Abstract
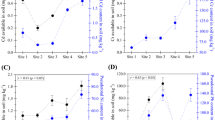
Lead/cadmium contamination in vegetables grown in peri-urban area of Nanjing, China was assessed and the route for metals entering into plants was investigated through lead isotopic tracing. Results show that agricultural soils have been polluted with Cd. Contents of Pb (22.1–37.5 mg kg−1 dw) and Cd (2.53–4.19 mg kg−1 dw) in vegetables’ edible parts nearby a lead/zinc mining/smelting plant were beyond their maximum allowable limit prescribed in the (EC) No 1881/2006. Pb isotope ratios in plants differed from those in the corresponding soils, suggesting that soils were not the only contamination source of Pb and Cd in plants.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bindler R, Renberg I, Klaminder J, Emteryd O (2004) Tree rings as Pb pollution archives? A comparison of 206Pb/207Pb isotope ratios in pine and other environmental media. Sci Total Environ 319:173–183
Cloquet C, Carignan J, Libourel G (2006) Isotopic composition of Zn and Pb atmospheric depositions in an urban-periurban area of Northeastern France. Environ Sci Technol 40(21):6594–6600
Commission European Communities (2006) Commission regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 of 19 December 2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs, Off J Eur Commun L364:5–24 (http://www.fsai.ie/legislation/food/eu_docs/contam_foodstuffs/General%20Provisions/Reg1881_2006.pdf)
Deng H, Ye ZH, Wong MH (2004) Accumulation of lead, zinc, copper and cadmium by 12 wetland plant species thriving in metal-contaminated sites in China. Environ Pollut 132:29–40
Douay F, Roussel H, Fourrier H, Heyman C, Chateau G (2007) Investigation of heavy metal concentrations on urban soils, dust and vegetables nearby a former smelter site in Mortagne du Nord, Northern France. J Soils Sediments 7(3):143–146
Erel Y, Dayan U, Rabi R, Rudich Y, Stein M (2006) Trans boundary transport of pollutants by atmospheric mineral dust. Environ Sci Technol 40(8):2525–2530
Fernandez-Turiel JL, Acënolaza P, Medina ME, Llorens JF, Sardi F (2001) Assessment of a smelter impact area using surface soils and plants. Environ Geochem Health 23:65–78
Finster ME, Gray KA, Binns HJ (2004) Lead levels of edibles grown in contaminated residential soils: a field survey. Sci Total Environ 320:245–257
Godoy JM, Godoya MLDP, Aronne CC (2007) Application of inductively coupled plasma quadrupole mass spectrometry for the determination of monazite ages by lead isotope ratios. J Braz Chem Soc 18(5):969–975
Hansmann W, Koppel V (2000) Lead-isotopes as tracers of pollutants in soils. Chem Geol 171:123–144
Harrison RM, Chirgawi MB (1989) The assessment of air and soil as contributors of some trace metals to vegetable plants I. Use of a filtered air growth cabinet. Sci Total Environ 83(1–2):13–34
ISO (1995) Soil quality. Extraction of trace elements soluble in Aqua Regia, ISO 11466
Jung MC, Thornton I (1996) Heavy metal contamination of soils and plants in the vicinity of a lead–zinc mine, Korea. Appl Geochem 11:53–59
Kachenkom AG, Singhm B (2006) Heavy metals contamination in vegetables grown in urban and metal smelter contaminated sites in Australia. Water Air and Soil Pollut 169:101–123
Komárek M, Ettler V, Chrastný V, Mihaljevič M (2008) Lead isotopes in environmental sciences: a review. Environ Int 34:562–577
Lim HS, Lee JS, Chon HT, Sager M (2008) Heavy metal contamination and health risk assessment in the vicinity of the abandoned Songcheon Au–Ag mine in Korea. J Geochem Explor 96(2–3):223–230
Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China (MEP, China) (1995) Environmental quality standards for soils (GB15612-1995)
Mukai H, Tanaka A, Fujii T, Zeng Y, Hong Y, Tang J, Guo S, Xue H, Sun Z, Zhou J, Xue D, Zhao J, Zhai G, Gu J, Zhai PY (2001) Regional characteristics of sulfur and lead isotope ratios in the atmosphere at several Chinese urban sites. Environ Sci Technol 35:1064–1071
Ng OH, Tan BC, Obbard JP (2005) Lichens as bioindicators of atmospheric heavy metal pollution in Singapore. Environ Monit Asses 123:63–74
Patrick GJ, Farmer JG (2007) A lead isotopic assessment of tree bark as a biomonitor of contemporary atmospheric. Sci Total Environ 388(1–3):343–356
Quétel CR, Thomas B, Donard OFX, Grousset FE (1997) Factorial optimization of data acquisition factors for lead isotope ratio determination by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Spectrochim Acta Part B 52:177–187
Rattan RK, Datta SP, Chhonkar PK, Suribabu K, Singh AK (2005) Long-term impact of irrigation with sewage effluents on heavy metal content in soils, crops and groundwater-a case study. Agric Ecosyst Environ 109:310–322
Sharma P, Dubey RS (2005) Lead toxicity in plants. Brazilian J Plant Physiol 17(1):35–52
Singh S, Kumar M (2006) Heavy metal load of soil, water and vegetables in peri-urban Delhi. Environ Monit Asses 120:79–91
Smit J (1996) Urban agriculture, progress and prospect 1975–2005. Report 18, Cities Feeding People Series, March 1996, IDRC, Canada
Sterckeman T, Douay F, Proix N, Fourrier H, Perdrix E (2002) Assessment of the contamination of cultivated soils by eighteen trace elements around smelters in the north of France. Water Air Soil Pollut 135:173–194
Temmerman LD, Hoenic M (2004) Vegetable crops for biomonitoring lead and cadmium deposition. J Atmos Chem 49:121–135
Voutsa D, Grimanis A, Samara C (1996) Trace elements in vegetables grown in an industrial area in relation to soil and air particulate matter. Environ Pollut 94(3):325–335
Weiss D, Shotyk W, Appleby PG, Kramers JD, Cheburkin AK (1999) Atmospheric Pb deposition since the industrial revolution recorded by five Swiss peat profiles: enrichment factors, fluxes, isotopic composition, and sources. Environ Sci Technol 33:1340–1352
Xia Z, Li S, Li Y (1987) Background values of soil elements and the study methods. Weather Press, Beijing, p 295
Yan S, Ling QC, Bao ZY (2007) Metals contamination in soils and vegetables in metal smelter contaminated sites in Huangshi, China. Bull Environ Contam Toxic 79:361–366
Zhang G, Yang F, Zhao Y, Zhao W, Yang JL, Gong ZT (2005) Historical change of heavy metals in urban soils of Nanjing, China during the past 20 centuries. Environ Int 31:913–919
Zheng N, Wang Q, Zheng D (2007) Health risk of Hg, Pb, Cd, Zn, and Cu to the inhabitants around Huludao Zinc Plant in China via consumption of vegetables. Sci Total Environ 383:81–89
Acknowledgment
This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (Grant No.: 20607010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, X., Ding, Z. Lead/Cadmium Contamination and Lead Isotopic Ratios in Vegetables Grown in Peri-Urban and Mining/Smelting Contaminated Sites in Nanjing, China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 82, 80–84 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-008-9562-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-008-9562-y