Abstract
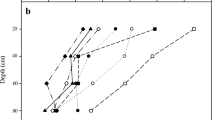
The purpose of this study was to determine the leaching characteristics of heavy metals from artificial soils composed of sewage sludge and fly ash. A leaching experiment was carried out over a period of 90 days. The leachates from artificial soils were collected every 15 days, and the concentrations of cadmium, lead, copper, zinc, chromium, and nickel in leachates were determined. Results showed that pH values of the artificial soils leachate were stable, ranging from 6.71 to 7.62 at the end of the experiment. Except of the cadmium, the concentrations of chromium, nickel, and copper in leachates of the artificial soils reached a stable level at the end of the experiment. The final concentrations of copper in leachates varied from 27.1 to 127.5 μg L−1, which was lower than European threshold value for drinking water, (1,000 μg L−1), while final nickel and chromium concentrations in leachates exceeded the European threshold ones. Amorpha fruticosa and Robina pseudoacacia grown in the artificial soils had different effects on cadmium, nickel, chromium, and copper leaching behavior. Amorpha fruticosa resulted in higher Ni and Cu concentrations in leachates, while Robina pseudoacacia enhanced leaching concentration of Cr.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott DE, Essington ME, Mullen MD, Ammons JT (2001) Fly ash and lime-stabilized biosolid mixtures in mine spoil reclamation: simulated weathering. J Environ Qual 30:608–616
Bonnissel-Gissinger P, Alnot M, Ehrhardt JJ (1998) Surface oxidation of pyrite as a function of pH. Environ Sci Technol 32:28–39
Brown SL, Henry CL, Chaney R, Compton H, DeVolder PS (2003) Using municipal biosolids in combination with other residuals to restore metal-contaminated mining areas. Plant Soil 249:203–215
Carlson CL, Adriano DC (1993) Environmental impacts of coal combustion residues. J Environ Qual 22:227–247
Choi SK, Lee S, Song YK, Moon HS (2002) Leaching characteristics of selected Korean fly ashes and its implications for the groundwater composition near the ash mound. Fuel 81:1080–1090
Egiarte G, Camps Arbestain M, Ruíz-Romera E, Pinto M (2006) Study of the chemistry of an acid soil column and of the corresponding leachates after the addition of an anaerobic municipal sludge. Chemosphere 65:2456–2467
Feng YJ, Li F, Wang XL, Liu XM, Zhang LN (2006) Principal chemical properties of artificial soil composed of fly ash and furfural residue. Pedosphere 16(5):668–672
GB 5749-85 (1986) Sanitary standards for drinking water. People’s Republic of China
Jackson BP, Miller WP (2000) Soil solution chemistry of a fly ash, poultry litter, and sewage sludge-amended soil. J Environ Qual 29:2430–2436
Lake DL, Kirk WW, Lester JN (1984) Fractionation, characterization, and speciation of heavy metals in sewage sludge and sludge-amended soils. J Environ Qual 13(2):175–183
Leviminzi R, Petruzzelli G (1984) The influence of phosphate fertilizers on Cd solubility in soil. Water Air Soil Pollut 23:423–429
Peng JF, Song YH, Yuan P, Cui XY, Qiu GL (2009) The remediation of heavy metals contaminated sediment. J Hazard Meter 161:633–640
Rodríguez L, Ruiz E, Alonso-Azcárate J, Rincón J (2009) Heavy metal distribution and chemical speciation in tailings and soils around a Pb-Zn mine in Spain. J Environ Manage 90:1106–1116
Schumann AW (1997) Plant nutrient supply from fly ash-biosolid mixtures. Ph.D. University of Georgia, Athens
Shen WS, Cao XZ, Jin Y (2004) The ecological damage and ecologicla reconstruction of mining areas. Environmental Science of China Press, Beijing, pp 1–8
Wang T, Liu TF, Sun C (2007) Application of MSWI fly ash on acid soil and its effect on the environment. Waste Manage. doi:10.1016/j.wasman.06.025
Yang X, Feng Y, He Z, Stoffella PJ (2005) Molecular mechanism of heavy metal hyperaccumulation and phytoremediation. J Trace Elem Med Biol 18:339–353
Zhang HL, Sun LN, Sun TH, Ma GF (2007) Principal physicochemical properties of artificial soil composed of fly ash, sewage sludge and mine tailing. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 79:562–565
Zhang HL, Sun LN, Sun TH (2008) Heavy metals and trace elements of sewage sludge stabilized by coal fly ash. J Liaoning Techni Univer Natura Sci 27(6):944–946
Acknowledgments
The project was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 40901282, 41071304), the High Technology Research and Development Program (863) of China (No. 2009AA06Z320), Excellent Person Program of Liaoning Province (2009R44) and Doctor Startup Fund Program (20212336).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Sun, L. & Sun, T. Leaching of Heavy Metals from Artificial Soils Composed of Sewage Sludge and Fly Ash. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 88, 406–412 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-011-0507-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-011-0507-5