Abstract
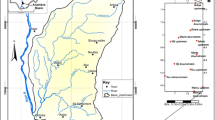
The Huayuan River in Hunan Province in China is subject to ongoing mining activity with Mn extraction. In this study, the level and environmental significance of metals (including Mn, Cd, Pb, Cu, Zn, Ni and Fe) concentrations in the surface water and river sediments have been investigated along a 187 km reach of the Huayuan River. Using the X-ray fluorescence (XRF) analysis, we analyzed the characterization of metals in manganese sulphate waste residue (MSWR) deposited along the bank of Huayuan River. The speciation of metals in both sediment and MSWR was established using the BCR-three step sequential extraction procedure. In the water samples, the average concentrations of Mn, Cd and Pb exceeded the acceptable concentrations for drinking water in the WHO Guidelines for drinking water quality, Vol. 1, Recommendations, Geneva (2004) and Chinese (GB 5749-2006) guidelines, respectively. The average concentrations of Mn, Cd, Pb and Zn in the river sediments were found to be considerably higher than the corresponding world average shale values. The percentages of Cd (31.4%), Mn (31.1%), Zn (12.8%) and Pb (8.1%) associated with exchangeable and weak acid fraction in the sediments were higher than other metals. Mn (5.81%), Zn (0.208%), Pb (0.0292%) and Cd (0.0113%) were identified in MSWR by XRF analysis. The percentages of Mn, Cd, Zn and Pb associated with the exchangeable and weak acid soluble fraction in MSWR were 41.9%, 31.1%, 23.8% and 9.8%, respectively. The peak solute and sediment-bound metal concentrations were found at the sites of MSWR deposited along the bank of Huayuan River. The results suggested that MSWR deposited along the bank may have a closely relation with the metal pollution of Huayuan River. The results obtained may be useful to assess both short and long-term environmental impact of the MSWR deposited activities and support decisions for a future remediation of this river.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
GB 5749-2006(2006) Standard for drinking water quality, standards press of China (in Chinese)
Gong C, Donahoe RJ (1997) An experimental study of heavy metal attenuation and mobility in sandy loam soils. Appl Geochem 12:243–254
Hu N, Zhuo JM, Liu YL, Peng QJ, Peng DJ, Zheng JF (2007) A study of the extraction procedure toxicity and harmless disposal of manganese sulphate waste residue. J Environ Monit-China 23:49–52 (in Chinese)
ISO 11466 (1995) Soil quality-extraction of trace elements soluble in aqua regia. ISO standards compendium, Switzerland
Jain CK (2004) Metal fractionation study on bed sediments of river Yamuna, India. Water Res 38:569–578
Kubová J, Streško V, Bujidoš M, Matúš P, Medved J (2004) Fractionation of various elements in CRMs and in polluted soils. Anal Bioanal Chem 379:108–114
Lake DL, Kirk PWW, Lester JN (1984) Fractionation, characterization, and speciation of heavy metals in sewage sludge and sludge-amended soils: a review. J Environ Qual 13:175–183
Modak DP, Singh KP, Chandra H, Ray PK (1992) Mobile and bound forms of trace metals in sediments of the lower Ganges. Water Res 26:1541–1548
National Environmental Bureau (NEB) (2002) Water and waste water analysis (fourth version). Chinese Environmental Science Publish House, Beijing (in Chinese)
Rauret G, López-Sánchez JF, Sahuquillo A, Rubio R, Davidson CM, Ure AM, Quevauviller Ph (1999) Improvement of the BCR three step sequential extraction procedure prior to certification of new sediment and soil reference materials. J Environ Monit 1:57–61
Simón M, Martín F, Ortiz I, García I, Fernández J, Fernández E, Dorronsoro C, Aguilar J (2001) Soil pollution by oxidation of tailings from toxic spill of a pyritemine. Sci Total Environ 279:63–74
Tessier A, Fortin D, Belzile N, DeVitre RR, Leppard GG (1996) Metal sorption to diagenetic iron and manganese oxyhydroxides and associated organic matter: narrowing the gap between field and laboratory measurements. Geochim Cosmochim Ac 60:387–404
Thompson HA, Parks GA, Brown GE (1999) Dynamic interactions of dissolution, surface adsorption, and precipitation in an aging cobalt (II)-clay-water system. Geochim Cosmochim Ac 63:1767–1779
Turekian KK, Wedepohl KH (1961) Distribution of the elements in some major units of the earth’s crust. Bull Geol Soc Amer 72:175–192
WHO (2004) Guidelines for drinking water quality, Vol. 1, Recommendations, 3rd edn. WHO, Geneva
Wu FC, Wu JW, Wang XY, Zou J (2000) Study on acid rain pollution in Hunan Province. Acta Sci Circum 20:807–809 (in Chinese)
Xie LL (2004) The exploitation and sustainable development of Zn and Mn natural resources in Huayuan County. Min Technol-China 4:12–14 (in Chinese)
Yao J, Zhuo FQ, Ma MY, Wu WX (1997) Study and countermeasure of the environmental from electrolytic manganese production precession. J Jishou Univ (Natural Sci Edi) 18:60–62 (in Chinese)
Zhang HB, Duan CQ, Hu B (2003) Dynamic of heavy metals in a lead-zinc tailings deposited in different years. J Agro-environl Sci-China 22:67–69 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Scientific Research Foundation for Doctor in University of South China (Grant No. 5-03-XJQ-03-044).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, N., Zheng, JF., Ding, DX. et al. Metal Pollution in Huayuan River in Hunan Province in China by Manganese Sulphate Waste Residue. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 83, 583–590 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-009-9802-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-009-9802-9