Abstract
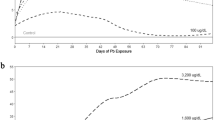
Behavior of an organism is affected by exposure to toxic chemicals. However, less has been known about behavioral responses of an organism to stresses of toxic chemicals with different toxic characteristics. In present work, Daphnia magna Straus was exposed to gradient concentrations of deltamethrin, chlorothalonil and nitrofen and the behavioral changes of Daphnia magna under different stress were examined. The results showed that the behavioral responses of Daphnia magna to the tested chemicals were affected in general by exposure concentration, rather than toxic characteristics of the chemicals. The duration of avoidance response (DAR) was in a power regression relationship with the toxic unit (TU), defined as the ratio of exposure concentration of the tested chemical to its LC50–48. DAR was independent of the toxic characteristics of chemicals. However, significant behavior adjustment could be observed after exposure to deltamethrin while only step-by-step decrease in behavior strength could be observed when exposed to chlorothalonil and nitrofen. It was suggested from the observation that avoidance behaviors of Daphnia magna to exposures of chemicals with different toxic characteristics could be similar, while their specific response could be different.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baier-Anderson C, Anderson RS (2000) The effects of Chlorothalonilon Oyster hemocyte activation: phagocytosis, reduced pyridine nucleotides, and reactive oxygen species production. Environ Res A 83:72–78. doi:10.1006/enrs.1999.4033
Bejarano AC, Chandler GT, Decho AW (2005) Influence of natural dissolved organic matter (DOM) on acute and chronic toxicity of the pesticides chlorothalonil, chlorpyrifos and fipronil on the meiobenthic estuarine copepod Amphiascus tenuiremis. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 321:43–57. doi:10.1016/j.jembe.2005.01.003
Brandsma AE, Tibboel D, Vulto IM, de Vijlder JJ, Ten Have-Opbroek AA, Wiersinga WM (1994) Inhibition of T3-receptor bindingby nitrofen. Biochim Biophys Acta 1201:266–270
Caux PY, Kent RA, Fan GT, Stephenson GL (1996) Environmental fate and effects of chlorothalonil: a Canadian perspective. Crit Rev Env Sci Tec 26:45–93
Duquesne S (2006) Effects of an organophosphate on Daphnia magna at suborganismal and organismal levels: implications for population dynamics. Ecotox Environ Safe 65:145–150. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2006.01.008
Erik H, Finn-Arne W, Joachim S, Svante W, Holger U (2005) Avoidance behavior and brain monoamines in fish. Brain Res 1032:104–110. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2004.10.050
Eriksson Wiklund A-K, Börjesson T, Wiklund SJ (2006) Avoidance response of sediment living amphipods to zinc pyrithione as a measure of sediment toxicity. Mar Pollut Bull 52:96–99. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2005.08.023
Ernst W, Doe K, Jonah P, Young J, Julien G, Hennigar P (1991) The toxicity of chlorothalonil to aquatic fauna and the impact of its operational use on a pond ecosystem. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 21:1–9. doi:10.1007/BF01055550
Fernández-Alba AR, Hernando MD, Piedra L, Chisti Y (2002) Toxicity evaluation of single and mixed antifouling biocides measured with acute toxicity bioassays. Anal Chim Acta 456:303–312. doi:10.1016/S0003-2670(02)00037-5
Gerhardt A (2001) A new multispecies freshwater biomonitor for ecological relevant control of surface waters. In: Butterworth F, Gunatilaka A, Gonsebatt ME (eds) Biomonitors and biomarkers as indicators of environmental change: environmental science forum 56, vol 2. Kluwer-Plenum Press, New York
Gerhardt A, Janssens B, Mo Z, Wang C, Yang M, Wang Z (2002) Short-term responses of Oryzias latipes (Pisces: Adrianichthyidae) and Macrobrachium nipponense (Crustacea: Palaemonidae) to municipal and pharmaceutical wastewater in Beijing, China: survival, behavior, biochemical biomarkers. Chemosphere 47:35–47. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(01)00223-5
