Abstract
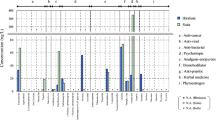
Aqueous solubilities (S w) and n-octanol–water partition coefficients (K ow) of five selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) were measured and sorption to two sediments and three soils with organic matter contents ranging from 0.16% to 1.77% and pH ranging between 5.0 and 7.8 was investigated using a batch equilibrium method. SSRIs had high S w (3,022–15,460 mg/l) and relatively low log K ow (1.12–1.39). Sorption isotherms followed the Freundlich equation. All SSRIs had sorption capacities of greater than 91% except fluvoxamine with a minimum capacity of 73%. Organic matter contents partly affected sorption, however no correlation between sorption characteristics and cation exchange capacity (CEC) or clay content was observed for any SSRI or adsorbent. Values of K f, K d, and log K oc ranged from 39 to 18,342, from 60 to 42,579, and 3.35 to 6.02 for the SSRIs. SSRIs likely exhibit mixed mechanisms of sorption such as ionic binding in addition to hydrophobic interactions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buser H-R, Müller MD (1998) Occurrence of the pharmaceutical drug clofibric acid and the herbicide mecoprop in various Swiss lakes and in the North Sea. Environ Sci Technol 32:188–192
Buser H-R, Poiger T, Müller MD (1998) Occurrence and fate of the pharmaceutical drug dichlofenac in surface water: rapid photodegradation in a lake. Environ Sci Technol 32:3449–3456
Buser H-R, Poiger T, Müller MD (1999) Occurrence and environmental behaviour of the chiral pharmaceutical drug ibuprofen in surface water and in wastewater. Environ Sci Technol 33:2529–2535
Calvet R (1989) Sorption of organic chemicals in soils. Environ Health Persp 83:145–177
Chen X, Cho SJ, Li Y, Venkatesh S (2002) Prediction of aqueous solubilities of organic compounds using a quantitative structure–property relationship. J Pharm Sci 91:1838–1852
Corwin DL, Farmer WJ (1984) Nonsingle-valued sorption–desorption of bromacil and diquat by freshwater sediments. Environ Sci Technol 18:507–514
Coyne R, Hiney M, O’Conner B, Cazabon D, Smith P (1994) Concentration and persistence of oxytetracycline in sediments under a marine salmon farm. Aquaculture 123:31–42
Cunningham VL, Constable DC, Hannah RE (2004) Environmental risk assessment of paroxetine. Environ Sci Technol 38:3351–3359
Dasmalchi S, Rashidi M, Rassi M (1995) Simultaneous determination of the pKa and n-octanol/water partition coefficient (Pm) of acetaminophen. J School Pharm Med Sci Univ Tehran 4:7–14
Daughton CG, Ternes TA (1999) Pharmaceuticals and personal care products in the environment: agents of subtle change? Environ Health Persp 107:907–938
Eckel WP, Ross B, Isensee R (1993) Pentobartial found in ground water. Ground Water 31:801–804
Eirkson C, Harrass MC, Osbourne CM, Sayre PG, Zeeman M (1987) Water solubility. In: Environmental assessment technical assistance handbook, vol 3.01. PB87–175345. U.S. Food and Drug Administration, Washington DC, pp 1–11
Furlong ET, Kinney CA, Ferrer I (2004) Pharmaceuticals and personal-care products in solids: analysis and field results for sediment, soil, and biosolid samples. In: Environmental aspects of pharmaceuticals and personal care products. 228th American Chemical Society national Meeting, Philadelphia, PA, USA, August 22–26
Giles CH, MacEwan TH, Nakhwa SN, Smith D (1960) Studies in sorption: Part XI. A system of classification of solution sorption isotherms, and its use in diagnosis of sorption mechanisms and in measurement of specific surface areas of solids. J Chem Soc 111:3973–3993
Holm JV, Rügge K, Bjerg PL, Christensen TH (1995) Occurrence and distribution of pharmaceutical organic compounds in the groundwater downgradient of a landfill. Environ Sci Technol 29:1415–1420
Kerry J, Hiney M, Coyne R, NicGabhainn S, Gilroy D, Cazabon D, Smith P (1995) Fish feed as a source of oxytetracycline-resistent bacteria in the sediment under fish farms. Aquaculture 131:101–113
