Abstract
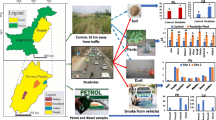
We investigated lead metal pollution induced by traffic fumes along roads with differing traffic intensity near abandoned battery factory (Niger Delta, Nigeria). Juvenile Achatina achatina were positioned as sentinels in plastic snaileries 2 m on road sides. Lead contamination in snail tissue by atomic absorption spectrophotometer increased with increasing vehicular traffic intensity. Snails showed low positive (r 2 = 0.40) relationship and significant (p < 0.05) accumulation of atmospheric lead pollution. Edible snails sold along road sides are prone to lead contamination.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berger B, Dallinger R (1993) Terrestrial snails as quantitative indicators of environmental metal pollution. Environ Monit Assess 25:65–84. doi:10.1007/BF00549793
CAI (Clean Air Intitative) (2007). www.cleanair.net.org/
Coeurdassier M, Gomot-de Vaufleury AD, Badot PM (2003) Bioconcentration of cadmium and toxic effects of life history traits of pond snails (Lymnaea palustris and L. stangnalis) in laboratory bioassays. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 45:102–109. doi:10.1007/s00244-002-0152-4
Ebenso IE (2002) Consumption and sales of domesticated snails Archachtina marginata in rural southern Nigeria. Trop Sci (England) 42(4):185–187
Ebenso IE (2003) Egg weight and egg shell thickness as affected by dietary calcium. Global J Agri Sci 2(1):1–4
Ebenso IE, Ologhobo AD (2008a) Edible land snail shell thickness as bioindicator of environmental lead metal pollution. Pollut Res (India) 27(2):75–76
Ebenso IE, Ologhobo AD (2008b) Effects of lead pollution at industrial contaminated sites on sentinel juvenile Achatina achatina. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. doi: 10.1007/s00128-008-9525-3
Garcia R, Millan E (1998) Assessment of Cd, Pb and Zn contamination in roadside soils and grasses from Gipuzkoa (Spain). Environ Technol 17:763–770. doi:10.1080/09593331708616443
Gomot-de Vaufleury A, Pihan F (2000) Growing snails used as sentinels to evaluate terrestrials environment contamination by trace elements. Chemosphere 40:275–284. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(99)00246-5
Hopkin SP (1990) Species-specific differences in the net assimilation of Zn, Cd, Pb, Cu and Fe by the terrestrial isopods Onicus asellus and Porcello scaber. J Appl Ecol 27:460–474. doi:10.2307/2404294
Maynard R (2004) Key airborne pollutants: the impact on health. Sci Total Environ 334(335):9–13. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2004.04.025
Regoli F, Gorbi S, Fathorini D, Telesco S, Notti A, Machella N, Boccheti R, Benedetti M, Piva F (2006) Use of the land snail Helix aspersa as sentinel organism for monitoring ecotoxicologic effects of urban pollution: an integrated approach. Environ Health Perspect 114(1):63–68
SAS (Statistical Analysis System) (1999) Users guide statistics, version 9. SAS Institute, New Carolina
Shotyk W, Norton SA, Farmer JG (1997) Summary of workshop on peat archives of atmospheric metal deposition. Water Air Soil Pollut 100:213–219. doi:10.1023/A:1018336828640
Simonetti A, Gapiery G, Carignan J (2000) Pb and Sr isotopic evidence for sources of atmospheric heavy metals and their deposition budgets in Northern North American. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 54:3439–3452. doi:10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00446-4
Sioutas C, Delfino RJ, Ray A (2005) Exposure assessment for atmosphere ultrafine particles (UFPs) and implications in epidemiological research. Environ Health Perspect 113:947–955
USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency) (1986) Air quality criteria for lead. Environmental criteria and assessment office, New Carolina
Van Gestel CAM, Van Straalen NM (1994) Ecotoxicological test systems for terrestrial invertebrates. In: Donker MH, Eijsackers H, Heimbach F (eds) Ecotoxicology of soil organisms. CRC Press, Boca Raton
WHO (World Health Organisation) (2000) WHO air quality guidelines for Europe, 2nd edn. European series 91, WHO regional office for Europe, Denmark
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ebenso, I.E., Ologhobo, A.D. Effects of Lead Pollution from Vehicular Exhaust Fumes Against Sentinel Juvenile Achatina achatina . Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 81, 513–515 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-008-9524-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-008-9524-4