Greer JJ, Babiuk RP, Thebaud B (2003) Etiology of congenital diaphragmatic hernia: the retinoid hypothesis. Pediatr Res 53:726–730. doi:10.1203/01.PDR.0000062660.12769.E6
Heckmann L-H, Callaghan A, Hooper HL, Connon R, Hutchinson TH, Maund SJ, Sibly RM (2007) Chronic toxicity of ibuprofen to Daphnia magna: effects on life history traits and population dynamics. Toxicol Lett 172:137–145. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2007.06.001
ISO (1996a) Water quality-determination of the acute lethal toxicity of substances to a freshwater fish [Brachdanio rerio (Hamilton-Buchanan), Teleostei, Cyprinidae]—part 3: flow-through method. ISO/DIS 7346/3
ISO (1996b) Water quality – determination of the mobility of Daphnia magna Straus (Cladocera, Crustacea). ISO 6341, Geneva, Switzerland
Kling DE, Aidlen JT, Fisher JC, Kinane TB, Donahoe PK, Schnitzer JJ (2005) Nitrofen induces a redox-dependent apoptosis associated with increased p38 activity in P19 teratocarcinoma cells. Toxicol In Vitro 19:1–10. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2004.04.010
Lefcort H, Abbott DP, Cleary DA, Howell E, Keller NC, Smith MM (2004) Aquatic snails from mining sites have evolved to detect and avoid heavy metals. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 46:478–484. doi:10.1007/s00244-003-3029-2
Mandrillon A, Saglio P (2007) Waterborne amitrole affects the predator – prey relationship between common frog tadpoles (Rana temporaria) and larval spotted salamander (Salamandra salamandra). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 53:233–240. doi:10.1007/s00244-006-0229-6
Manson JM (1986) Mechanism of nitrofen teratogenesis. Environ Health Persp 70:137–147. doi:10.2307/3430350
Martínez-Jerónimo F, Villaseňor R, Ríos G, Espinosa-Chavez F (2005) Toxicity of the crude oil water-soluble fraction and kaolin-adsorbed crude oil on Daphnia magna (Crustacea: Anomopoda). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 48:444–449. doi:10.1007/s00244-003-0220-4
Mascrez B, Mark M, Dierich A, Ghyselinck NB, Kastner P, Chambon P (1998) The RXR (alpha) ligand-dependent activation function 2 (AF-2) is important for mouse development. Development 125:4691–4707
Moore A, Waring CP (2001) The effects of a synthetic pyrethroid pesticide on some aspects of reproduction in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Aquat Toxicol 52:1–12. doi:10.1016/S0166-445X(00)00133-8
Narahashi T, Frey J, Ginsburg K, Roy M (1992) Sodium and GABA-activated channels as targets of pyrethroids and cyclodienes. Toxicol Lett 64:429–436. doi:10.1016/0378-4274(92)90216-7
Pedder SCJ, Maly EJ (1985) The effect of lethal copper solutions on the behavior of rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 14:501–507. doi:10.1007/BF01055537
Pimpão CT, Zampronio AR, Silva de Assis HC (2007) EVects of deltamethrin on hematological parameters and enzymatic activity in Ancistrus multispinis (Pisces, Teleostei). Pestic Biochem Phys 88:122–127. doi:10.1016/j.pestbp.2006.10.002
Ren ZM, Ma M, Wang ZJ (2006) On-line biomonitoring of accidental drinking water organophosphorous pesticides contamination. Water Wastewater Eng 32:17–20
Ren ZM, Zha JM, Ma M, Wang ZJ, Gerhardt A (2007) The early warning of aquatic organophosphorus pesticide contamination by on-line monitoring behavioral changes of Daphnia magna. Environ Monit Assess 134:373–383. doi:10.1007/s10661-007-9629-y
Reynaldi S, Duquesne S, Jung K, Liess M (2006) Linking feeding activity and maturation of Daphnia magna following short-term exposure to fenvalerate. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:1826–1830. doi:10.1897/05-469R.1
Riddell DJ, Culp JM, Baird DJ (2005) Behavioral responses to sublethal cadmium exposure within an experimental aquatic food web. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:431–441. doi:10.1897/04-026R.1