Kinney CA, Furlong ET, Werner SL, Cahill JD (2006) Presence and distribution of wastewater-derived pharmaceuticals in soils irrigated with reclaimed water. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:317–326
Kolpin DW, Furlong ET, Meyer MT, Thurman EM, Zaugg SD, Barber LB, Buxton HT (2002) Pharmaceuticals, hormones, and other organic wastewater contaminants in U.S. streams, 1999–2000: A national reconnaissance. Environ Sci Technol 36:1202–1211
Kulkarni SG, Pegram AA (2000) Disposition of acetaminophen and indocyanine green in cystic fibrosis knockout mice. AAPS Pharmsci 2(2;18):1–8
Kwon J-W, Armbrust KL (2004) Hydrolysis and photolysis of paroxetine, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, in aqueous solutions. Environ Toxicol Chem 23:1394–1399
Kwon J-W, Armbrust KL (2005a) Photo-isomerization of fluvoxamine in aqueous solutions. J Pharm Biomed Anal 37:643–648
Kwon J-W, Armbrust KL (2005b) Degradation of citalopram by simulated sunlight. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:1618–1623
Lamas JP, Salgado-Petinal C, García-Jares C, Llompart M, Cela R, Gómez M (2004) Solid-phase microextraction-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for the analysis selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in environmental water. J Chromatogr A 1046:241–247
Lyman WJ, Reehl WF, Rosenblatt DH (1990) Handbook of chemical property estimation methods. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC
Metcalfe CD, Miao X-S, Koenig BG, Struger J (2003) Distribution of acidic and neutral drugs in surface waters near sewage treatment plants in the lower Great Lakes, Canada. Environ Toxicol Chem 22:2881–2889
Müller C, Vogt S, Goerke R, Kordon A, Weinmann W (2000) Identification of selected psychopharmaceuticals and their metabolites in hair by LC/ESI-CID/MS and LC/MS/MS. Forensic Sci Int 113:415–421
Patakioutas G, Albanis TA (2002) Sorption–desorption studies of alachlor, metolachlor, EPTC, chlorothalonil and pirimiphos-methyl in contrasting soils. Pest Manag Sci 58:352–362
Snyder SA, Westerhof P, Yoon Y, Sedlak DL (2003) Pharmaceuticals, personal care products and endocrine disruptors in water: implications for the water industry. Environ Eng Sci 20:449–469
Stan H-J, Heberer T, Linkerhägner M (1994) Occurrence of clofibric acid in the aquatic system – Is the use in human medical care the source of the contamination of surface, ground and drinking water? Vom Wasser 83:57–68
Stan H-J, Linkerhägner M (1992) Identification of 2-(4-chlorophenoxy)-2-methyl-propionis acid in grounfwater with GC-AED and GC-MS. Vom Wasser 79:75–88
Tolls J (2001) Sorption of veterinary pharmaceuticals in soils: a review. Environ Sci Technol 35:3397–3406
U.S. EPA (1982) Partition coefficient CG-1400. In: Chemical fate test guidelines. EPA 560/6-82-003. National Technical Information Services, Springfield, VA
U.S. EPA (2003) Pollution prevention (p2) framework. United States Environmental Agency Office of Pollution Prevention and Toxics, p 170
Vasskog T, Berger U, Samuelsen P-J, Kallenborn R, Jensen E (2006) Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in sewage influents and effluents from Tromsø, Norway. J Chromatogr A 1115:187–195
Weigel S, Berger U, Jensen E, Kallenborn R, Thoresen H, Hühnerfuss H (2004) Determination of selected pharmaceuticals and caffeine in sewage and seawater Tromsø/Norway with emphasis on ibuprofen and its metabolites. Chemosphere 56:583–592
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the US EPA-Science To Achieve Results (STAR) Program (Grant #R-82900601). We thank Dr. Joseph H. Massey in the Department of Plant and Soil Science for his assistance with soil samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwon, JW., Armbrust, K.L. Aqueous Solubility, n-Octanol–Water Partition Coefficient, and Sorption of Five Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors to Sediments and Soils. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 81, 128–135 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-008-9401-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-008-9401-1