to DR.S.S. Khan, Department of Microbiology, Saifia Sciences PG College, Bhopal for his constant help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siddiqui, S., Meghvansi, M.K. & Khan, S.S. Glyphosate, Alachor and Maleic Hydrazide have Genotoxic Effect on Trigonella foenum-graecum L.. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 88, 659–665 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-012-0570-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-012-0570-6