Rosa E, Barata C, Damasio J, Bosch MP, Guerrero A (2006) Aquatic ecotoxicity of a pheromonal antagonist in Daphnia magna and Desmodesmus subspicatus. Aquat Toxicol 79:296–303. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2006.06.019
Sager DR, Hocutt CH, StaufferJr JR (2000) Avoidance behavior of Morone americana, Leiostomus xanthurus and Brevoortia tyrannus to strobe light as a method of impingement mitigation. Environ Sci Policy 3:393–403. doi:10.1016/S1462-9011(00)00046-0
Saglio P, Trijasse S (1996) Behavioral effects of waterborne carbofuran in Goldfish. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 31(2):232–238. doi:10.1007/BF00212371
Sandbacka M, Christianson I, Isomaa B (2000) The acute toxicity of surfactants on fish cells, Daphnia magna and fish-a comparative study. Toxicol In Vitro 14:61–68. doi:10.1016/S0887-2333(99)00083-1
Scarfe AD, Jones KA, Steele CW, Kleerekoper H, Corbett M (1983) Locomotor behavior of four marine teleosts in response to sublethal copper exposure. Aquat Toxicol 2:335–353. doi:10.1016/0166-445X(82)90020-0
Selye H (1973) The evolution of the stress concept. Am Sci 61:692–699
Şener Ural M, Sağlam N (2005) A study on the acute toxicity of pyrethroid deltamethrin on the fry rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum, 1792). Pestic Biochem Phys 83:124–131. doi:10.1016/j.pestbp.2005.04.004
Soderlund DM, Bloomquist JR (1989) Neurotoxic actions of pyrethroid insecticides. Ann Rev Entomol 34:77–96. doi:10.1146/annurev.en.34.010189.000453
Steele CW, Strickler-Shaw S, Taylor DH (1989) Behavior of tadpoles of the bullfrog, Rana catesbeiana, in response to sublethal lead exposure. Aquat Toxicol 14:331–343. doi:10.1016/0166-445X(89)90031-3
Sturm A, Hansen PD (1999) Altered cholinesterase and monooxygenase levels in Daphnia magna and Chironomus riparius exposed to environmental pollutants. Ecotox Environ Safe 42:9–15. doi:10.1006/eesa.1998.1721
Tillman RW, Siegel MR, Long JW (1973) Mechanism of action and fate of the fungicide chlorothalonil (2,4,5,6-tetrachloroisophalonitrile) in biological systems: 1. Reactions with cells and subcellular components of Saccharomyces pastorians. Pestic Biochem Phys 3:160–167. doi:10.1016/0048-3575(73)90100-4
Tomasik P, Warren DM (1996) The use of Daphnia in studies of metal pollution of aquatic systems. Environ Res 4:25–64
Untersteiner H, Kahapka J, Kaiser H (2003) Behavioral response of the cladoceran Daphnia magna STRAUS to sublethal Copper stress – validation by image analysis. Aquat Toxicol 65:435–442
Villegas-Navarro A, Romero GMC, Rosas LE, Dominguez AR, Sachetin MW (1999) Evaluation of Daphnia magna as an indicator of toxicity and treatment efficacy of textile wastewaters. Environ Int 25(5):619–624. doi:10.1016/S0160-4120(99)00034-3
West CW, Ankley GT (1998) A laboratory assay to assess avoidance of contaminated sediments by the freshwater Oligochaete Lumbriculus variegates. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 35:20–24. doi:10.1007/s002449900343
WHO (World Health Organization) (1990) Deltamethrin, environmental health criteria 97. World Health Organization, Geneva, p 133
Wiles JA, Jepson PC (1994) Substrate-mediated toxicity of deltamethrin residues to beneficial invertebrates: estimation of toxicity factors to aid risk assessment. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 27:384–391. doi:10.1007/BF00213175
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by Chinese Academy of Science (KZCX1-YW-06), National High-Tech R&D Program of China (2007AA061502) and Tianjin Municipality (06FZZDSH00900).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, Z., Li, Z., Ma, M. et al. Behavioral Responses of Daphnia Magna to Stresses of Chemicals with Different Toxic Characteristics. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 82, 310–316 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-008-9588-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-008-9588-1