Abstract
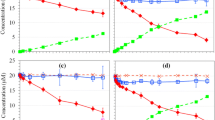
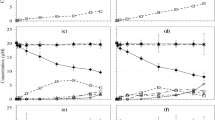
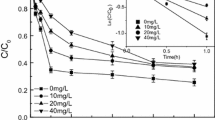
The dechlorination of pentachlorophenol (PCP) by zerovalent iron (Fe0) in presence of low molecular weight carboxylic acids was investigated. The experimental results showed that oxalic acid was advantaged among the selected acids for the dechlorination of PCP. The lower pH value and the higher dosage of Fe0 were favorable for the enhancement of dechlorination efficiency. With their strong complexing and pH buffering properties, carboxylic acids favored the fresh surface of iron, which benefits to the dechlorination of PCP by Fe0. Moreover, the oxalate-iron complexes have more reductive activities and then lead to the highest dechlorination efficiency of PCP by Fe0.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson LD, Kent DB, Davis JA (1994) Batch experiments characterizing the reduction of chromium(VI) using suboxic material from a mildly reducing sand and gravel aquifer. Environ Sci Technol 28:178–185. doi:10.1021/es00050a025
Buerge IJ, Hug SJ (1998) Chromium(VI) reduction by iron(II). Environ Sci Technol 32:2092–2099. doi:10.1021/es970932b
Cornell RM, Schwertmann U (2003) The iron oxides structure, properties, reactions occurrences and uses. WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co, KgaA, Weinheim
Cotter-Howells JD, Campbell LS, Valsami-Jones E, Batchelder M (2000) Environmental mineralogy: microbial interactions, anthropogenic influences. contaminated land and waste management. The Mineralogical Society of Great Britain & Ireland, London, UK
Fu HB, Quan X (2006) Complexes of fulvic acid on the surface of hematite, goethite, and akaganeite: FTIR observation. Chemosphere 63:403–410. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.08.054
He JH, Ela WP, Betterton EA, Arnold RG, Eduardo Saez A (2004) Reductive dehalogenation of aqueous-phase chlorinated hydrocarbons in an electrochemical reactor. Ind Eng Chem Res 43:963–7974
Hyun S, Lee LS (2004) Hydrophilic and hydrophobic sorption of organic acids by variable-charge soils: effect of chemical acidity and acidic functional group. Environ Sci Technol 38:413–5419. doi:10.1021/es0494914
Johnson SB, Yoon TH, Slowey AJ, Brown GE Jr (2004) Adsorption of organic matter at mineral/water interfaces: 3 implications of surface dissolution for adsorption of oxalate. Langmuir 20:11480–11492. doi:10.1021/la048559q
Jordi C, Jiechar G (2006) The effects of organic acids on the dissolution of silicate minerals: a case study of oxalate catalysis of kaolinite dissolution. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 70:191–2209
Kim Y-H, Carraway ER (2000) Dechlorination of pentachlorophenol by zero valent iron and modified zero valent irons. Environ Sci Technol 34:2014–2017. doi:10.1021/es991129f
Klose BS, Jentoft FC, Schlögl R, Subbotina IR, Kazansky VB (2005) Effect of Mn and Fe on the reactivity of sulfated zirconia toward H2 and n-butane: a diffuse reflectance IR spectroscopic investigation. Langmuir 21:10564–10572. doi:10.1021/la051574q
Leen JD, Dirk B, Agathos SN, Diels L (2005) Combined removal of chlorinated ethenes and heavy metals by zerovalent iron in batch and continuous flow column systems. Environ Sci Technol 39:8460–8465. doi:10.1021/es050251d
Li C, Hoffman MZ (1999) One-electron redox potentials of phenols in aqueous solution. J Phys Chem B 103:6653–6656. doi:10.1021/jp983819w
Ma XD, Zheng MH, Liu WB, Qian Y, Zhang B, Liu WX (2005) Dechlorination of hexachlorobenzene using ultrafine Ca–Fe composite oxides. J Hazard Mater B 127:156–162. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.06.034
Mikhlin YL, Kuklinskiy AV, Pavlenko NI, Varnek VA, Asanov IP, Okotrub AV, Selyutin GE, Solovyev LA (2002) Spectroscopic and XRD studies of the air degradation of acid-reacted pyrrhotites. Geochimica et Cosmochica Acta 66:4057–4067. doi:10.1016/S0016-7037(02)00989-4
Smith RM, Martell AE (1979) Critical stability constants. Plenum Press, New York, USA
Stumm W, Morgan JJ (1996) Aquatic chemistry, chemical equilibria and rates in natural waters. John Wiley & Sons, Inc, New York, USA
Stumm W, Sulzberger B (1992) The cycling of iron in natural environments: considerations based on laboratory studies of heterogeneous redox processes. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 56:3233–3257. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(92)90301-X
Su CM, Puls RW (2004) Nitrate reduction by zerovalent iron: effects of formate, oxalate, citrate, chloride, sulfate, borate, and phosphate. Environ Sci Technol 38:2715–2720. doi:10.1021/es034650p
Wang Y, Stone Alan T (2006) Reaction of MnIII, IV(hydr)oxides with oxalic acid, glyoxylic acid, phosphonoformic acid, and structurally-related organic compounds. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 70:4477–4490. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2006.06.1548
Xu Y, Axe L (2005) Synthesis and characterization of iron oxide-coated silica and its effect on metal adsorption. J Colloid & Interface Sci 282:11–19. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2004.08.057
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the suggestions of Prof. X. Z. Li from The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, and thank the Foundation of Natural Science of Guangdong Province (No. 04002223; No. 7006764) and Guangdong Technological Foundation (No. 2006B14801002; No. 2005B10301001) for financial supports to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, M., Wan, H., Zhou, Q. et al. The Dechlorination of Pentachlorophenol by Zerovalent Iron in Presence of Carboxylic Acids. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 82, 137–144 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-008-9574-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-008-9574-7