Abstract
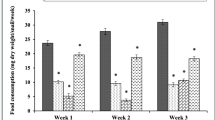
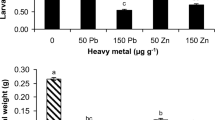
We investigated juvenile Achatina achatina snails by feeding graded levels of inorganic lead metal contaminated artificial diet in plastic snaileries in the laboratory. Snails were tolerant of all levels of lead contamination with no mortalities. Results indicated significant (p < 0.05) transfer of lead from diet to snail with high positive (r 2 = 0.98) relationship. Our data suggests that decreased feed intake and growth were found at elevated lead levels. Tissue lead accumulations were lower than dose in artificial diet.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey SER (1989) Foraging behaviour of terrestrial gastropods: integrating field and laboratory studies. J Moll Stud 55:521–540. doi:10.1093/mollus/55.2.263
Cortet J, Gomot-de Vaufleury A, Poin-sot-Balaguer N, Gomot L, Texie C, Cluzeau D (1999) The use of invertebrate fauna in monitoring pollutants effects. Eur J Soil Biol 35(3):115–134. doi:10.1016/S1164-5563(00)00116-3
Ebenso IE (2003) Egg weight and shell thickness as affected by dietary calcium. Global J Agri Sci 2(1):1–4
Ebenso IE (2004) Molluscicidal effects of neem (Azadirachta indica) extracts on edible tropical land snails. Pest Manag Sci 60(2):178–182. doi:10.1002/ps.810
Ebenso IE (2006) A note on the effect of water on incubating eggs of edible tropical land snail Limicolaria aurora. Liv Res Rural Devt 18(150). www.cipav.org.co/lrrd/lrrd18/10/eben18150.htm. Accessed 25 July 2008
Ebenso IE, Ologhobo AD (2008a) Effects of lead pollution at industrial contaminated sites on sentinel juvenile Achatina achatina. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. doi:10.1007/s00128-008-9525-3 [Epub ahead of print]
Ebenso IE, Ologhobo AD (2008b) Effects of lead pollution from vehicular exhaust fumes against sentinel juvenile Achatina achatina. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 81:513–515
Gimbert F, Gomot-de Vaufleury A, Douay F, Scheifler R, Coeurdassier M, Badot PM (2006) Modeling chronic exposure to contaminated soil: a toxicokinetic approach with the terrestrial snail Helix aspersa. Environ Int 32:866–875. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2006.05.006
Gomot-de Vaufleury A (2000) Standardized growth toxicity testing (Cu, Zn, Pb and Pentachlorophenol) with Helix aspersa. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 46:41–50. doi:10.1006/eesa.1999.1872
Gomot-de Vaufleury A, Kerhoas I (2000) Methods for toxicity assessment of contaminated soil by oral or dermal uptake in land snails: sublethal effects on growth. Environ Sci Technol 34:1865–1870. doi:10.1021/es9907212
Gomot-de Vaufleury A, Pihan F (1997) Comparison of the bioaccumulation capacities of Cu and Zn in two small subspecies Helix. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 38:85–94. doi:10.1006/eesa.1997.1566
Hopkin SP (1993) In situ biological monitoring of pollution in terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. In: Calcow P (ed) Handbook of ecotoxicology. Blackwell, Oxford
Laskowski R, Hopkin SP (1996) Accumulation of Zn, Cu, Pb and Cd in the garden snail Helix aspersa: implications for predators. Environ Pollut 91(3):289–297. doi:10.1016/0269-7491(95)00070-4
Notten MJM, Oosthoek AJP, Rozema J, Aerts R (2005) Heavy metal concentrations in a soil–plant–snail food chain along a terrestrial soil pollution gradient. Environ Pollut 135:178–190. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2005.01.011
Notten MJM, Oosthoek AJP, Rozema J, Aerts R (2006) Heavy metal pollution affects consumption and reproduction of land snail Capaea nemoralis fed on naturally polluted Urtica dioica leaves. Ecotoxicology 15:295–304. doi:10.1007/s10646-006-0059-3
Pawert M, Triebskorn R, Graff S, Berkus M, Schulz J, Kohler HR (1996) Plasticity of collembolan midgut cells in reaction to heavy metal exposure: ultra structure and intracellular metal distribution. Sci Tot Environ 181:187–200. doi:10.1016/0048-9697(95)05009-4
Russell LK, De Haven JI, Botts RP (1981) Toxic effects of cadmium on garden snail Helix aspersa. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 26:634–640. doi:10.1007/BF01622148
SAS (Statistical Analysis System) (1999) Users guide statistics, version 9. SAS Institute, New Carolina
Swaileh KM, Ezzughayyar A (2001) Dose-dependent effects of dietary Pb and Zn on feeding and growth rates of land snail Helix engaddensis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 50:9–14. doi:10.1006/eesa.2001.2051
Walker EH, Hopkin SP, Sibly RM, Peakall DB (2001) Principles of ecotoxicology, 2nd edn. Taylor and Francis, London
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ebenso, I.E., Ologhobo, A.D. Effects of Lead Pollution Against Juvenile Achatina achatina Fed on Contaminated Artificial Diet. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 82, 583–585 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-008-9625-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-008-9625-0